 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
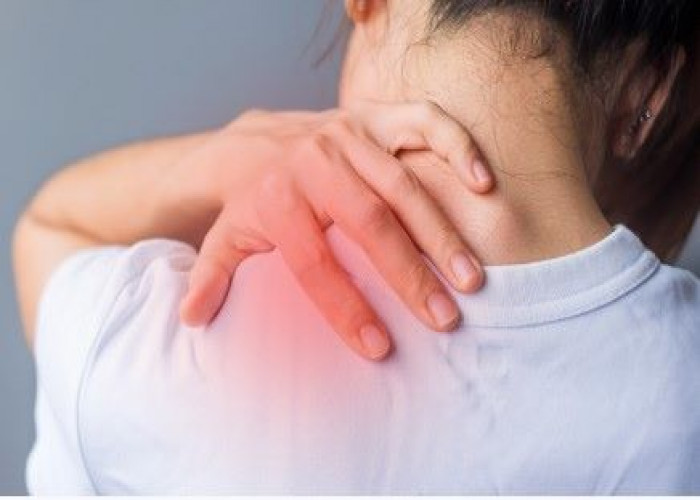
Fibromyalgia
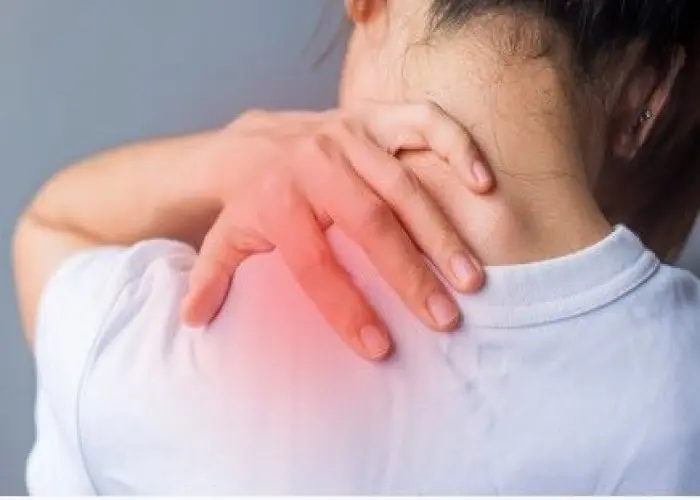
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, tenderness, and stiffness in the muscles and soft tissues of the body. It is often accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties such as memory problems and difficulty concentrating.
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but it is believed to be related to the abnormal processing of pain signals in the brain and changes in the levels of certain neurotransmitters, including serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It may also be triggered or worsened by physical or emotional trauma, infections, or other medical conditions.
There is no single test to diagnose fibromyalgia, and it can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are similar to those of many other conditions. Diagnosis usually involves a thorough medical history, a physical examination, and ruling out other possible causes of the symptoms.
Treatment for fibromyalgia typically involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and other therapies. Medications such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants may be used to help manage the pain and other symptoms of fibromyalgia. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, stress management, and a healthy diet, can also help to alleviate symptoms. Other therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and physical therapy, may also be recommended to help manage the condition.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome
- Migraine and other types of headaches
- Postural tachycardia syndrome
- Strong depression
- Anxiety
- Migraine
- Headaches
- Loss of bowel or bladder function
- Temporomandibular joint disorders
Disease Causes
Fibromyalgia
Many researchers believe that repeated nerve stimulation causes the brain and spinal cord of people with fibromyalgia to change. This change involves an abnormal increase in levels of certain chemicals in the brain that signal pain.
In addition, the brain's pain receptors seem to develop a sort of memory of the pain and become sensitized, meaning they can overreact to painful and nonpainful signals.
There are likely many factors that lead to these changes, including:
- Genetics. Because fibromyalgia tends to run in families, there may be certain genetic mutations that may make you more susceptible to developing the disorder.
- Infections. Some illnesses appear to trigger or aggravate fibromyalgia.
- Physical or emotional events. Fibromyalgia can sometimes be triggered by a physical event, such as a car accident. Prolonged psychological stress may also trigger the condition.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
In general, treatments for fibromyalgia include both medication and self-care strategies. The emphasis is on minimizing symptoms and improving general health. No one treatment works for all symptoms, but trying a variety of treatment strategies can have a cumulative effect.
Medications
Medications can help reduce the pain of fibromyalgia and improve sleep. Common choices include:
- Pain relievers. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve, others) may be helpful. Opioid medications are not recommended, because they can lead to significant side effects and dependence and will worsen the pain over time.
- Antidepressants. Duloxetine (Cymbalta) and milnacipran (Savella) may help ease the pain and fatigue associated with fibromyalgia. Your doctor may prescribe amitriptyline or the muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine to help promote sleep.
- Anti-seizure drugs. Medications designed to treat epilepsy are often useful in reducing certain types of pain. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is sometimes helpful in reducing fibromyalgia symptoms, while pregabalin (Lyrica) was the first drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat fibromyalgia.
Therapies
A variety of different therapies can help reduce the effect that fibromyalgia has on your body and your life. Examples include:
- Physical therapy. A physical therapist can teach you exercises that will improve your strength, flexibility and stamina. Water-based exercises might be particularly helpful.
- Occupational therapy. An occupational therapist can help you make adjustments to your work area or the way you perform certain tasks that will cause less stress on your body.
- Counseling. Talking with a counselor can help strengthen your belief in your abilities and teach you strategies for dealing with stressful situations.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Fibromyalgia and Learn More about Diseases

Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Q fever
Raynaud's disease

Bronchiolitis
Perimenopause

Nasal and paranasal tumors
Farsightedness

Yips
fibromyalgia, ফাইব্রোমায়ালগিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
