Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Neurodermatitis
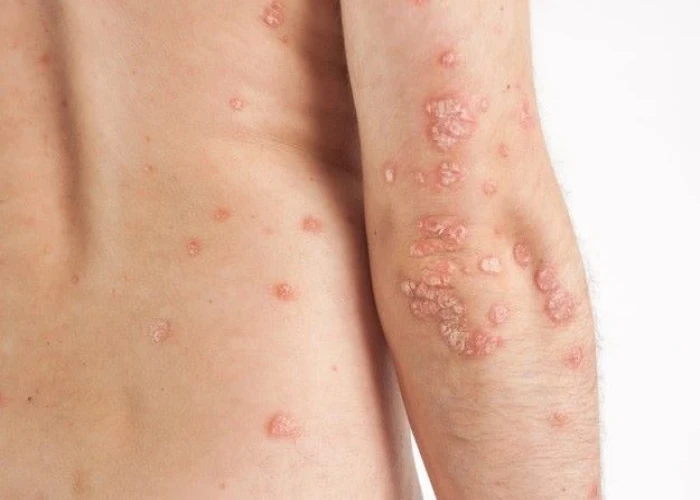
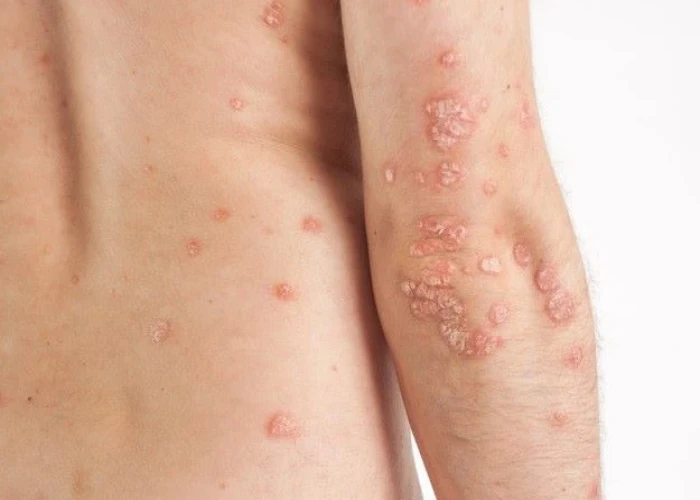
Neurodermatitis, also known as lichen simplex chronicus, is a skin condition characterized by chronic itching and scratching that leads to thick, scaly patches of skin. The condition is often related to stress or anxiety, and can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as insect bites, rough clothing, or emotional stress.
Symptoms of neurodermatitis may include itchy or scaly patches of skin that are thick and leathery in texture. The affected areas may be located on the neck, scalp, wrists, ankles, or other areas of the body.
Diagnosis of neurodermatitis may involve a physical exam, skin biopsy, or patch test to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms.
Treatment options for neurodermatitis may include topical creams or ointments to relieve itching and inflammation, as well as oral antihistamines to reduce itching and promote sleep. In some cases, stress reduction techniques such as meditation or counseling may also be helpful in managing symptoms.
It is important to avoid scratching the affected areas, as this can worsen the condition and lead to skin infections. Wearing loose clothing and using moisturizers can also help to reduce itching and prevent further skin damage.
While neurodermatitis can be uncomfortable and frustrating, it is typically not a serious or life-threatening condition. With proper treatment and self-care measures, most people with neurodermatitis can manage their symptoms and maintain good skin health.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Itching
Disease Causes
Neurodermatitis
The cause of neurodermatitis is unknown. The persistent rubbing and scratching that characterize the condition may begin with something that simply irritates the skin, such as tight clothing or a bug bite. As you rub or scratch the area, it gets itchier. The more you scratch, the more it itches.
In some cases, neurodermatitis is associated with chronic skin conditions — such as dry skin, eczema or psoriasis. Stress and anxiety can trigger itching too.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment is aimed at controlling the itching, preventing scratching and addressing underlying causes.
- Anti-itch medicated creams. If over-the-counter corticosteroid cream isn't helping, your doctor may prescribe a stronger corticosteroid or a nonsteroidal anti-itch product. A calcineurin inhibitor (tacrolimus) ointment may help if the vulva is involved.
- Corticosteroid injections. Your doctor may inject corticosteroids directly into the affected skin to help it heal.
- Medicine to ease itching. Prescription antihistamines help relieve itching in many people with neurodermatitis. Some of these drugs may cause drowsiness and help with alleviating scratching while you sleep.
- Anti-anxiety drugs. Because anxiety and stress can trigger neurodermatitis, anti-anxiety drugs may help prevent the itchiness.
- Medicated patches. For stubborn itching, your doctor may suggest topical lidocaine 5 percent or capsaicin 8 percent patches.
- Light therapy. Exposing the affected skin to particular types of light is sometimes helpful.
- Psychotherapy. Talking with a counselor can help you learn how your emotions and behaviors can fuel — or prevent — itching and scratching.
Emerging therapies
If your itching persists despite treatment, your doctor may suggest a nontraditional approach. For example, in small studies some people whose symptoms didn't improve with corticosteroid use did report success with the following treatments.
- OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) injection. This technique may reduce itching and clear up rough skin patches.
- An oral drug to ease the compulsion to pick and scratch. An oral drug called N-acetylcysteine has been shown in a small study to help some people with picking and scratching disorders and may be of help to people with neurodermatitis.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Neurodermatitis and Learn More about Diseases
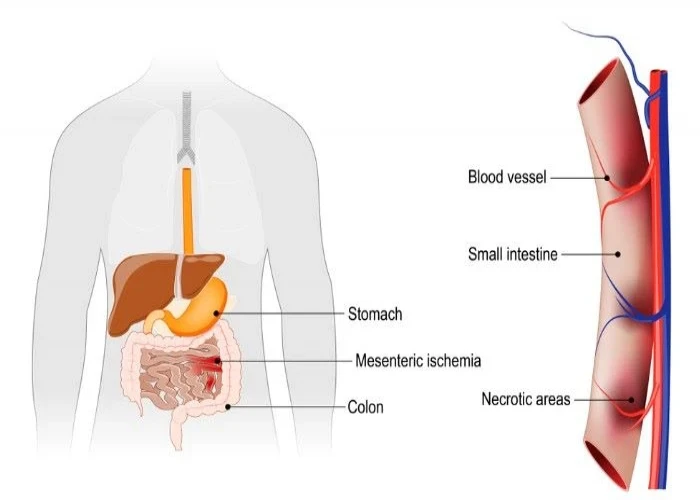
Mesenteric ischemia

