Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
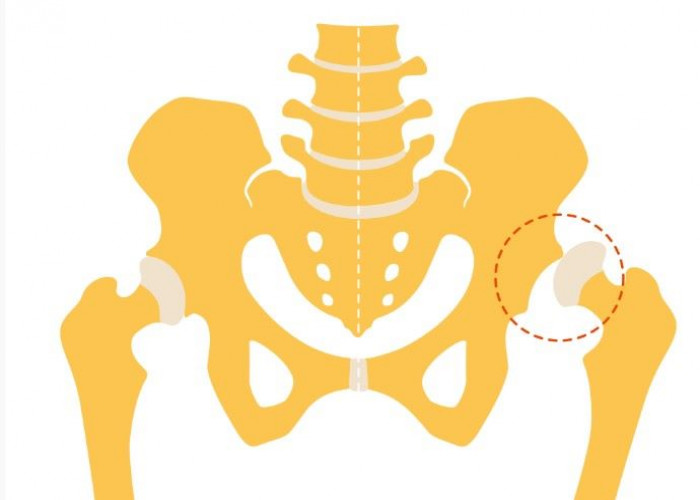
Hip dysplasia
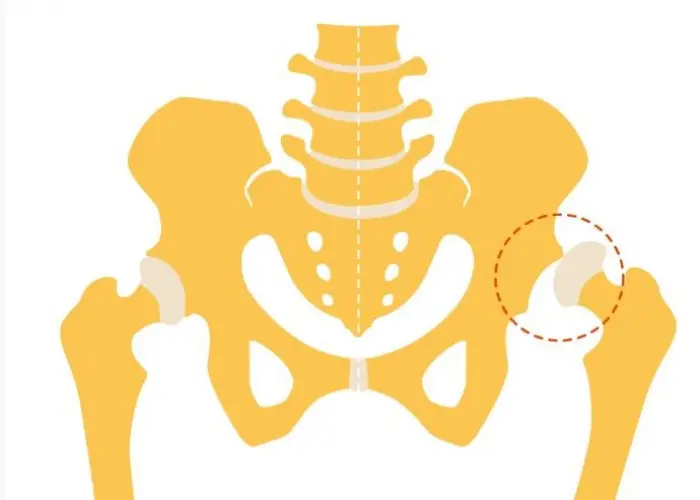
Hip dysplasia is a medical condition that occurs when the hip joint does not develop properly, causing the ball of the hip joint to partially or completely slip out of the socket. It is a common condition that affects both infants and adults.
In infants, hip dysplasia is often referred to as developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). It can be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, being born in the breech position, and a family history of the condition. In infants, hip dysplasia may be detected during a routine physical exam or ultrasound.
In adults, hip dysplasia may be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, prior injury to the hip joint, and a structural abnormality in the hip joint. Symptoms of hip dysplasia in adults may include hip pain, stiffness, and difficulty walking.
Treatment for hip dysplasia depends on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient. In infants, treatment may involve the use of a brace or harness to keep the hips in the correct position. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to realign the hip joint.
In adults, treatment for hip dysplasia may involve physical therapy, pain management, and surgery. Surgical options may include a hip replacement or a procedure to realign the hip joint.
It is important to seek medical attention if you have any concerns or symptoms related to hip dysplasia. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious health complications and improve outcomes.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Hip joint disease
- Groin pain or hip pain
Disease Causes
Hip dysplasia
At birth, the hip joint is made of soft cartilage that gradually hardens into bone. The ball and socket need to fit together well because they act as molds for each other. If the ball isn't seated firmly into the socket, the socket will not fully form around the ball and will become too shallow.
During the final month before birth, the space within the womb can become so crowded that the ball of the hip joint moves out of its proper position, which results in a shallower socket. Factors that may reduce the amount of space in the womb include:
- First pregnancy
- Large baby
- Breech presentation
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Hip dysplasia treatment depends on the age of the affected person and the extent of the hip damage. Infants are usually treated with a soft brace, such as a Pavlik harness, that holds the ball portion of the joint firmly in its socket for several months. This helps the socket mold to the shape of the ball.
The brace doesn't work as well for babies older than 6 months. Instead, the doctor may move the bones into the proper position and then hold them there for several months with a full-body cast. Sometimes surgery is needed to fit the joint together properly.
If the dysplasia is more severe, the position of the hip socket can also be corrected. In a periacetabular (per-e-as-uh-TAB-yoo-lur) osteotomy, the socket is cut free from the pelvis and then repositioned so that it matches up better with the ball.
Hip replacement surgery might be an option for older people whose dysplasia has severely damaged their hips over time, resulting in debilitating arthritis.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Hip dysplasia and Learn More about Diseases

