 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Vulvodynia

Vulvodynia is a chronic pain condition that affects the vulva, the external female genitalia. It can cause burning, stinging, or rawness in the vulva, and can make sexual activity, tampon use, and even sitting or wearing tight clothing uncomfortable or painful. The pain may be constant, or it may come and go.
The exact cause of vulvodynia is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to nerve damage or irritation. Risk factors for vulvodynia include a history of yeast infections or other vulvar infections, chronic pelvic pain, and a history of sexual abuse.
Diagnosis of vulvodynia involves a thorough physical exam, including a pelvic exam, to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as infections or skin conditions. Additional tests, such as a biopsy or cultures to test for infections, may also be performed.
Treatment for vulvodynia typically involves a combination of approaches, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Medications may include pain relievers, such as over-the-counter pain relievers, topical numbing creams, and antidepressants or anticonvulsants that can help to relieve nerve pain. Physical therapy may include pelvic floor muscle relaxation exercises, biofeedback, or manual therapy. Lifestyle modifications may include avoiding tight clothing, using a lubricant during sexual activity, and practicing stress reduction techniques.
While vulvodynia can be a challenging condition to manage, with appropriate treatment and self-care, most women with vulvodynia are able to find relief from their symptoms and maintain an active and healthy lifestyle.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Vaginal itching
- Vaginal pain or burning
- It might occur only when the sensitive area is touched (provoked).
- A similar condition, vestibulodynia, causes pain only when pressure is applied to the area surrounding the entrance to the vagina.
Disease Causes
Vulvodynia
Doctors don't know what causes vulvodynia, but possible contributing factors include:
- Injury to or irritation of the nerves surrounding your vulvar region
- Past vaginal infections
- Allergies or sensitive skin
- Hormonal changes
- Muscle spasm or weakness in the pelvic floor, which supports the uterus, bladder and bowel
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Vulvodynia treatments focus on relieving symptoms. No one treatment works in every case. For many, a combination of treatments works best. It can take time to find the right treatments, and it can take time after starting a treatment before you notice relief.
Treatment options include:
- Medications. Steroids, tricyclic antidepressants or anticonvulsants can help lessen chronic pain. Antihistamines might reduce itching.
- Biofeedback therapy. This therapy can help reduce pain by teaching you how to relax your pelvic muscles and control how your body responds to the symptoms.
- Local anesthetics. Medications, such as lidocaine ointment, can provide temporary symptom relief. Your doctor might recommend applying lidocaine 30 minutes before sexual intercourse to reduce your discomfort. Using lidocaine ointment can cause your partner to have temporary numbness after sexual contact.
- Nerve blocks. Women who have long-standing pain that doesn't respond to other treatments might benefit from local nerve block injections.
- Pelvic floor therapy. Many women with vulvodynia have tension in the muscles of the pelvic floor, which supports the uterus, bladder and bowel. Exercises to relax those muscles can help relieve vulvodynia pain.
- Surgery. In cases of localized vulvodynia or vestibulodynia, surgery to remove the affected skin and tissue (vestibulectomy) relieves pain in some women.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
Amoxicillin can be given in the initial stage.
1 service every 6 hours.
-
Diclofenac Sodium
Injections containing diclofenac sodium can be given to reduce pain.
1 injection into the flesh.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
Medicines containing ranitidine to prevent gas in the stomach.
1 injection into the flesh.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Vulvodynia and Learn More about Diseases

