Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Hip impingement
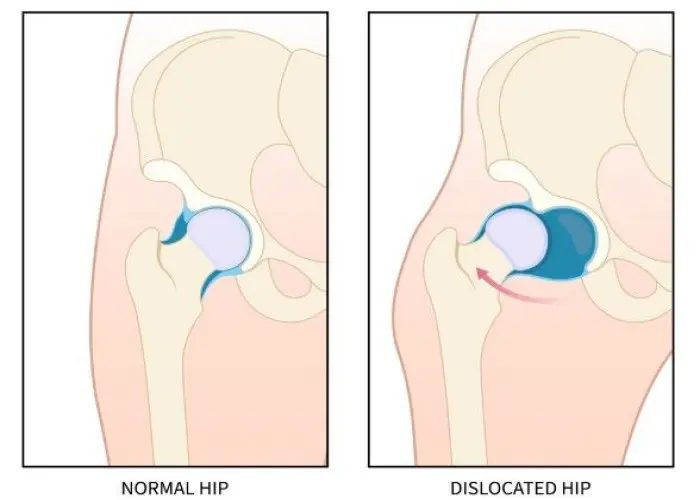
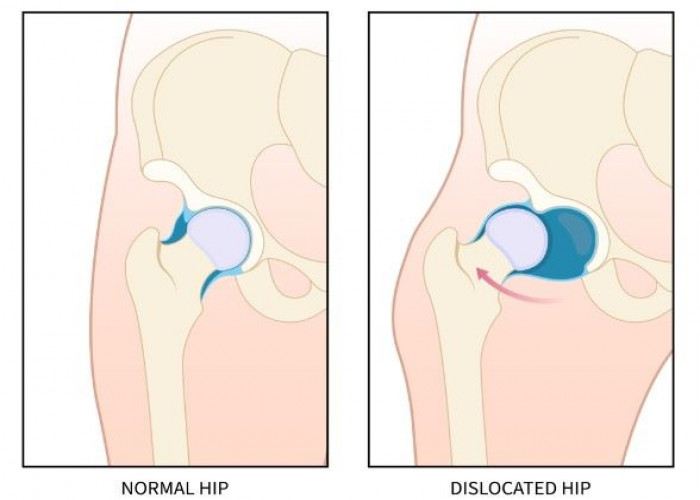
Hip impingement, also known as femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), is a condition in which there is abnormal contact between the ball and socket of the hip joint, which can lead to pain and damage to the joint over time.
FAI can be caused by a variety of factors, including structural abnormalities of the hip joint such as an abnormality of the femoral head or the acetabulum (the socket of the hip joint), or from repetitive microtrauma to the joint from activities like running, jumping, or twisting.
The symptoms of hip impingement can include hip pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion. These symptoms may worsen with activity and may cause difficulty with sports or other physical activities.
Treatment for hip impingement typically begins with conservative measures, such as physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and activity modification. If conservative measures do not provide relief, surgery may be recommended. Surgery for hip impingement typically involves the reshaping of the bones of the hip joint to relieve the impingement and improve the joint's overall function.