Factor V Leiden
Mitral valve prolapse
Addison's disease
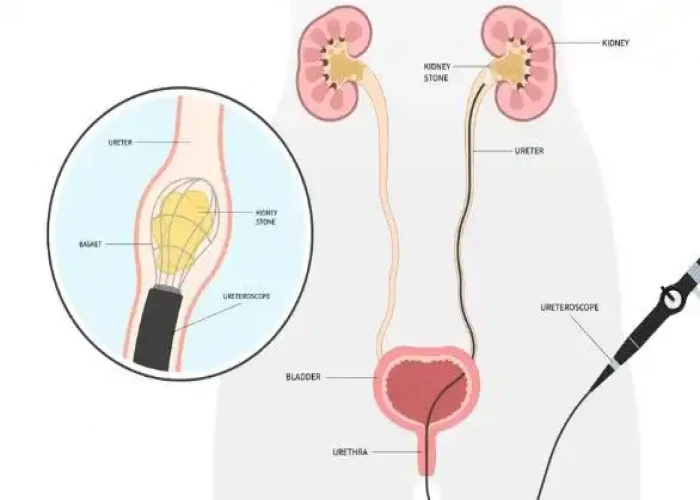
Ureteral obstruction
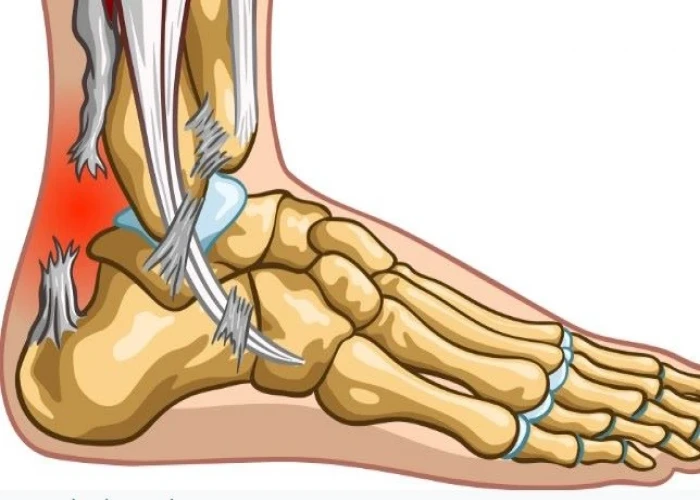
Median arcuate ligament syndrome (MALS)

Athlete's foot

Lip cancer
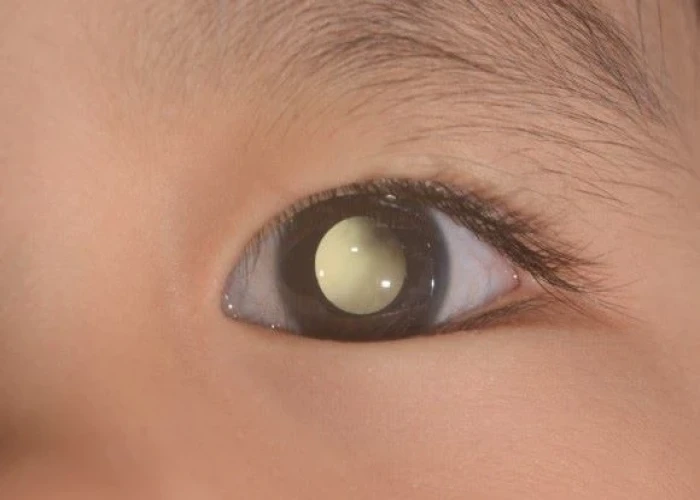
Retinoblastoma
hip dysplasia, হিপ ডিসপ্লাসিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.