Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Tapeworm infection
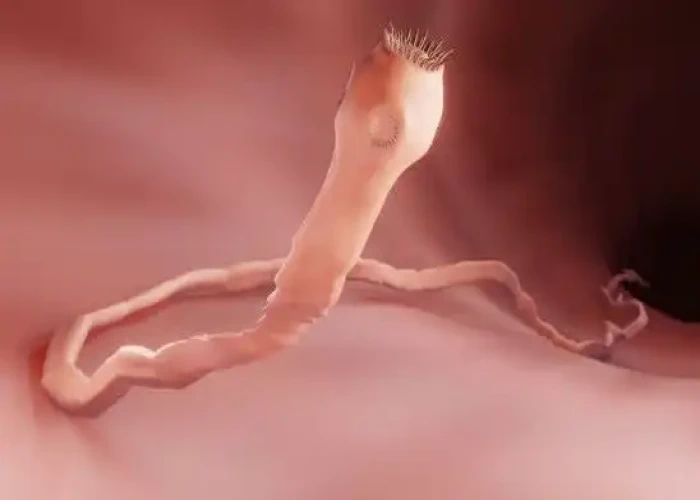
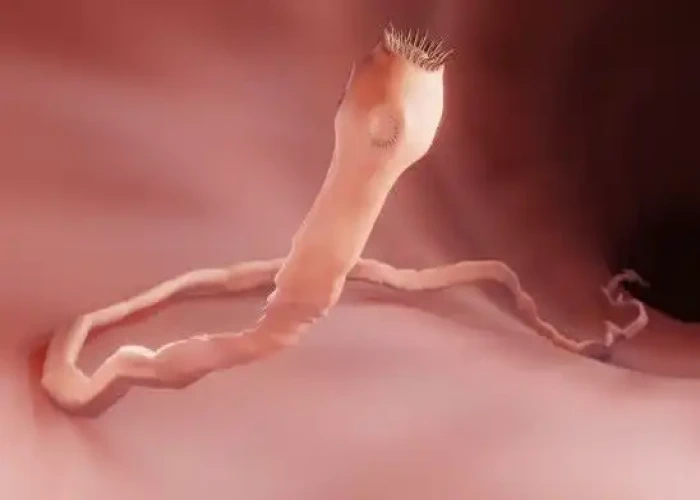
Tapeworm infection, also known as taeniasis, is a parasitic infection caused by one of several species of tapeworms. Tapeworms are flat, segmented parasites that can live in the intestines of animals, including humans. Infection with tapeworms typically occurs through the consumption of raw or undercooked meat that contains tapeworm larvae.
Symptoms of tapeworm infection can vary depending on the species of tapeworm and the location and extent of the infection, but may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Weakness
- Malnutrition
In some cases, people with tapeworm infections may not experience any symptoms.
Diagnosis of tapeworm infection typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests such as stool tests to identify tapeworm eggs or segments. Treatment for tapeworm infection typically involves medications such as praziquantel or nitazoxanide, which are effective in killing the adult tapeworms in the intestine. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove tapeworm cysts in the liver or other organs.
Preventing tapeworm infection involves cooking meat to a safe temperature (usually above 63°C or 145°F), washing hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling food, and avoiding the consumption of raw or undercooked meat or fish.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Nausea or vomiting
- Allergy
- Seizures
- Headaches
- Weight loss
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Diarrhea
- Abdomen pain
- Weakness
- Weight loss and inadequate absorption of nutrients from food
Disease Causes
Tapeworm infection
A tapeworm infection starts after ingestion of tapeworm eggs or larvae.
- Ingestion of eggs.. If you eat food or drink water contaminated with feces from a person or animal with tapeworm, you ingest microscopic tapeworm eggs. For example, a dog infected with a tapeworm will pass tapeworm eggs in its feces, which get into the soil.
- If this same soil comes in contact with a food or water source, it becomes contaminated. You can then be infected when you eat or drink something from the contaminated source.
- Once inside your intestines, the eggs develop into larvae. At this stage, the larvae become mobile. If they migrate out of your intestines, they form a cyst in the liver or other tissues.
- Ingestion of larvae cysts in meat or muscle tissue. When an animal has a tapeworm infection, it has tapeworm larvae in its muscle tissue. If you eat raw or undercooked meat from an infected animal, you ingest the larvae, which then develop into adult tapeworms in your intestines.
- Adult tapeworms can measure more than 80 feet (25 meters) long and can survive as long as 30 years in a host. Some tapeworms attach themselves to the walls of the intestines, where they cause irritation or mild inflammation, while others may pass through to your stool and exit your body.
Disease Prevents
Tapeworm infection
To prevent tapeworm infection:
- Wash your hands with soap and water before eating or handling food and after using the toilet.
- When traveling in areas where tapeworm is more common, wash and cook all fruits and vegetables with safe water before eating. If water might not be safe, be sure to boil it for at least a minute and then let it cool off before using it.