Early diagnosis and treatment of hip impingement is important to prevent further damage to the joint and to improve overall joint function. If you are experiencing hip pain or limited mobility, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Hip joint disease
- Groin pain or hip pain
Disease Causes
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Hip impingement and Learn More about Diseases
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Autonomic neuropathy
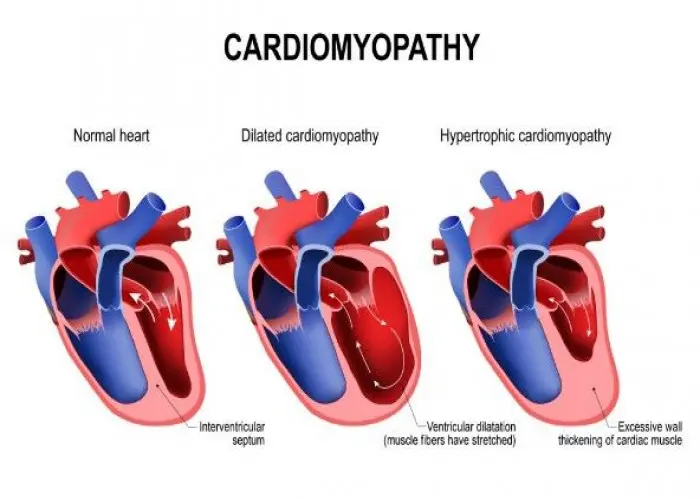
Dilated cardiomyopathy
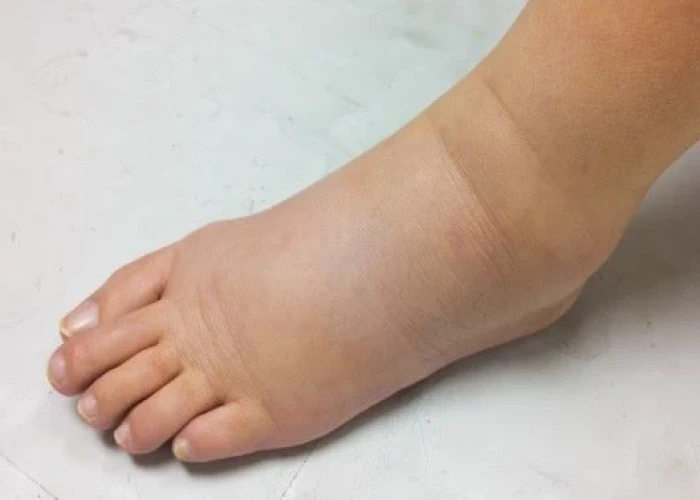
Lymphedema

Scabies
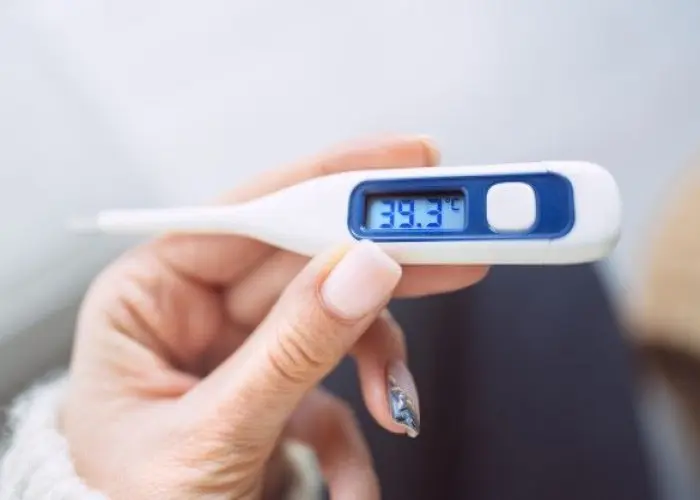
Fever
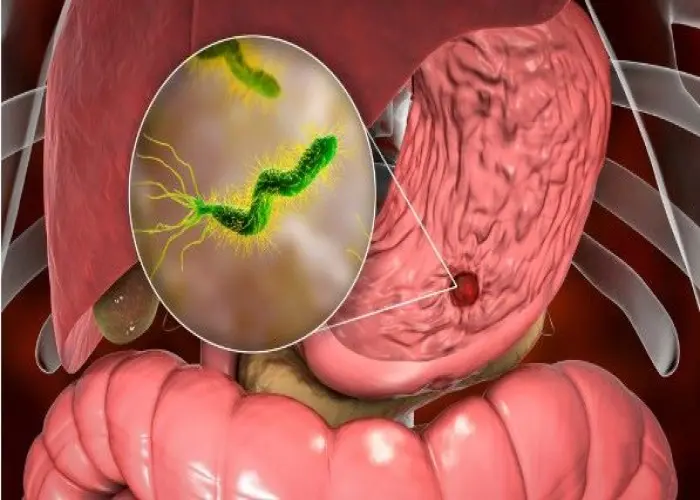
Duodenal Ulcer

Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
Hip impingement, নিতম্বের আঘাত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.