 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Diarrhea

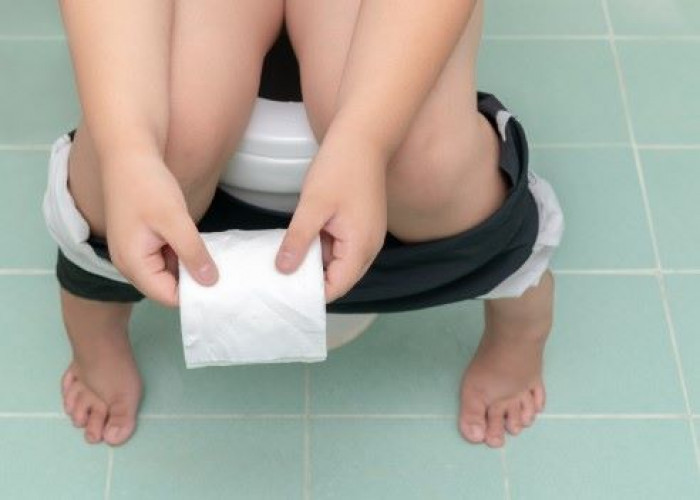
Diarrhea is a condition that involves loose or watery stools, and can occur for a variety of reasons. It is a common digestive problem that can range from a mild, short-term inconvenience to a more serious health issue.
Some common causes of diarrhea include viral or bacterial infections, food intolerances or allergies, medication side effects, and stress. In some cases, diarrhea can also be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, or celiac disease.
Symptoms of diarrhea may include frequent, loose or watery stools, abdominal cramps, nausea or vomiting, and dehydration. In severe cases, diarrhea can lead to dehydration, which can be especially dangerous for infants, young children, and older adults.
Preventing diarrhea involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly, especially before preparing or eating food. It is also important to ensure that any food you eat is prepared and cooked properly. If you have a food allergy or intolerance, avoiding the offending foods can help prevent diarrhea. Staying hydrated is also important, especially when experiencing diarrhea, as it can lead to dehydration.
Treatment of diarrhea typically involves rest, plenty of fluids, and a bland diet that is easy to digest. Over-the-counter medications such as loperamide (Imodium) can help control diarrhea by slowing down the digestive system. In cases of bacterial or parasitic infections, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed.
In conclusion, diarrhea is a common digestive problem that can occur for a variety of reasons. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding food allergens or intolerances, and staying hydrated can help prevent diarrhea. If you do experience diarrhea, rest, plenty of fluids, and a bland diet can help manage symptoms. If you experience severe or persistent diarrhea, or if you develop other symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, or blood in your stool, it is important to seek medical attention.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Abdomen pain
- Black, tarry or bloody stools
- Frequent bowel movements
- Mucus with stool
- Blood in stool
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdomen bloating
- Abdomen cramps
- Diarrhea
Disease Causes
Diarrhea
A number of diseases and conditions can cause diarrhea, including:
- Viruses. Viruses that can cause diarrhea include Norwalk virus (also known as norovirus), enteric adenoviruses, astrovirus, cytomegalovirus and viral hepatitis. Rotavirus is a common cause of acute childhood diarrhea. The virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has also been associated with gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
- Bacteria and parasites. Exposure to pathogenic bacteria, such as E. coli or parasites through contaminated food or water, leads to diarrhea. When traveling in developing countries, diarrhea caused by bacteria and parasites is often called traveler's diarrhea. Clostridioides difficile (also known as C. diff) is another type of bacterium that causes diarrhea, and it can occur after a course of antibiotics or during a hospitalization.
- Medications. Many medications, such as antibiotics, can cause diarrhea. Antibiotics alleviate infections by killing bad bacteria, but they also kill good bacteria. This disturbs the natural balance of bacteria in your intestines, leading to diarrhea or a superimposed infection such as C. diff. Other drugs that cause diarrhea are anti-cancer drugs and antacids with magnesium.
- Lactose intolerance. Lactose is a sugar found in milk and other dairy products. People who have difficulty digesting lactose have diarrhea after eating dairy products. Lactose intolerance can increase with age because levels of the enzyme that helps digest lactose drop as you get older.
- Fructose. Fructose is a sugar found naturally in fruits and honey. It's sometimes added as a sweetener to certain beverages. Fructose can lead to diarrhea in people who have trouble digesting it.