- Eliminate livestock exposure to tapeworm eggs by properly disposing of animal and human feces.
- Thoroughly cook meat at temperatures of at least 145 F (63 C) to kill tapeworm eggs or larvae.
- Freeze meat for as long as seven to 10 days and fish for at least 24 hours in a freezer with a temperature of -31 F (-35 C) to kill tapeworm eggs and larvae.
- Avoid eating raw or undercooked pork, beef and fish.
- Promptly treat dogs infected with tapeworm.
Disease Treatments
Some people with tapeworm infections never need treatment, for the tapeworm exits the body on its own. Others don't realize they have it because they have no symptoms. However, if you're diagnosed with intestinal tapeworm infection, medication will likely be prescribed to get rid of it.
Treatments for intestinal infections
The most common treatment for tapeworm infection involves oral medications that are toxic to the adult tapeworm, including:
- Praziquantel (Biltricide)
- Albendazole (Albenza)
- Nitazoxanide (Alinia)
Which medication your doctor prescribes depends on the species of tapeworm involved and the site of the infection. These drugs target the adult tapeworm, not the eggs, so it's important to avoid reinfecting yourself. Always wash your hands after using the toilet and before eating.
To be certain that your tapeworm infection has cleared, your doctor will probably have your stool samples checked at certain intervals after you've finished taking your medication. Successful treatment — meaning that your stool is free of tapeworm eggs, larvae or proglottids — is most likely if you receive appropriate treatment for the type of tapeworm causing your infection.
Treatments for invasive infections
Treating an invasive infection depends on the location and effects of the infection.
- Anthelmintic drugs. Albendazole (Albenza) can shrink some tapeworm cysts. Your doctor may monitor the cysts periodically using imaging studies such as ultrasound or X-ray to be sure the drug is effective.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. Dying tapeworm cysts can cause swelling or inflammation in tissues or organs, so your doctor may recommend prescription corticosteroid medication, such as prednisone or dexamethasone, to reduce inflammation.
- Anti-epileptic therapy. If the disease is causing seizures, anti-epileptic medications can stop them.
- Shunt placement. One type of invasive infection can cause too much fluid on the brain, called hydrocephalus. Your doctor may recommend placing a permanent tube (shunt) in your head to drain the fluid.
- Surgery. Whether cysts can be removed surgically depends on their location and symptoms. Cysts that develop in the liver, lungs and eyes are typically removed, since they can eventually threaten organ function.
- Your doctor might recommend a drainage tube as an alternative to surgery. The tube allows aggressive rinsing (irrigation) of the area with anti-parasitic solutions.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Tapeworm infection and Learn More about Diseases

Progeria

Thoracic outlet syndrome
Diabetic coma
Endometriosis

Acoustic neuroma

Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)

Peyronie's disease

Nail fungus
tapeworm infection, টেপওয়ার্ম সংক্রমণ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.