Pseudogout
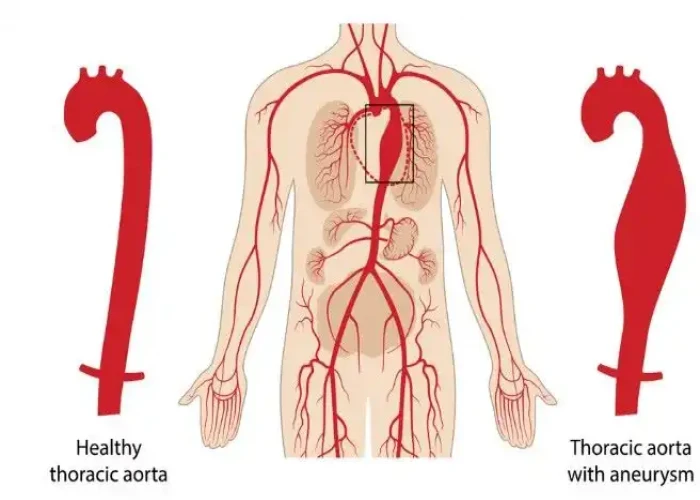
Thoracic aortic aneurysm

Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome
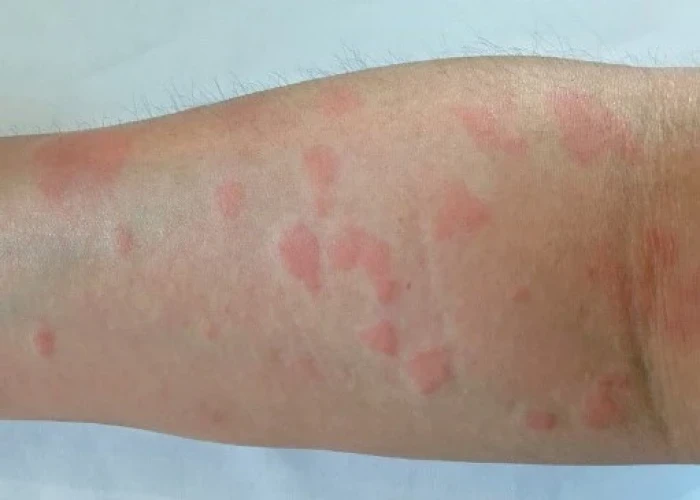
Lupus
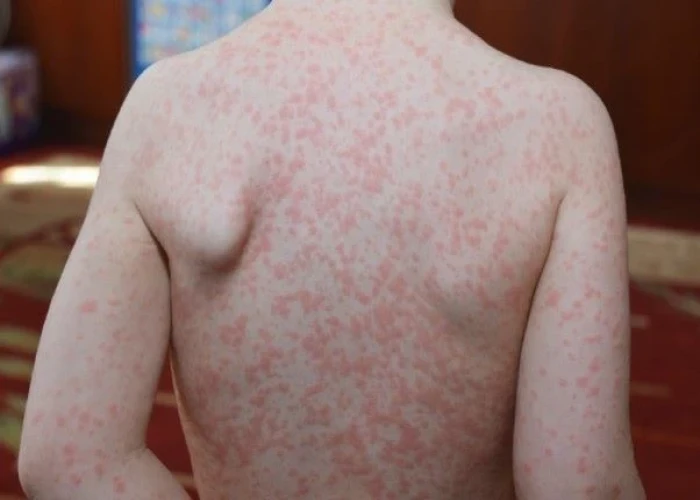
Mononucleosis
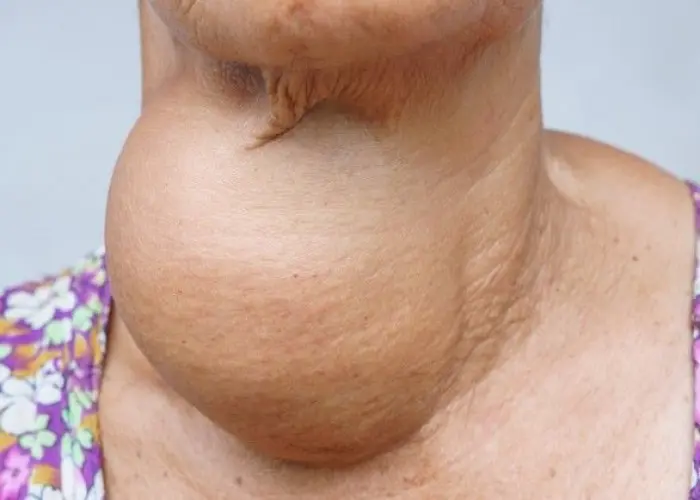
Goiter
Long QT syndrome

Bipolar disorder
vulvodynia, ভালভোডাইনিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