Male breast cancer

Female sexual dysfunction
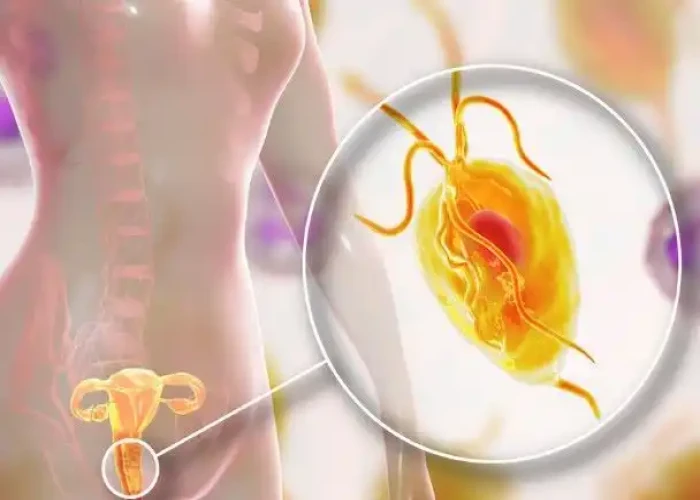
Trichomoniasis

Specific phobias
Aortic dissection
Graves' disease

Scarlet fever
neurodermatitis, নিউরোডার্মাটাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.