- Artificial sweeteners. Sorbitol, erythritol and mannitol — artificial sweeteners are nonabsorbable sugars found in chewing gum and other sugar-free products — can cause diarrhea in some otherwise healthy people.
- Surgery. Partial intestine or gallbladder removal surgeries can sometimes cause diarrhea.
- Other digestive disorders. Chronic diarrhea has a number of other causes, such as IBS, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, microscopic colitis and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
Disease Prevents
Diarrhea
Preventing infectious diarrhea
Wash your hands to prevent the spread of infectious diarrhea. To ensure adequate hand-washing:
- Wash frequently. Wash your hands before and after preparing food. Wash your hands after handling uncooked meat, using the toilet, changing diapers, sneezing, coughing and blowing your nose.
- Lather with soap for at least 20 seconds. After putting soap on your hands, rub your hands together for at least 20 seconds. This is about as long as it takes to sing "Happy Birthday" twice through.
- Use hand sanitizer when washing isn't possible. Use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer when you can't get to a sink. Apply the hand sanitizer as you would hand lotion, making sure to cover the fronts and backs of both hands. Use a product that contains at least 60% alcohol.
Vaccination
You can help protect your infant from rotavirus, the most common cause of viral diarrhea in children, with one of two approved vaccines. Ask your baby's doctor about having your baby vaccinated.
Preventing traveler's diarrhea
Diarrhea commonly affects people who travel to countries where there's inadequate sanitation and contaminated food. To reduce your risk:
- Watch what you eat. Eat hot, well-cooked foods. Avoid raw fruits and vegetables unless you can peel them yourself. Also avoid raw or undercooked meats and dairy foods.
- Watch what you drink. Drink bottled water, soda, beer or wine served in its original container. Avoid tap water and ice cubes. Use bottled water even for brushing your teeth. Keep your mouth closed while you shower.
- Beverages made with boiled water, such as coffee and tea, are probably safe. Remember that alcohol and caffeine can aggravate diarrhea and worsen dehydration.
- Ask your doctor about antibiotics. If you're traveling to a developing country for an extended time, ask your doctor about antibiotics before you go, especially if you have a weakened immune system.
- Check for travel warnings. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention maintains a travelers' health website where disease warnings are posted for various countries. If you're planning to travel outside of the United States, check there for warnings and tips for reducing your risk.
Disease Treatments
Most cases of acute diarrhea clear on their own within a couple of days without treatment. If you've tried lifestyle changes and home remedies for diarrhea without success, your doctor might recommend medications or other treatments.
Antibiotics or anti-parasitics
Antibiotics or anti-parasitic medications might help treat diarrhea caused by bacteria or parasites. If a virus is causing your diarrhea, antibiotics won't help.
Treatment to replace fluids
Your doctor likely will advise you to replace the fluids and salts. For most adults, that means drinking water with electrolytes, juice or broth. If drinking liquids upsets your stomach or causes vomiting, your doctor might recommend getting IV fluids.
Water is a good way to replace fluids, but it doesn't contain the salts and electrolytes — minerals such as sodium and potassium — that are essential for your body to function. You can help maintain your electrolyte levels by drinking fruit juices for potassium or eating soups for sodium. But certain fruit juices, such as apple juice, might make diarrhea worse.
For children, ask your doctor about using an oral rehydration solution, such as Pedialyte, to prevent dehydration or replace lost fluids.
Adjusting medications you're taking
If your doctor determines that an antibiotic caused your diarrhea, he or she might lower your dose or switch to another medication.
Treating underlying conditions
