Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Smallpox
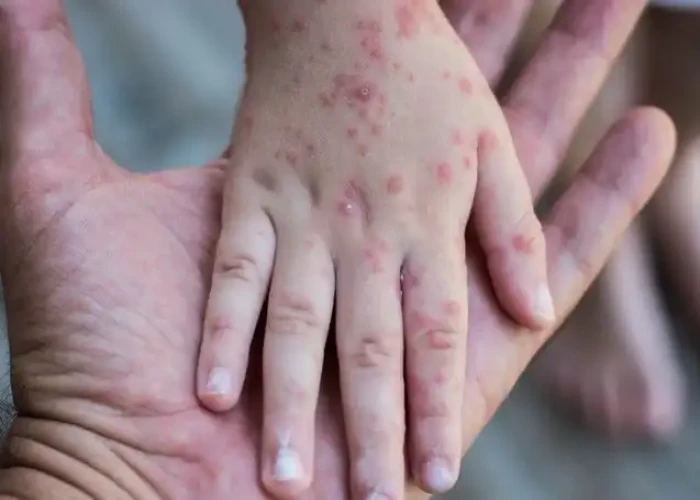
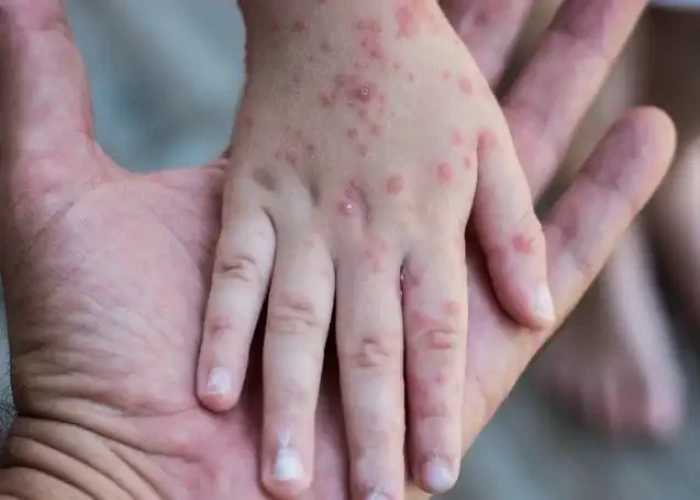
Smallpox is a highly contagious and sometimes fatal viral disease caused by the variola virus. It is characterized by fever and a distinctive rash that forms blisters filled with pus. Smallpox has been responsible for millions of deaths throughout human history, and it was one of the deadliest diseases before it was eradicated in 1980 through a global vaccination campaign.
The symptoms of smallpox typically begin with a fever, headache, and body aches. After a few days, a rash appears on the face and then spreads to the arms and legs. The rash progresses to form small, fluid-filled blisters that eventually scab over and form a crust. These scabs eventually fall off, leaving scars on the skin.
Smallpox is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with infected fluids or through the air. The virus can also survive on surfaces for long periods, making it easy to transmit in environments with poor hygiene.
The smallpox vaccine was developed in the late 18th century and became widely available in the mid-20th century. The global eradication of smallpox is considered one of the greatest achievements of modern medicine. Today, the variola virus is stored only in highly secure labs, and routine vaccination against smallpox is no longer recommended for the general public.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fever
- Headaches
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Back pain
- Nausea or vomiting
Disease Causes
Smallpox
Smallpox is caused by infection with the variola virus. The virus can be transmitted:
- Directly from person to person. Direct transmission of the virus requires fairly prolonged face-to-face contact. The virus can be transmitted through the air by droplets that escape when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks.
- Indirectly from an infected person. In rare instances, airborne virus can spread farther, possibly through the ventilation system in a building, infecting people in other rooms or on other floors.
- Via contaminated items. Smallpox can also spread through contact with contaminated clothing and bedding, although the risk of infection from these sources is less common.
- As a terrorist weapon, potentially. A deliberate release of smallpox is a remote threat. However, because any release of the virus could spread the disease quickly, government officials have taken numerous precautions to protect against this possibility, such as stockpiling smallpox vaccine.
Disease Prevents
Smallpox
In the event of an outbreak, people who had smallpox would be kept in isolation in an effort to control the spread of the virus. Anyone who had contact with someone who developed an infection would need a smallpox vaccine, which can prevent or lessen the severity of the disease if given within four days of exposure to the smallpox virus.
Two vaccines are available. One vaccine (ACAM2000) uses a live virus that's related to smallpox, and it can occasionally cause serious complications, such as infections affecting the heart or brain. That's why it's not recommended that everyone be vaccinated at this time. The potential risks of the vaccine outweigh the benefits, in the absence of an actual smallpox outbreak.
A second vaccine, a modified vaccinia Ankara vaccine (Jynneos), has been found to be safe, and it can be used in people who aren't able to take ACAM2000, who have weakened immune systems or who have skin disorders.
If you were vaccinated as a child
Immunity or partial immunity after a smallpox vaccine may last up to 10 years, and 20 years with revaccination. If an outbreak ever occurred, people who were vaccinated as children would still likely receive a new vaccination after direct exposure to someone with the virus.
Disease Treatments
No cure for smallpox exists. In the event of an infection, treatment would focus on relieving symptoms and keeping the person from becoming dehydrated. Antibiotics might be prescribed if the person also develops a bacterial infection in the lungs or on the skin.
Tecovirimat (Tpoxx), an antiviral drug, was approved for use in the U.S. in 2018. However, it wasn't tested in people who are sick with smallpox, so it's not known if it is an effective drug option. A trial tested its safety in humans and found it to be as safe as the placebo. Other antiviral drugs continue to be studied.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
In case of secondary infection, i.e. if affected by additional bacteria, the patient should be treated with amoxicillin from the first day.
1 each 3 times a day for 7 days. or 1+0+1 (750mg).
-
Flucloxacillin Sodium
Adults 1 a day at night 4 times for 7 days. Children take 1/2 teaspoon 3 times a day.
-
Paracetamol
for pain 1 or 2 spoons 3 times a day.
-
Vitamin C [Ascorbic acid]
1 pill should be sucked 2/3 times a day.
-
Vitamin B complex
Consume 1/4 teaspoon 3 times a day after meals.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Variolinum
6, 30, 200 Shakti 4 times a day.
-
Antimonium tartaricum
3, 6, 30 power.
-
Crotalus
3X, 30 strength
-
Apis mellifica
6, 30 strength
-
Belladonna
6, 30 strength
-
Arsenicum
30 strength
-
Rhus toxicodendron
6, 30 strength
Disease yoga
Smallpox and Learn More about Diseases

