Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
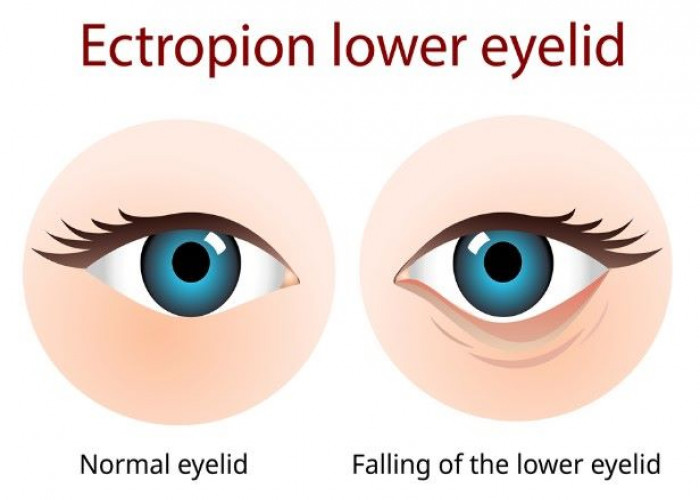
Ectropion
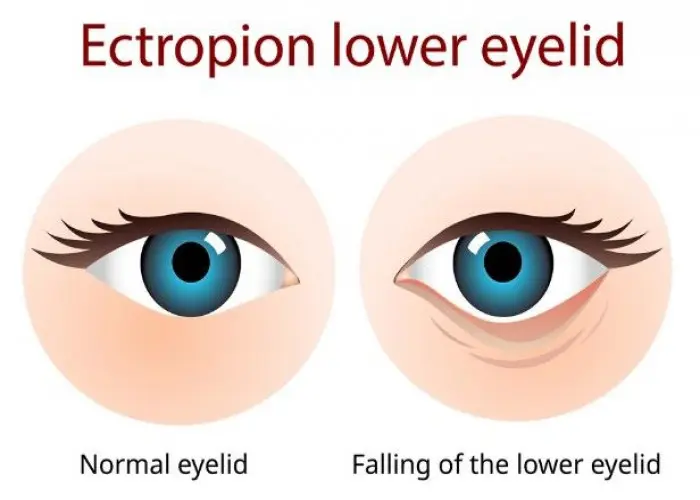
Ectropion is a condition where the lower eyelid turns outward, away from the eye, and does not rest against the eyeball as it normally should. This can cause the inner surface of the eyelid to be exposed, leading to irritation, dryness, redness, and increased tearing.
Ectropion is most commonly caused by aging, as the tissues and muscles that support the eyelid weaken over time. Other causes include injury, nerve damage, scarring, and certain skin conditions. In some cases, it may be a congenital condition that is present from birth.
The symptoms of ectropion can include dryness, itching, irritation, and tearing in the affected eye. Treatment for ectropion typically involves surgical repair, which may include tightening the eyelid muscles and tissues, and repositioning the eyelid. In some cases, artificial tears, ointments, and lubricating drops may be used to alleviate symptoms of dryness and irritation.
If left untreated, ectropion can lead to corneal damage, infection, and vision loss. It is important to see an eye doctor if you experience any symptoms of ectropion, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve the outlook for the condition.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Excessive tears in eyes
- Dry eyes
- Eye pain or burning
- Sensitivity to light (Photophobia)
- Blurred vision of eye
Disease Causes
Ectropion
Ectropion can be caused by:
- Muscle weakness. As you age, the muscles under your eyes tend to weaken, and tendons stretch out. These muscles and tendons hold your eyelid taut against your eye. When they weaken, your eyelid can begin to droop.
- Facial paralysis. Certain conditions, such as Bell's palsy, and certain types of tumors can paralyze facial nerves and muscles. Facial paralysis that affects eyelid muscles can lead to ectropion.
- Scars or previous surgeries. Skin that has been damaged by burns or trauma, such as a dog bite, can affect the way that your eyelid rests against your eye. Previous eyelid surgery (blepharoplasty) can cause ectropion, particularly if a considerable amount of skin was removed from the eyelid at the time of surgery.
- Eyelid growths. Benign or cancerous growths on your eyelid can cause the lid to turn outward.
- Genetic disorders. Rarely is ectropion present at birth (congenital). When it is, it's usually associated with genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
If your ectropion is mild, your doctor might recommend artificial tears and ointments to ease the symptoms. Surgery is generally required to fully correct ectropion.
Surgery
The type of surgery you have depends on the condition of the tissue surrounding your eyelid and on the cause of your ectropion:
- Ectropion caused by muscle and ligament relaxation due to aging. Your surgeon will likely remove a small part of your lower eyelid at the outer edge. When the lid is stitched back together, the tendons and muscles of the lid will be tightened, causing the lid to rest properly on the eye. This procedure is generally relatively simple.
- Ectropion caused by scar tissue from injury or previous surgery. Your surgeon might need to use a skin graft, taken from your upper eyelid or behind your ear, to help support the lower lid. If you have facial paralysis or significant scarring, you might need a second procedure to completely correct your ectropion.
Before surgery, you'll receive a local anesthetic to numb your eyelid and the area around it. You may be lightly sedated using oral or intravenous medication to make you more comfortable, depending on the type of procedure you're having and whether it's done in an outpatient surgical clinic.
After surgery you might need to:
- Wear an eye patch for 24 hours
- Use an antibiotic and steroid ointment on your eye several times a day for one week
- Use cold compresses periodically to decrease bruising and swelling
After surgery you will likely experience:
- Temporary swelling
- Bruising on and around your eye
Your eyelid might feel tight after surgery. But as you heal, it will become more comfortable. Stitches are usually removed about a week after surgery. You can expect the swelling and bruising to fade in about two weeks.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Ectropion and Learn More about Diseases

