Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
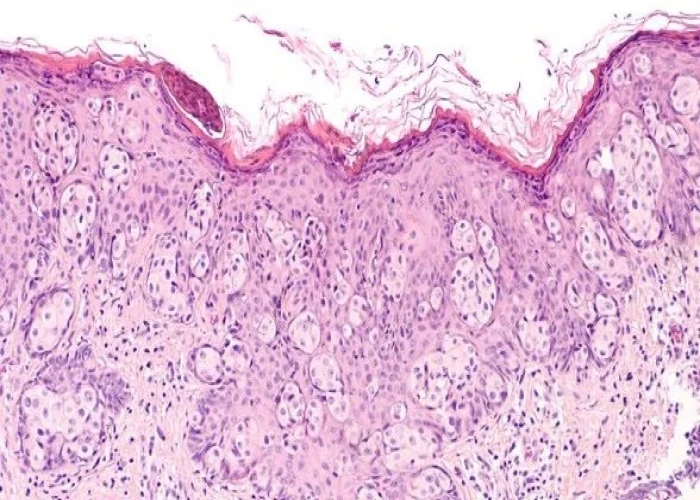
Paget's disease of the breast

Paget's disease of the breast is a rare form of breast cancer that affects the skin of the nipple and areola. The condition is named after Sir James Paget, a British surgeon who first described it in 1874.
Symptoms of Paget's disease of the breast include:
- Flaky, crusty or scaly skin on the nipple or areola
- Itching or burning sensation on the nipple or areola
- Redness or a rash on the nipple or areola
- A thickened or hardened area of skin on the nipple or areola
- Discharge from the nipple
Paget's disease of the breast is usually associated with underlying ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or invasive breast cancer, which may or may not be palpable. Therefore, diagnosis of the condition usually involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies such as mammography or ultrasound, and biopsy of the affected area.
Treatment for Paget's disease of the breast usually involves surgery, which may include a mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery, along with radiation therapy. Chemotherapy and hormone therapy may also be used, depending on the extent and characteristics of the cancer.
Early diagnosis and treatment of Paget's disease of the breast is important, as the condition can be aggressive and may spread to other areas of the body if left untreated. Therefore, individuals who notice any changes in their breast or nipple should consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Crusty, oozing or hardened skin resembling eczema on the nipple, areola or both
- Breast lump
- Nipple discharge
- Redness or changes in skin color
- Itching
- Flaky or scaly skin on the nipple
- Dry scaly skin
- Pain only at sexual entry (penetration)
- A flattened or turned-in (inverted) nipple
- Thickening of breast tissue, or a breast lump
Disease Causes
Paget's disease of the breast
Doctors don't know what causes Paget's disease of the breast. The most widely accepted theory is that the disease results from an underlying ductal breast cancer. The cancer cells from the original tumor then travel through milk ducts to the nipple and its surrounding skin. Another theory is that the disease can develop independently in the nipple.
Disease Prevents
Paget's disease of the breast
Breast cancer risk reduction for people with an average risk
Making changes in your daily life may help reduce your risk of breast cancer. Try to:
- Ask your doctor about breast cancer screening. Discuss with your doctor when to begin breast cancer screening exams and tests, such as clinical breast exams and mammograms.
- Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks of screening. Together, you can decide what breast cancer screening strategies are right for you.
- Become familiar with your breasts through breast self-exam for breast awareness. You may choose to become familiar with your breasts by occasionally inspecting your breasts during a breast self-exam for breast awareness. If there is a new change, lumps or other unusual signs in your breast, talk to your doctor promptly.
- Breast awareness can't prevent breast cancer, but it may help you to better understand the normal changes that your breasts undergo and identify any unusual signs and symptoms.
- Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For healthy adults, that means up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men.
- Exercise most days of the week. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise on most days of the week. If you haven't been active lately, ask your doctor whether it's OK and start slowly.
- Limit postmenopausal hormone therapy. Combination hormone therapy may increase the risk of breast cancer. Talk with your doctor about the benefits and risks of hormone therapy.
- You may experience bothersome signs and symptoms during menopause and, for you, the increased risk of breast cancer may be acceptable in order to relieve menopause signs and symptoms.
- To reduce the risk of breast cancer, use the lowest dose of hormone therapy possible for the shortest amount of time.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If your weight is healthy, work to maintain that weight. If you need to lose weight, ask your doctor about healthy strategies to accomplish this. Reduce the number of calories you eat each day and slowly increase the amount of exercise.
- Choose a healthy diet. Eating a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil and mixed nuts may reduce your risk of breast cancer. The Mediterranean diet focuses mostly on plant-based foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. People who follow the Mediterranean diet choose healthy fats, such as olive oil, over butter and fish instead of red meat.
Breast cancer risk reduction for people with a high risk
If your doctor has determined that you have an increased risk of breast cancer, you may discuss options to reduce your risk, such as:
- Preventive medications (chemoprevention). Estrogen-blocking medications reduce the risk of breast cancer if you have a high risk of the disease.
- These medications carry a risk of side effects, so doctors reserve these medications for those who have a very high risk of breast cancer. Discuss the benefits and risks with your doctor.
- Preventive surgery. If you have a very high risk of breast cancer, you may choose to have your healthy breasts surgically removed (prophylactic mastectomy). You may also choose to have your healthy ovaries removed (prophylactic oophorectomy) to reduce the risk of both breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Disease Treatments
If you have Paget's disease of the breast, you will likely need surgery. The type of surgery depends on the condition of the skin around your nipple and how advanced the underlying cancer is.
Surgical options include:
- Removing the entire breast (mastectomy). A mastectomy is an operation to remove all of your breast tissue. Most mastectomy procedures remove all of the breast tissue — the lobules, ducts, fatty tissue and some skin, including the nipple and areola (total or simple mastectomy).
- Removing the breast cancer (lumpectomy). During a lumpectomy, which may be referred to as breast-conserving surgery or wide local excision, the surgeon removes the cancer and a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue. If you and your doctor choose this option, you will also receive radiation therapy afterward.
- Removing a limited number of lymph nodes (sentinel node biopsy). To determine whether cancer has spread to your lymph nodes, your surgeon will discuss with you the role of removing the lymph nodes that are the first to receive the lymph drainage from your cancer.
- If no cancer is found in those lymph nodes, the chance of finding cancer in any of the remaining lymph nodes is small and no other nodes need to be removed.
- Removing several lymph nodes (axillary lymph node dissection). If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph nodes, your surgeon will discuss with you the role of removing additional lymph nodes in your armpit.
- Removing both breasts. Some people with cancer in one breast may choose to have their other (healthy) breast removed (contralateral prophylactic mastectomy) if they have a very increased risk of cancer in the other breast because of a genetic predisposition or strong family history.
You may choose to have breast reconstruction after surgery. Discuss your options and preferences with your surgeon.
Consider a referral to a plastic surgeon before your surgery. Your options may include reconstruction with a breast implant or reconstruction using your own tissue. These operations can be performed at the time of your mastectomy or at a later date.
Adjuvant therapy
After your operation, your doctor may recommend additional treatment (adjuvant therapy) with anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapy), radiation therapy or hormone therapy to prevent a recurrence of breast cancer.
Your specific treatment will depend on the extent of the cancer and whether your cancer tests positive for certain characteristics, such as having estrogen or progesterone receptors.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Paget's disease of the breast and Learn More about Diseases