Low blood pressure (hypotension)

Tachycardia

Calciphylaxis

Schizoaffective disorder

Anaphylaxis
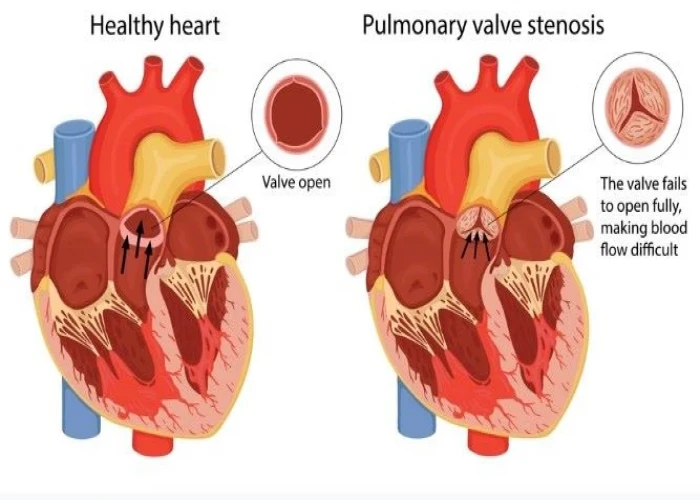
Pulmonary valve stenosis
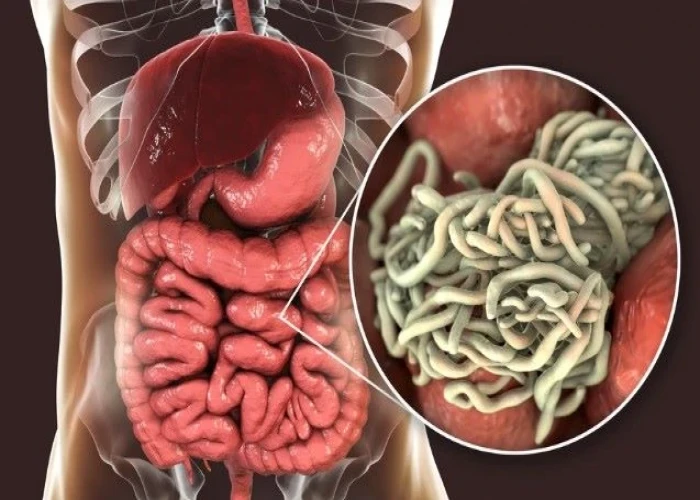
Pinworm infection

Fetal alcohol syndrome
smallpox, গুটি বসন্ত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.