Alcohol use disorder
Knee pain

Orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension)
Hairy cell leukemia

Pediatric thrombocytopenia
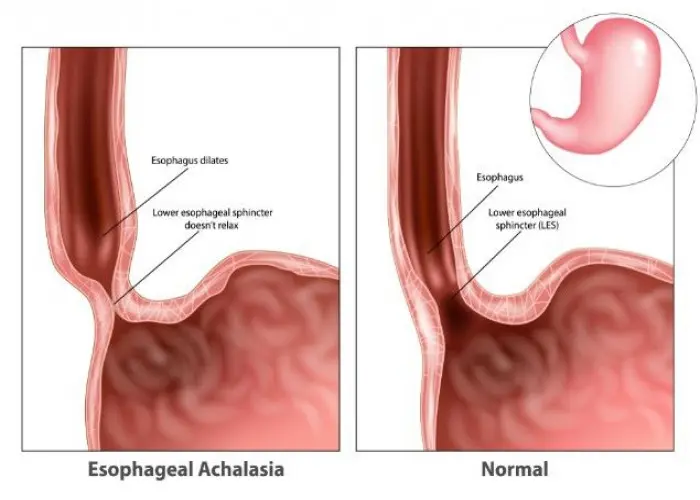
Esophagitis
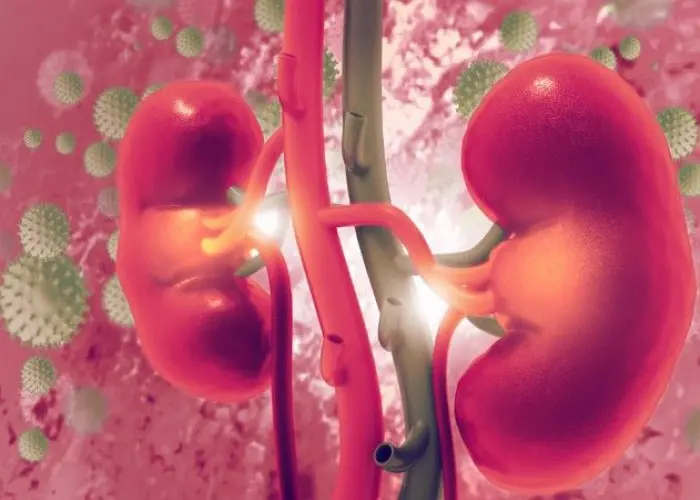
Kidney infection
Systemic mastocytosis
ectropion, ইট্রোপিয়ন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.