Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
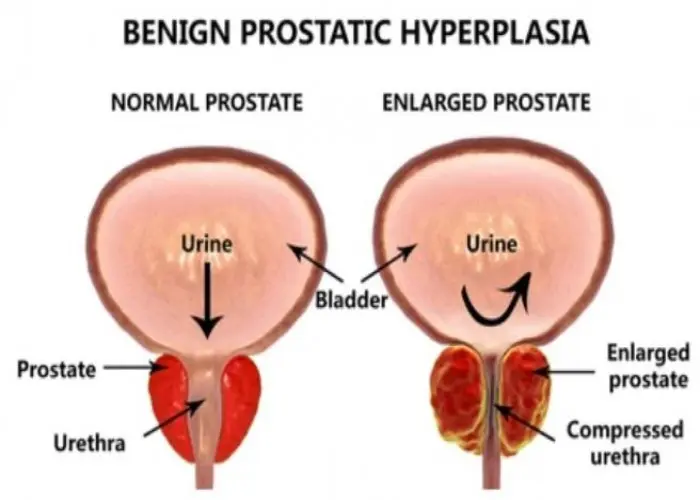
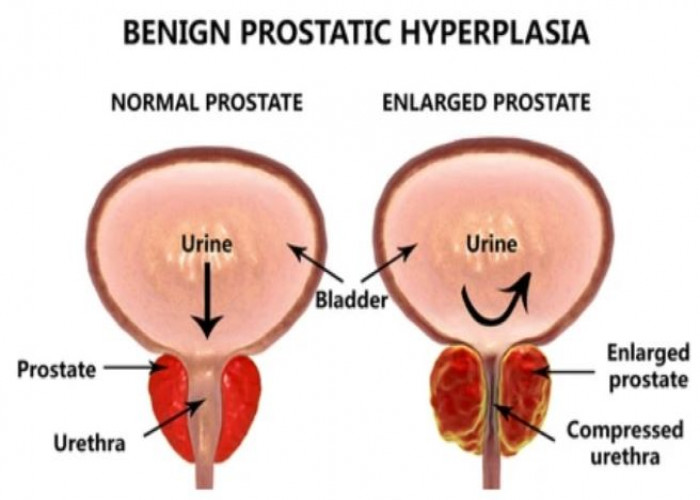
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that commonly affects men as they age. As the prostate enlarges, it can squeeze the urethra, which can cause urinary symptoms such as a weak or interrupted urine stream, frequent urination, and the need to urinate at night. Treatment options for BPH may include medication to relax the muscles around the prostate or shrink the prostate, minimally invasive procedures such as laser therapy or transurethral microwave therapy (TUMT), or surgery to remove part or all of the prostate. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the individual's overall health.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Inability to hold urine
- Frequent urination
- Frequent urination at night (nocturia)
- Difficulty urinating such as dribbling or hesitant urination
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
Disease Causes
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
The prostate gland is located beneath your bladder. The tube that transports urine from the bladder out of your penis (urethra) passes through the center of the prostate. When the prostate enlarges, it begins to block urine flow.
Most men have continued prostate growth throughout life. In many men, this continued growth enlarges the prostate enough to cause urinary symptoms or to significantly block urine flow.
It isn't entirely clear what causes the prostate to enlarge. However, it might be due to changes in the balance of sex hormones as men grow older.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
A wide variety of treatments are available for enlarged prostate, including medication, minimally invasive therapies and surgery. The best treatment choice for you depends on several factors, including:
- The size of your prostate
- Your age
- Your overall health
- The amount of discomfort or bother you are experiencing
If your symptoms are tolerable, you might decide to postpone treatment and simply monitor your symptoms. For some men, symptoms can ease without treatment.
Medication
Medication is the most common treatment for mild to moderate symptoms of prostate enlargement. The options include:
- Alpha blockers. These medications relax bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate, making urination easier. Alpha blockers — which include alfuzosin (Uroxatral), doxazosin (Cardura), tamsulosin (Flomax) and silodosin (Rapaflo) — usually work quickly in men with relatively small prostates. Side effects might include dizziness and a harmless condition in which semen goes back into the bladder instead of out the tip of the penis (retrograde ejaculation).
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. These medications shrink your prostate by preventing hormonal changes that cause prostate growth. These medications — which include finasteride (Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart) — might take up to six months to be effective. Side effects include retrograde ejaculation.
- Combination drug therapy. Your doctor might recommend taking an alpha blocker and a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor at the same time if either medication alone isn't effective.
- Tadalafil (Cialis). Studies suggest this medication, which is often used to treat erectile dysfunction, can also treat prostate enlargement.
Minimally invasive or surgical therapy
Minimally invasive or surgical therapy might be recommended if:
- Your symptoms are moderate to severe
- Medication hasn't relieved your symptoms
- You have a urinary tract obstruction, bladder stones, blood in your urine or kidney problems
- You prefer definitive treatment
Minimally invasive or surgical therapy might not be an option if you have:
- An untreated urinary tract infection
- Urethral stricture disease
- A history of prostate radiation therapy or urinary tract surgery
- A neurological disorder, such as Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis
Any type of prostate procedure can cause side effects. Depending on the procedure you choose, complications might include:
- Semen flowing backward into the bladder instead of out through the penis during ejaculation (retrograde ejaculation)
- Temporary difficulty with urination
- Urinary tract infection
- Bleeding
- Erectile dysfunction
- Very rarely, loss of bladder control (incontinence)
There are several types of minimally invasive or surgical therapies.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and Learn More about Diseases

Suicide and suicidal thoughts
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
Fever

Tay-Sachs disease

Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)

Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)

Chronic daily headaches

Alcohol intolerance
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, BPH symptoms, Prostatic hyperplasia, বেনিজন প্রোস্ট্যাটিক হাইপারপ্লাজিয়া, বিপিএইচ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.