Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
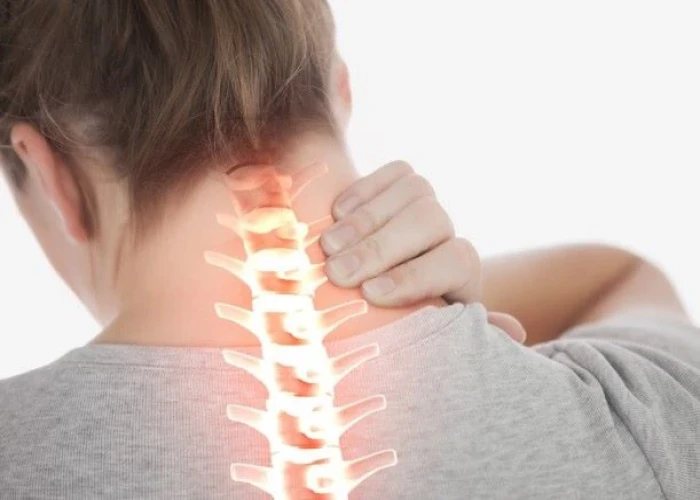
Neck pain

Neck pain is a common condition that affects many people at some point in their lives. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor posture, injury, aging, and underlying health conditions.
Symptoms of neck pain may include a stiff or sore neck, pain that radiates down the arms or into the shoulders or upper back, headaches, and difficulty moving the neck. In some cases, neck pain may also be accompanied by numbness or tingling in the arms or hands.
Diagnosis of neck pain may involve a physical exam, imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, and blood tests to rule out underlying health conditions.
Treatment options for neck pain may include rest, over-the-counter pain relievers, heat or ice therapy, physical therapy or exercise, and in some cases, prescription medications or injections to manage pain and inflammation. Lifestyle changes, such as improving posture and reducing stress, may also be recommended to prevent or manage neck pain.
In some cases, neck pain may be a sign of a more serious underlying health condition, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. It is important to seek medical attention if neck pain is severe, accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or difficulty breathing, or if it persists for an extended period of time.
Prevention of neck pain can include practicing good posture, taking frequent breaks if working at a desk or computer, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise or stretching to maintain neck mobility and flexibility.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Headaches
- Numbness
- Neck pain
- Limited ability to move the affected joint
Disease Causes
Neck pain
Your neck is flexible and supports the weight of your head, so it can be vulnerable to injuries and conditions that cause pain and restrict motion. Neck pain causes include:
- Muscle strains. Overuse, such as too many hours hunched over your computer or smartphone, often triggers muscle strains. Even minor things, such as reading in bed or gritting your teeth, can strain neck muscles.
- Worn joints. Just like the other joints in your body, your neck joints tend to wear down with age. Osteoarthritis causes the cushions (cartilage) between your bones (vertebrae) to deteriorate. Your body then forms bone spurs that affect joint motion and cause pain.
- Nerve compression. Herniated disks or bone spurs in the vertebrae of your neck can press on the nerves branching out from the spinal cord.
- Injuries. Rear-end auto collisions often result in whiplash injury, which occurs when the head is jerked backward and then forward, straining the soft tissues of the neck.
- Diseases. Certain diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, meningitis or cancer, can cause neck pain.
Disease Prevents
Neck pain
Most neck pain is associated with poor posture combined with age-related wear and tear. To help prevent neck pain, keep your head centered over your spine. Some simple changes in your daily routine may help. Consider trying to:
- Use good posture. When standing and sitting, be sure your shoulders are in a straight line over your hips and your ears are directly over your shoulders.
- Take frequent breaks. If you travel long distances or work long hours at your computer, get up, move around and stretch your neck and shoulders.
- Adjust your desk, chair and computer so that the monitor is at eye level. Knees should be slightly lower than hips. Use your chair's armrests.
- Avoid tucking the phone between your ear and shoulder when you talk. Use a headset or speakerphone instead.
- If you smoke, quit. Smoking can put you at higher risk of developing neck pain.
- Avoid carrying heavy bags with straps over your shoulder. The weight can strain your neck.
- Sleep in a good position. Your head and neck should be aligned with your body. Use a small pillow under your neck. Try sleeping on your back with your thighs elevated on pillows, which will flatten your spinal muscles.
Disease Treatments
The most common types of mild to moderate neck pain usually respond well to self-care within two or three weeks. If neck pain persists, your doctor might recommend other treatments.
Medications
Your doctor might prescribe stronger pain medicine than what you can get over-the-counter, as well as muscle relaxants and tricyclic antidepressants for pain relief.
Therapy
- Physical therapy. A physical therapist can teach you correct posture, alignment and neck-strengthening exercises, and can use heat, ice, electrical stimulation and other measures to help ease your pain and prevent a recurrence.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Electrodes placed on your skin near the painful areas deliver tiny electrical impulses that may relieve pain.
- Traction. Traction uses weights, pulleys or an air bladder to gently stretch your neck. This therapy, under supervision of a medical professional and physical therapist, may provide relief of some neck pain, especially pain related to nerve root irritation.
- Short-term immobilization. A soft collar that supports your neck may help relieve pain by taking pressure off the structures in your neck. However, if used for more than three hours at a time or for more than one to two weeks, a collar might do more harm than good.
Surgical and other procedures
- Steroid injections. Your doctor might inject corticosteroid medications near the nerve roots, into the small facet joints in the bones of the cervical spine or into the muscles in your neck to help with pain. Numbing medications, such as lidocaine, also can be injected to relieve your neck pain.
- Surgery. Rarely needed for neck pain, surgery might be an option for relieving nerve root or spinal cord compression.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Neck pain and Learn More about Diseases
Myasthenia gravis
Delayed ejaculation
Q fever
Behcet's disease

Valley fever
Cryoglobulinemia

Common variable immunodeficiency

Polymyalgia rheumatica
neck pain, ঘাড় ব্যথা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.