Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
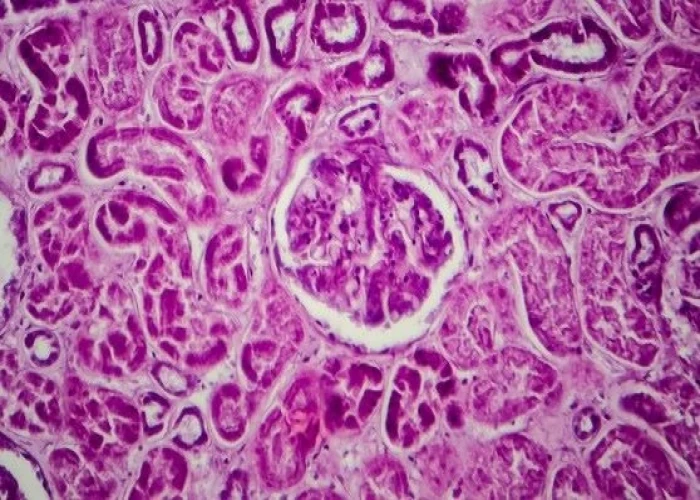
Lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis is a type of kidney disease that is caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. Lupus nephritis occurs when the immune system attacks the kidneys, causing inflammation and damage. It is a serious complication of SLE and can lead to kidney failure if not treated promptly.
Symptoms of lupus nephritis may include swelling in the legs, feet, or ankles, high blood pressure, foamy urine, blood in the urine, and fatigue. Some people with lupus nephritis may not have any symptoms.
Diagnosis of lupus nephritis involves a thorough medical history, physical exam, and laboratory tests, including blood tests and urine tests. A kidney biopsy may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of kidney damage.
Treatment of lupus nephritis depends on the severity of the disease and the extent of kidney damage. Treatment may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, and medications to control blood pressure and reduce protein in the urine. In some cases, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be necessary.
People with lupus nephritis should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan that is right for them. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are important to manage the disease and prevent complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Excess protein or cloudy urine (proteinuria)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Swollen arms or hands
- Swollen feet and ankles (edema)
- High levels of a waste product called creatinine in the blood
Disease Causes
Lupus nephritis
As many as half of adults with systemic lupus develop lupus nephritis. Systemic lupus causes immune system proteins to damage the kidneys, harming their ability to filter out waste.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
There's no cure for lupus nephritis. Treatment aims to:
- Reduce symptoms or make symptoms disappear (remission)
- Keep the disease from getting worse
- Maintain remission
- Avoid the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
Conservative treatments
In general, doctors may recommend these treatments for people with kidney disease:
- Diet changes. Limiting the amount of protein and salt in your diet can improve kidney function.
- Blood pressure medications. Drugs called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) can help control blood pressure. These drugs also prevent protein from leaking from the kidneys into the urine. Drugs called diuretics can help you get rid of excess fluid.
However, conservative treatment alone isn't effective for lupus nephritis.
Drug therapy
For severe lupus nephritis, you might take medications that slow or stop the immune system from attacking healthy cells, such as:
- Steroids, such as prednisone
- Cyclosporine
- Tacrolimus
- Cyclophosphamide
- Azathioprine (Imuran)
- Mycophenolate (CellCept)
- Rituximab (Rituxan)
- Belimumab (Benlysta)
Clinical trials may also be available for new therapies. Determining what medications might help you requires a careful discussion of the benefits and risks with your doctor.
Treatment options for kidney failure
For people who progress to kidney failure, treatment options include:
- Dialysis. Dialysis helps remove fluid and waste from the body, maintain the right balance of minerals in the blood, and manage blood pressure by filtering your blood through a machine.
- Kidney transplant. You may need a new kidney from a donor if your kidneys can no longer function.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
Above 12 years 1 capsule 3 times a day. The dose may be increased every 2 to 8 hours depending on the severity of the disease.
-
Oxytetracycline
1 capsule every 6 hours. If severe, 500mg 2 capsules 6/8 hours apart.
-
Cephalexin
250mg/500mg 1 capsule every 6 hours. (7 days)
-
Erythromycin (Oral)
1 service every 6 hours. In severe infection 500mg 1 every 6 hours for 7-10 days.
-
Ciprofloxacin
It is not advisable to use laxatives for adult severe urinary tract infections. However, other drugs for acute nephritis are similar to those for sub-acute nephritis.
-
Frusemide (Furosemide)
1/2 pill every morning after breakfast 1/2 times a day or 1 day after serving, 2/3 days. The dose of the medicine should be determined based on the severity of the disease.
-
Hydrochlorothiazide
Dosage: 25-75mg daily after meals. 100 mg may be required in exceptional cases.
-
Methyldopa
Medicines containing methyldopa can be used in high blood pressure. However, it cannot be given if you have heart disease.
-
Ferrous Sulfate
Take 2 spoons of medicine daily after food.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Lupus nephritis and Learn More about Diseases

Tension headache
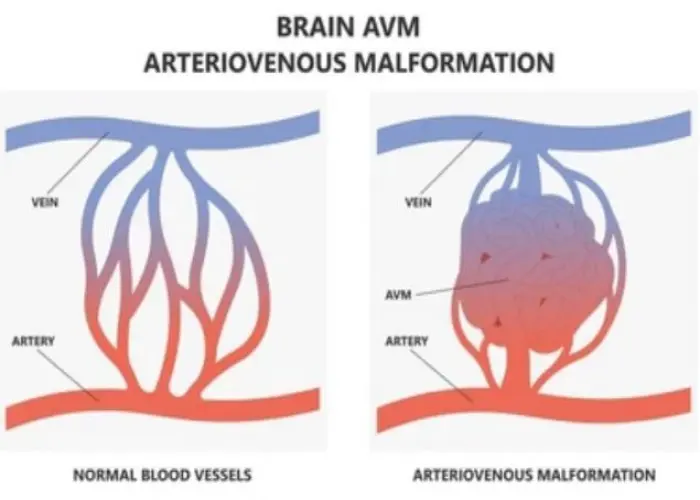
Arteriovenous malformation
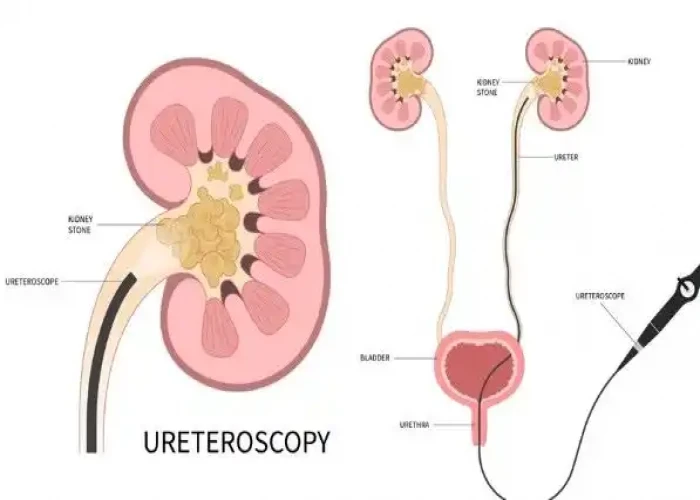
Ureteral cancer

Nightmare disorder

Temporal lobe seizure
Giardia infection (Giardiasis)
Endometrial cancer

Atypical depression
lupus nephritis, লুপাস নেফ্রাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.