Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Poison ivy rash
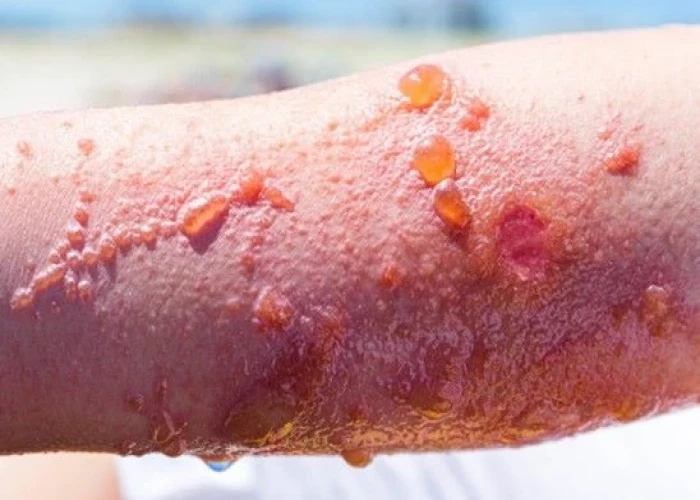
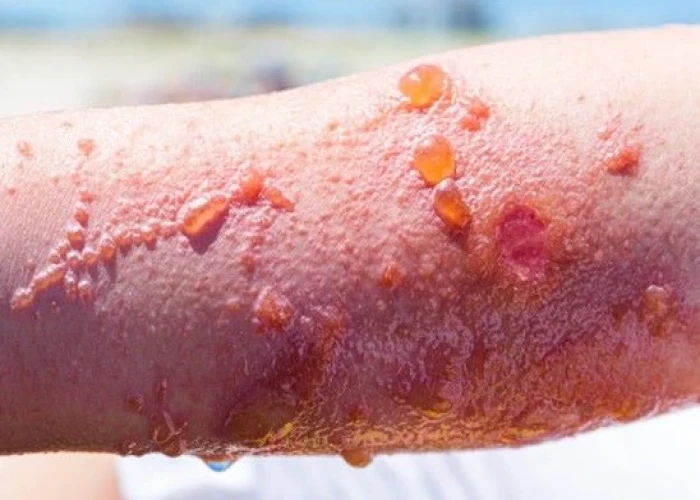
A poison ivy rash is a type of allergic reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with the sap of poison ivy, poison oak, or poison sumac plants. The sap contains a substance called urushiol, which can cause an itchy, red rash and blisters on the skin.
Symptoms of a poison ivy rash usually appear within a few hours to several days after exposure to the plant. The rash typically begins as small red bumps that may develop into fluid-filled blisters. The affected area may also be swollen, itchy, and tender to the touch.
Treatment for a poison ivy rash typically involves washing the affected area with soap and water as soon as possible after exposure to remove any remaining urushiol. Over-the-counter creams or lotions containing calamine or hydrocortisone can help relieve itching and inflammation. Oral antihistamines may also be used to help reduce itching and swelling.
In most cases, a poison ivy rash will go away on its own within one to three weeks. However, if the rash is severe or widespread, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications such as oral steroids or prescription-strength creams or ointments.
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding a poison ivy rash. It is important to learn how to identify poison ivy, oak, and sumac plants and to avoid contact with them. If you do come into contact with these plants, wash the affected area with soap and water as soon as possible to help reduce the risk of developing a rash.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Redness or changes in skin color
- Itching
- Swollen skin
- Blisters
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
Disease Causes
Poison ivy rash
Poison ivy rash is caused by an allergic reaction to an oily resin called urushiol. It's found in poison ivy, poison oak and poison sumac. This oily resin is very sticky, so it easily attaches to your skin, clothing, tools, equipment and pet's fur. You can get a poison ivy reaction from:
- Touching the plant. If you touch the leaves, stem, roots or berries of the plant, you may have a reaction.
- Touching contaminated objects. If you walk through some poison ivy and then later touch your shoes, you might get urushiol on your hands. You might then transfer it to your face or body by touching or rubbing. If the contaminated object isn't cleaned, the urushiol on it can still cause a skin reaction years later.
- Inhaling smoke from the burning plants. Even the smoke from burning poison ivy, poison oak and poison sumac can irritate or harm your nasal passages or lungs.
Pus that oozes from blisters doesn't contain urushiol and won't spread the rash. But it's possible to get poison ivy rash from someone if you touch plant resin that's still on the person or contaminated clothing.
Disease Prevents
Poison ivy rash
To prevent poison ivy rash, follow these tips:
- Avoid the plants. Learn how to identify poison ivy, poison oak and poison sumac in all seasons. When hiking or engaging in other activities that might expose you to these plants, try to stay on cleared pathways. Wear socks, pants and long sleeves when outdoors. If camping, make sure you pitch your tent in an area free of these plants.
- Keep pets from running through wooded areas so that urushiol doesn't stick to their fur, which you then may touch.
- Wear protective clothing. If needed, protect your skin by wearing socks, boots, pants, long sleeves and heavy gloves.
- Remove or kill the plants. Identify and remove poison ivy, poison oak and poison sumac from your yard or garden. You can get rid of such plants by applying an herbicide or pulling them out of the ground, including the roots, while wearing heavy gloves. Afterward remove the gloves carefully and wash them and your hands. Don't burn poison ivy or related plants because the urushiol can be carried by the smoke.
- Wash your skin or your pet's fur. Within 30 minutes after exposure to urushiol, use soap and water to gently wash off the harmful resin from your skin. Scrub under your fingernails too. Even washing after an hour or so can help reduce the severity of the rash.
- If you think your pet may be contaminated with urushiol, put on some long rubber gloves and give your pet a bath.
- Clean contaminated objects. If you think you've come into contact with poison ivy, wash your clothing promptly in warm soapy water — ideally in a washing machine. Handle contaminated clothing carefully so that you don't transfer the urushiol to yourself, furniture, rugs or appliances.
- Also wash as soon as possible any other items that came in contact with the plant oil — such as outdoor gear, garden tools, jewelry, shoes and even shoelaces. Urushiol can remain potent for years. So if you put away a contaminated jacket without washing it and take it out a year later, the oil on the jacket may still cause a rash.
- Apply a barrier cream. Try over-the-counter skin products that are intended to act as a barrier between your skin and the oily resin that causes poison ivy rash.
Disease Treatments
Poison ivy treatments usually involve self-care methods at home. And the rash typically goes away on its own in two to three weeks.
If the rash is widespread or causes many blisters, your doctor may prescribe an oral corticosteroid, such as prednisone, to reduce swelling. If a bacterial infection has developed at the rash site, your doctor might prescribe an oral antibiotic.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Poison ivy rash and Learn More about Diseases

Wilson's disease

Medication overuse headaches
Arteriovenous malformation

Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)

Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)

Diabetic hypoglycemia
Bladder cancer
Colon cancer
Poison ivy rash, পয়জন আইভি রাস, বিষ আইভি ফুসকুড়ি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.