Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Indigestion
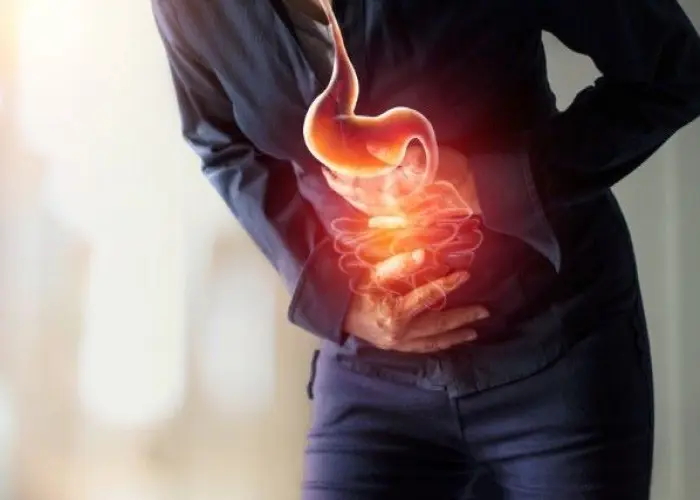
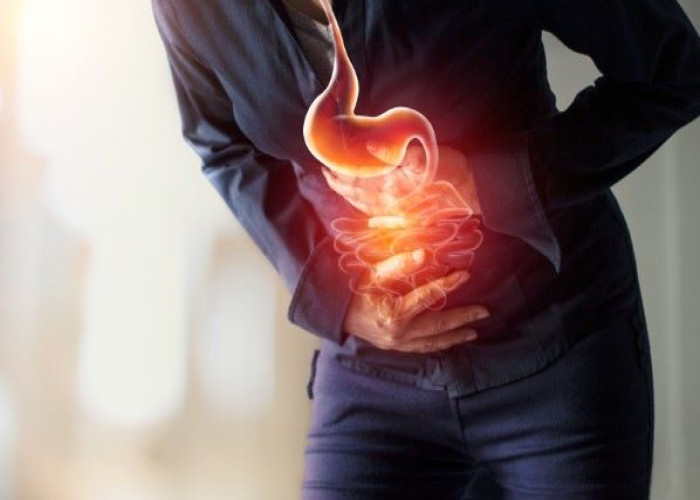
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, is a term used to describe discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen that is often accompanied by bloating, nausea, and a feeling of fullness. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including overeating, eating too quickly, consuming spicy or fatty foods, drinking alcohol or caffeine, smoking, and stress.
The symptoms of indigestion can range from mild to severe, and may include:
- A burning sensation in the upper abdomen or chest
- Feeling overly full or bloated after eating
- Nausea or vomiting
- Belching or gas
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Acidic taste in the mouth
Fortunately, indigestion is usually a mild and temporary condition that can be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications. Some tips to help relieve indigestion include:
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoiding foods that are known to trigger indigestion
- Chewing food slowly and thoroughly
- Drinking plenty of water and other non-caffeinated, non-alcoholic beverages
- Avoiding lying down after eating
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation
If indigestion symptoms persist or become more severe, it's important to consult a healthcare provider to rule out more serious conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or stomach ulcers.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Early fullness during a meal
- An uncomfortable feeling of fullness after eating
- Upper abdomen pain
- Abdomen bloating
- Nausea or vomiting
- Feel mild to severe pain in the area between the bottom of the breastbone and navel.
- Feel an uncomfortable heat or burning sensation between the bottom of breastbone and navel.
- Feel an uncomfortable sensation of tightness due to a buildup of gas.
Disease Causes
Indigestion
Indigestion has many possible causes. Often, indigestion is related to lifestyle and may be triggered by food, drink or medication. Common causes of indigestion include:
- Overeating or eating too quickly
- Fatty, greasy or spicy foods
- Too much caffeine, alcohol, chocolate or carbonated beverages
- Smoking
- Anxiety
- Certain antibiotics, pain relievers and iron supplements
A condition known as functional or nonulcer dyspepsia, which is related to irritable bowel syndrome, is a very common cause of indigestion.
Sometimes indigestion is caused by other conditions, including:
- Inflammation of the stomach (gastritis)
- Peptic ulcers
- Celiac disease
- Gallstones
- Constipation
- Pancreas inflammation (pancreatitis)
- Stomach cancer
- Intestinal blockage
- Reduced blood flow in the intestine (intestinal ischemia)
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disease
- Pregnancy
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Lifestyle changes may help ease indigestion. Your doctor may recommend:
- Avoiding foods that trigger indigestion
- Eating five or six small meals a day instead of three large meals
- Reducing or eliminating the use of alcohol and caffeine
- Avoiding certain pain relievers, such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve)
- Finding alternatives for medications that trigger indigestion
- Controlling stress and anxiety
If your indigestion persists, medications may help. Over-the-counter antacids are generally the first choice. Other options include:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which can reduce stomach acid. PPIs may be recommended particularly if you experience heartburn along with indigestion.
- H-2-receptor blockers, which can also reduce stomach acid.
- Prokinetics, which may be helpful if your stomach empties slowly.
- Antibiotics, which can help if H. pylori bacteria are causing your indigestion.
- Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications, which may ease the discomfort from indigestion by decreasing your sensation of pain.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Pancreatin
1 pill 2/3 times a day after meals.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
China officinalis
6, 30 Mix 10/15 drops in a glass of water and use it every 30 minutes. Children 1/2 tsp.
-
Nux vomica
Q Mix 10/15 drops in a glass of water and consume every 30 minutes. Half a spoonful of children.
-
Pulsatilla
6 3/4 drops of medicine should be taken every hour with little water.
-
Lycopodium clavatum
3X the power. Mix 3/4 drops with little water and consume every hour.
Disease yoga
Indigestion and Learn More about Diseases

Giant cell arteritis
Polyhydramnios
Factitious disorder
Meningitis

Broken ribs

Malaria Fever
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C. difficile infection
indigestion, বদহজম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.