Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
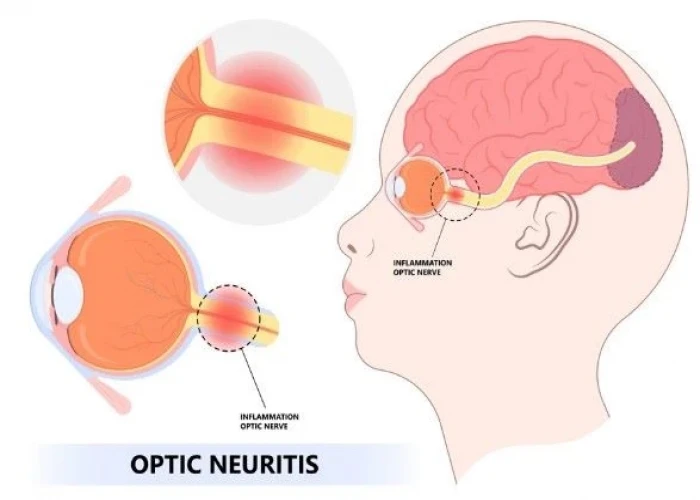
Optic neuritis
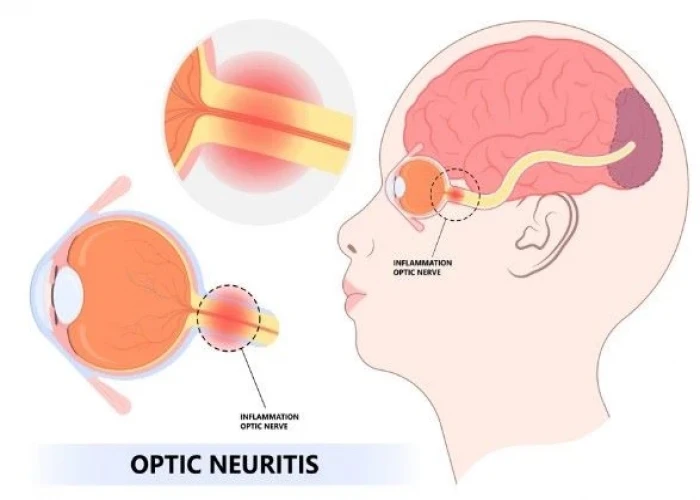
Optic neuritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the optic nerve, which can cause temporary or permanent loss of vision. The optic nerve is responsible for carrying visual information from the eye to the brain, and inflammation of this nerve can disrupt this process.
Symptoms of optic neuritis may include:
- Loss of vision in one eye, which may occur gradually or suddenly
- Blurred or hazy vision
- Diminished color vision
- Eye pain, especially with eye movement
- Loss of visual contrast sensitivity
The exact cause of optic neuritis is not always clear, but it is thought to be an autoimmune condition in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the optic nerve. It may be associated with other autoimmune conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS).
Diagnosis of optic neuritis may involve a comprehensive eye exam, visual acuity test, and imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. Treatment may involve medications such as corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and pain, as well as management of any underlying conditions such as MS.
Most people with optic neuritis experience a partial or complete recovery of vision within a few weeks to several months, but some may experience permanent vision loss. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms of optic neuritis, as early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Eye pain or burning
- Blurred vision of eye
- Difficulty with night vision
- Flashes of light in one or both eyes (photopsia)
Disease Causes
Optic neuritis
The exact cause of optic neuritis is unknown. It's believed to develop when the immune system mistakenly targets the substance covering your optic nerve, resulting in inflammation and damage to the myelin.
Normally, the myelin helps electrical impulses travel quickly from the eye to the brain, where they're converted into visual information. Optic neuritis disrupts this process, affecting vision.
The following autoimmune conditions often are associated with optic neuritis:
- Multiple sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis is a disease in which your autoimmune system attacks the myelin sheath covering nerve fibers in your brain. In people with optic neuritis, the risk of developing multiple sclerosis after one episode of optic neuritis is about 50% over a lifetime.
- Your risk of developing multiple sclerosis after optic neuritis increases further if an MRI scan shows lesions on your brain.
- Neuromyelitis optica. In this condition, inflammation affects the optic nerve and spinal cord. Neuromyelitis optica has similarities to multiple sclerosis, but neuromyelitis optica doesn't cause damage to the nerves in the brain as often as multiple sclerosis does. Still, neuromyelitis optica is more severe than MS, often resulting in a diminished recovery after an attack compared with MS.
- Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) antibody disorder. This condition can cause inflammation to the optic nerve, spinal cord or brain. Similar to MS and neuromyelitis optica, recurrent attacks of inflammation can occur. Recovery from MOG attacks is usually better than recovery from neuromyelitis optica.
When symptoms of optic neuritis are more complex, other associated causes need to be considered, including:
- Infections. Bacterial infections, including Lyme disease, cat-scratch fever and syphilis, or viruses, such as measles, mumps and herpes, can cause optic neuritis.
- Other diseases. Diseases such as sarcoidosis, Behcet's disease and lupus can cause recurrent optic neuritis.
- Drugs and toxins. Some drugs and toxins have been associated with the development of optic neuritis. Ethambutol, used to treat tuberculosis, and methanol, a common ingredient in antifreeze, paints and solvents, are associated with optic neuritis.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Optic neuritis usually improves on its own. In some cases, steroid medications are used to reduce inflammation in the optic nerve. Possible side effects from steroid treatment include weight gain, mood changes, facial flushing, stomach upset and insomnia.
Steroid treatment is usually given by vein (intravenously). Intravenous steroid therapy quickens vision recovery, but it doesn't appear to affect the amount of vision you'll recover for typical optic neuritis.
When steroid therapy fails and severe vision loss persists, a treatment called plasma exchange therapy might help some people recover their vision. Studies haven't yet confirmed that plasma exchange therapy is effective for optic neuritis.
Preventing multiple sclerosis (MS)
If you have optic neuritis, and you have two or more brain lesions evident on MRI scans, you might benefit from multiple sclerosis medications, such as interferon beta-1a or interferon beta-1b, that may delay or help prevent MS. These injectable medications are used for people at high risk of developing MS. Possible side effects include depression, injection site irritation and flu-like symptoms.
Prognosis
Most people regain close to normal vision within six months after an optic neuritis episode.
People whose optic neuritis returns have a greater risk of developing MS, neuromyelitis optica or MOG antibody associated disorder. Optic neuritis can recur in people without underlying conditions, and those people generally have a better long-term prognosis for their vision than do people with MS or neuromyelitis optica.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Optic neuritis and Learn More about Diseases
Amoebic Dysentry
Peritonitis
Mononucleosis

Lead poisoning

Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Pulmonary edema
Cor Pulmonale
Gum Boil
optic neuritis, অপটিক নিউরাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.