Ebola virus and Marburg virus
Myelofibrosis
Hip fracture

Muscle cramp
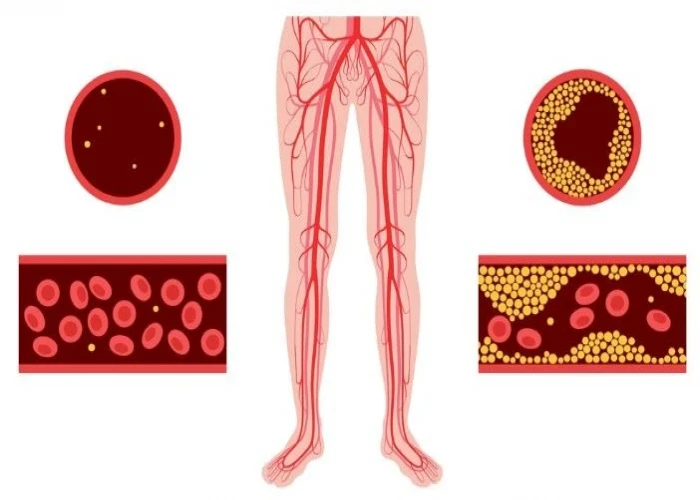
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)

Stress fractures

Rosacea
Tapeworm infection
paget's disease of the breast, স্তনের পেগেট রোগ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.