 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Delirium

Delirium is a state of confusion that can occur suddenly, typically as a result of an underlying medical condition or medication side effect. It is characterized by a disturbance in consciousness and a change in cognition or perception, such as disorientation, hallucinations, or delusions. Delirium can occur in individuals of any age, but it is more common in older adults.
The causes of delirium can vary and may include medical conditions such as infections, metabolic imbalances, or neurological disorders, as well as medication side effects or drug and alcohol withdrawal. The onset of delirium is often sudden, and the symptoms can fluctuate throughout the day.
The management of delirium involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause. Treatment may involve medications to manage symptoms, such as antipsychotics to treat hallucinations or delusions, as well as addressing any medical conditions that may be contributing to delirium. Non-pharmacological interventions such as reorienting the person to their surroundings, providing a calm and soothing environment, and providing supportive care may also be beneficial.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of delirium, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Delirium can be a serious condition, and prompt treatment can help to improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Memory loss
- Reversal of night-day sleep-wake cycle
- Not knowing where you are or who you are
- Being easily distracted by unimportant things
- Getting stuck on an idea rather than responding to questions or conversation
- An inability to stay focused on a topic or to switch topics
- Apathy
- Excessive anger
- Irritability
- Strong depression
- Anxiety
- Difficulty speaking
- Poor memory, particularly of recent events
- Rapid mood chang
Disease Causes
Delirium
Delirium occurs when the normal sending and receiving of signals in the brain become impaired. This impairment is most likely caused by a combination of factors that make the brain vulnerable and trigger a malfunction in brain activity.
Delirium may have a single cause or more than one cause, such as a combination of a medical condition and drug toxicity. Sometimes no cause can be identified. Possible causes include:
- Certain medications or drug toxicity
- Alcohol or drug intoxication or withdrawal
- A medical condition, such as a stroke, heart attack, worsening lung or liver disease, or an injury from a fall
- Metabolic imbalances, such as low sodium or low calcium
- Severe, chronic or terminal illness
- Fever and acute infection, particularly in children
- Urinary tract infection, pneumonia or the flu, especially in older adults
- Exposure to a toxin, such as carbon monoxide, cyanide or other poisons
- Malnutrition or dehydration
- Sleep deprivation or severe emotional distress
- Pain
- Surgery or other medical procedures that include anesthesia
Several medications or combinations of drugs can trigger delirium, including some types of:
- Pain drugs
- Sleep medications
- Medications for mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression
- Allergy medications (antihistamines)
- Asthma medications
- Steroid medicines called corticosteroids
- Parkinson's disease drugs
- Drugs for treating spasms or convulsions
Disease Prevents
Delirium
The most successful approach to preventing delirium is to target risk factors that might trigger an episode. Hospital environments present a special challenge — frequent room changes, invasive procedures, loud noises, poor lighting, and lack of natural light and sleep can worsen confusion.
Evidence indicates that certain strategies — promoting good sleep habits, helping the person remain calm and well-oriented, and helping prevent medical problems or other complications — can help prevent or reduce the severity of delirium.
Disease Treatments
The first goal of treatment for delirium is to address any underlying causes or triggers — for example, by stopping use of a particular medication, addressing metabolic imbalances or treating an infection. Treatment then focuses on creating the best environment for healing the body and calming the brain.
Supportive care
Supportive care aims to prevent complications by:
- Protecting the airway
- Providing fluids and nutrition
- Assisting with movement
- Treating pain
- Addressing incontinence
- Avoiding use of physical restraints and bladder tubes
- Avoiding changes in surroundings and caregivers when possible
- Encouraging the involvement of family members or familiar people
Medications
If you're a family member or caregiver of someone who experiences delirium, talk with the doctor about avoiding or minimizing the use of drugs that may trigger delirium. Certain medications may be needed to control pain that's causing delirium.
Other types of medications may help calm a person who has severe agitation or confusion or who misinterprets the environment in a way that leads to severe paranoia, fear or hallucinations. These medications may be needed when certain behaviors:
- Prevent the performance of a medical exam or treatment
- Endanger the person or threaten the safety of others
- Don't lessen with nondrug treatments
These medications are usually reduced in dose or discontinued when the delirium resolves.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Belladonna
6, 30 strength.
-
Hyoscyamus
30, 200 strength.
-
Opium
6, 30 strength.
-
Nux vomica
30, 200 strength.
-
Hydrastis
Q strength.
-
Arsenicum
30 strength.
-
Coffea
6 strength.
-
Lachesis
6, 30 strength.
-
Stramonium
6, 30 strength.
-
Sulphuric acid
Q strength.
Disease yoga
Delirium and Learn More about Diseases

Balance problems

Lip cancer
Thread Worm
Colon cancer

Lactose intolerance
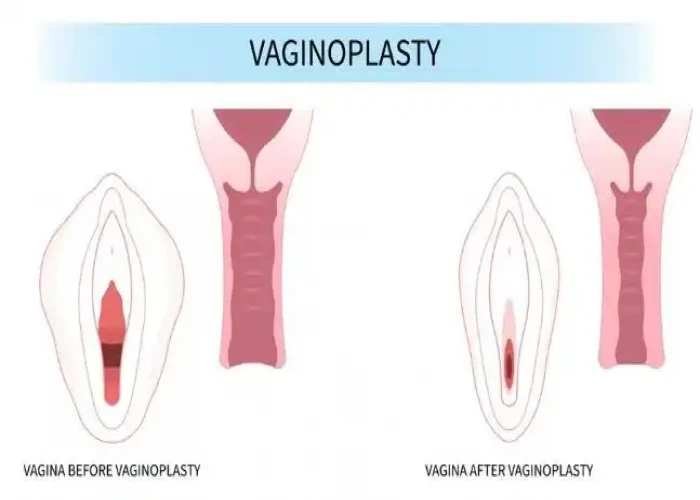
Vaginal agenesis

Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD)
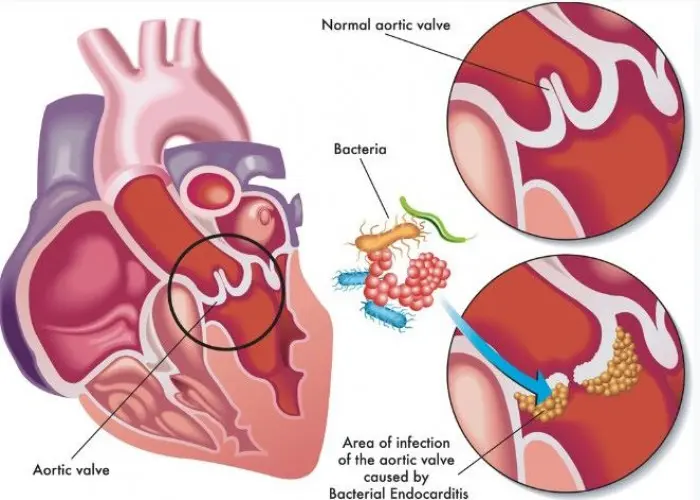
Endocarditis
Delirium, Deli rium, Delirium tremens, প্রলাপ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