If your diarrhea is caused by a more serious condition, such as inflammatory bowel disease, your doctor will work to control that condition. You might be referred to a specialist, such as a gastroenterologist, who can help devise a treatment plan for you.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Metoclopramide Hydrochloride
1 injection intramuscularly every 8/12 hours or in 1 ampoule of saline.
-
Hyoscine Butylbromide
Medicines containing hyoscine-n-butylbromide for stomach pain.
1/2 pill 3 times a day.
-
Drotaverine
1/2 pill 3 times a day.
-
Cholera Saline
For dehydration.
2000/3000ml may be required at 80-100 drips per minute into the vein.
-
Metronidazole
Medicines with metronidazole if dysentery occurs later.
1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Vitamin B complex
Foods containing vitamins can be given after stomach upset subsides.
2/4 teaspoon 3 times a day after meals.
-
Oxytetracycline
Tetracycline-containing medications for diarrhea.
500 mg every 6 hours. In this case tetracycline is better than oxytetracycline.
-
Loperamide Hydrochloride
Adults: 2 capsules for the first time and 1 after each bowel movement, not more than 8 capsules in 24 hours.
-
Doxycycline Hydrochloride
3 capsules together 1 time a day from the next day to 1 2 times a day.
-
Ciprofloxacin
Medicines containing ciprofloxacin for mild, moderate and severe diarrhea.
Adults 1 pill of 500 mg in the morning and 1 pill in the evening. Boys and girls 1 pill of 250mg in the evening for 7-10 days.
-
Promethazine Theoclate
If the patient has nausea or vomiting, the drug contains promethazine thioclate.
1/2 pill 3 times a day according to age.
-
Prochlorperazine Maleate
1 pill 3 times a day.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Aconite
Mix 15/20 drops of 3X Shakti in a glass of water and take one spoon every hour.
-
Argentum sulphuricum
6, 30 strength 2/3 drop 4 times daily after meals with a little water.
-
Apis mellifica
6 Shakti Mix 3/4 drops with little water and consume 4 times a day.
-
Pulsatilla
3, 6 Shakti 3/4 drops mixed with little water, 4 times a day.
- Antimonium crudum
-
Bryonia alba
6 drops four times a day.
-
China officinalis
6 strength 2/3 drops 4 times a day with a little water.
-
Chamomilla
6 strength 2/3 drops 4 times a day with a little water.
-
Veratrum album
3 strength 3/4 drops 4/5 times a day with a little water.
-
Colchicum autumnale
30 Shakti Mix 3/4 drops of medicine with little water and use 4 times a day.
-
Arsenicum
6 Shakti Mix 2/3 drops with little water and consume 4 times a day.
-
Ipecacuanha
6 Strength 3/4 drops 4/5 times a day with a little water.
-
Podophyllum peltatum
6 Strength 2/3 drops 4 times a day with a little water.
-
Antimonium crudum
6 strength 2/3 drop medicine with little water every 2 hours.
-
Bryonia alba
6 strength 2/3 drops medicine with little water four times a day.
-
China officinalis
6 strength 2/3 drops medicine with little water four times a day.
-
Chamomilla
6 strength 2/3 drops medicine with little water four times a day.
-
Veratrum album
3 strength 3/4 drops with little water 4/5 times a day.
-
Colchicum autumnale
30 strength medicine 3/4 drops with equal amount of water 4 times a day.
-
Arsenicum
৬ শক্তি সামন্য জলের সাথে ৩/৪ ফোঁটা করে ঔষধ দিনে ৪ বার সেব্য।
-
Ipecacuanha
6 Shakti 3/4 drops with equal amount of water 4/5 times a day.
-
Podophyllum peltatum
6 Shakti 3/4 drops with equal amount of water 4 times a day.
-
Sulphur
3X strength 2 grain drops with a little water 4 times a day.
-
Nux vomica
3X Shakti 20/25 drops of medicine in one spoonful of 1 oz of water every hour.
-
Opium
6 strength with a little water 3/4 drop 4 times a day.
-
Podophyllum peltatum
30 3/4 drops medicine with little water 4 times a day.
-
Sulphur
30 strength 2/3 drops medicine three times a day with little water.
-
Alumina silicata
6 strength 2/3 drop medicine with little water every hour.
-
Plumbum metallicum
6 strength 2/3 drop medicine with little water every hour.
Disease yoga
Diarrhea and Learn More about Diseases

Esophageal spasms

Incompetent cervix
Preeclampsia

Left ventricular hypertrophy
Leukoplakia

Wrinkles

Umbilical hernia

Ear infection (middle ear)
diarrhea, উদারময়
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
