Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Baker's cyst
A Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled sac that forms behind the knee joint. It is usually caused by an underlying condition such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or a knee injury. Symptoms may include swelling, pain, and stiffness behind the knee, and the cyst may feel like a bulge or knot. Treatment may include addressing the underlying condition, using pain relief medication, and in some cases, draining the cyst or surgery. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Knee pain
- Swollen knee
- Difficulty straightening knee fully
Disease Causes
Baker's cyst
A lubricating fluid called synovial (sih-NO-vee-ul) fluid helps your leg swing smoothly and reduces friction between the moving parts of your knee.
But sometimes the knee produces too much synovial fluid, resulting in buildup of fluid in an area on the back of your knee (popliteal bursa), causing a Baker's cyst. This can happen because of:
- Inflammation of the knee joint, such as occurs with various types of arthritis
- A knee injury, such as a cartilage tear
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Sometimes a Baker's cyst will disappear on its own. However, if the cyst is large and causes pain, your doctor may recommend the following treatments:
- Medication. Your doctor may inject a corticosteroid medication, such as cortisone, into your knee to reduce inflammation. This may relieve pain, but it doesn't always prevent recurrence of the cyst.
- Fluid drainage. Your doctor may drain the fluid from the knee joint using a needle. This is called needle aspiration and is often performed under ultrasound guidance.
- Physical therapy. Icing, a compression wrap and crutches may help reduce pain and swelling. Gentle range-of-motion and strengthening exercises for the muscles around your knee also may help to reduce your symptoms and preserve knee function.
If possible, doctors treat the underlying cause of the cyst. If your doctor determines that a cartilage tear is causing the overproduction of synovial fluid, he or she may recommend surgery to remove or repair the torn cartilage.
Baker's cysts associated with osteoarthritis usually improve with treatment of the arthritis. Surgical intervention is rarely needed.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Baker's cyst and Learn More about Diseases
Type 2 diabetes in children
Myocardial ischemia

Restless legs syndrome

Chemo brain

Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)

Chiari malformation
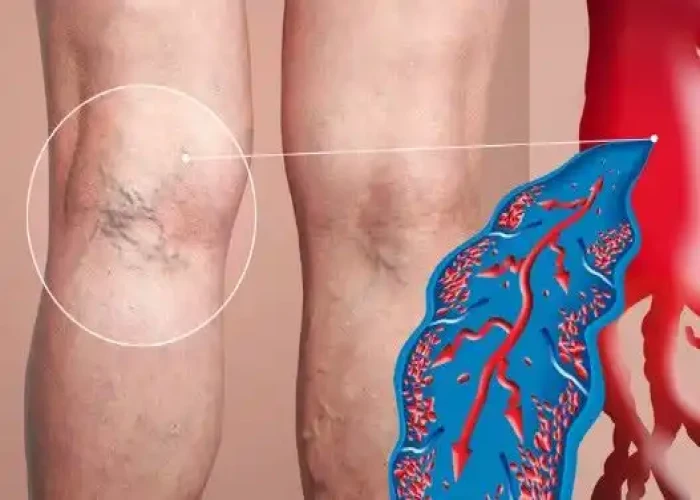
Varicose veins

Carpal tunnel syndrome
Baker's cyst, Bakers cyst treatment, Popliteal cyst, বেকারস সিস্ট
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.