Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
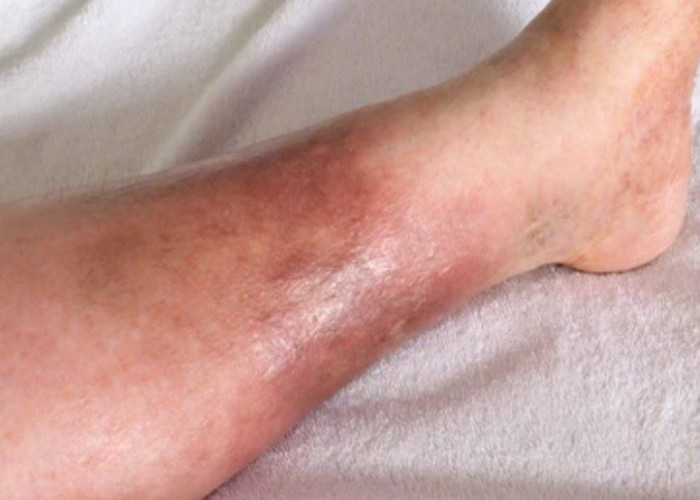
Cellulitis

Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. It is typically caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus, and may occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly affects the legs, arms, and face. Cellulitis can cause redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area, as well as fever and chills in more severe cases. Treatment for cellulitis typically involves antibiotics to eliminate the infection, as well as supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary, especially for individuals with severe symptoms or other underlying health conditions. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you may have cellulitis, as early treatment can help to prevent the spread of infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Red skin
- Swollen skin
- Fever
- Red spots in skin
- Watery blisters
- Skin dimpling
- The red area of skin that tends to expand
Disease Causes
Cellulitis
Cellulitis occurs when bacteria, most commonly streptococcus and staphylococcus, enter through a crack or break in your skin. The incidence of a more serious staphylococcus infection called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is increasing.
Although cellulitis can occur anywhere on your body, the most common location is the lower leg. Bacteria are most likely to enter disrupted areas of skin, such as where you've had recent surgery, cuts, puncture wounds, an ulcer, athlete's foot or dermatitis.
Animal bites can cause cellulitis. Bacteria can also enter through areas of dry, flaky skin or swollen skin.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Cellulitis treatment usually includes a prescription oral antibiotic. Within three days of starting an antibiotic, let your doctor know whether the infection is responding to treatment. You'll need to take the antibiotic for as long as your doctor directs, usually five to 10 days but possibly as long as 14 days.
In most cases, signs and symptoms of cellulitis disappear after a few days. You may need to be hospitalized and receive antibiotics through your veins (intravenously) if:
- Signs and symptoms don't respond to oral antibiotics
- Signs and symptoms are extensive
- You have a high fever
Usually, doctors prescribe a drug that's effective against both streptococci and staphylococci. It's important that you take the medication as directed and finish the entire course of medication, even after you feel better.
Your doctor also might recommend elevating the affected area, which may speed recovery.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Cloxacillin Sodium
Medicines containing cloxacillin for inflammation.
1 capsule every 6 hours for 5/7 days.
-
Flucloxacillin Sodium
Medicines containing cloxacillin for inflammation.
1 capsule every 6 hours for 7 days.
-
Doxycycline Hydrochloride
2 capsules the first time, 1 capsule the next day.
-
Erythromycin (Oral)
1 pill every 6 hours. 500mg in severe inflammation.
-
Ciprofloxacin
1 each 2 times a day for 10 days.
-
Vitamin B complex
1 in the morning after breakfast and 1 in the evening after dinner.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Cellulitis and Learn More about Diseases
Hemangioma

Bronchiolitis

Priapism
Heart palpitations

Gonorrhea

Croup
Diphtheria

Porphyria
Cellulitis, Cellulitis treatment, Orbital cellulitis, সেলুলাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.