 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Bronchitis
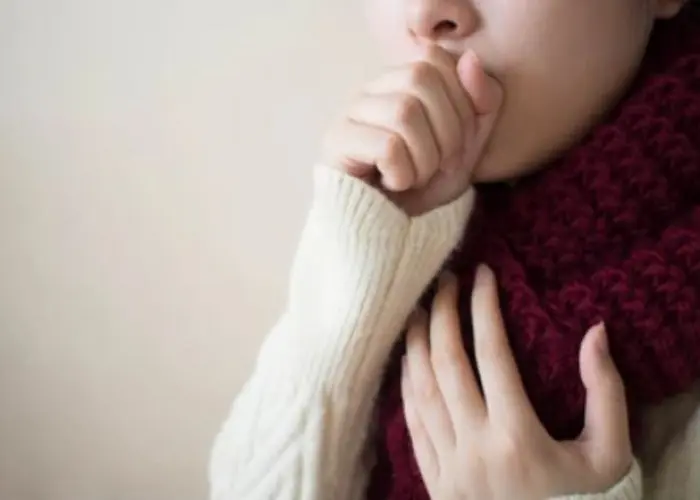

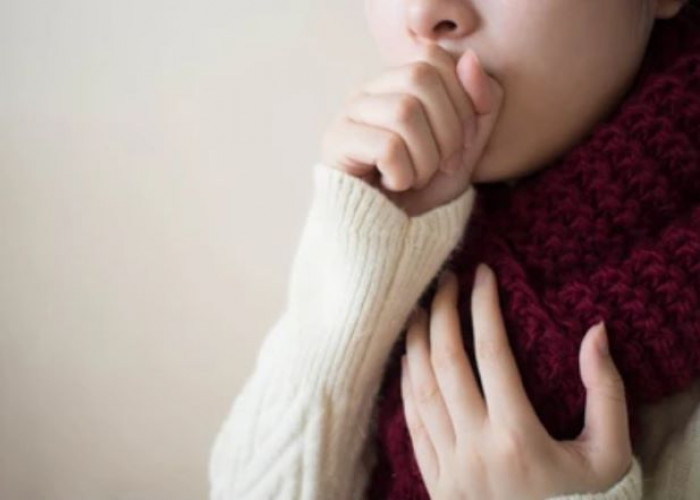
Bronchitis is a condition where the bronchial tubes, which carry air to the lungs, become inflamed. It can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection, as well as exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke or air pollution. Symptoms may include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Treatment options may include rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to manage symptoms, as well as antibiotics or other medications prescribed by a healthcare provider if the cause is bacterial. It is important to quit smoking and avoid exposure to irritants to prevent future episodes of bronchitis.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Cough
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Fever and chills
- Chest pain
- Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color — rarely, it may be streaked with blood
- At those times, may have an acute infection on top of chronic bronchitis.
- Chest pain when breathing
- Bronchitis
Disease Causes
Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by viruses, typically the same viruses that cause colds and flu (influenza). Antibiotics don't kill viruses, so this type of medication isn't useful in most cases of bronchitis.
The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is cigarette smoking. Air pollution and dust or toxic gases in the environment or workplace also can contribute to the condition.
Disease Prevents
Bronchitis
To reduce your risk of bronchitis, follow these tips:
- Avoid cigarette smoke. Cigarette smoke increases your risk of chronic bronchitis.
- Get vaccinated. Many cases of acute bronchitis result from influenza, a virus. Getting a yearly flu vaccine can help protect you from getting the flu. You may also want to consider vaccination that protects against some types of pneumonia.
- Wash your hands. To reduce your risk of catching a viral infection, wash your hands frequently and get in the habit of using alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
- Wear a surgical mask. If you have COPD, you might consider wearing a face mask at work if you're exposed to dust or fumes, and when you're going to be among crowds, such as while traveling.
Disease Treatments
Most cases of acute bronchitis get better without treatment, usually within a couple of weeks.
Medications
Because most cases of bronchitis are caused by viral infections, antibiotics aren't effective. However, if your doctor suspects that you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe an antibiotic.
In some circumstances, your doctor may recommend other medications, including:
- Cough medicine. If your cough keeps you from sleeping, you might try cough suppressants at bedtime.
- Other medications. If you have allergies, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), your doctor may recommend an inhaler and other medications to reduce inflammation and open narrowed passages in your lungs.
Therapies
If you have chronic bronchitis, you may benefit from pulmonary rehabilitation — a breathing exercise program in which a respiratory therapist teaches you how to breathe more easily and increase your ability to exercise.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
1 every 8 hours for 7-10 days.
-
Doxycycline Hydrochloride
Medicines containing doxycycline can be given for pneumonia.
1 in the morning and 1 in the evening for 10 days in severe infections.
-
Cephalexin
Medicines containing cephalexin can also be given in acute bronchitis.
Usually 250mg 1+1+1. 1+1+1 of 500mg in severe condition for 7-10 days. Boys and girls 1/2 adult size.
Syrup: 1/2 teaspoon after 6 hours.
-
Cephradine
Medicines containing cephalosporins can also be used in acute bronchitis.
250mg 1+1+1 or 500mg 1+1+1.
Drops: 1ml 4 times a day at night.
-
Ciprofloxacin
Medicines containing ciprofloxacin are used to treat acute bronchitis.
1+0+1 (10-14 days)
-
Pefloxacin Mesylate Dihydrate
Medicines containing Pefloxacin are used to treat acute bronchitis.
1+0+1 (10-14 days)
-
Ofloxacin (Oral & Injection)
Medicines containing Ofloxacin are used to treat acute bronchitis.
1 pill in the morning, 1 pill in the evening, if necessary increase the dosage to 400 mg 2 times a day.
-
Azithromycin Dihydrate
Medicines containing azithromycin are used to treat acute bronchitis.
1 pill or 1 spoon daily for 5 days.
-
Cefuroxime Axetil
Medications containing securitoxime are used to treat acute bronchitis.
The usual dose is 250mg 2 times a day. However, in case of bronchitis, the dosage should be doubled. Boys and girls over 6 years 125mg 2 times a day.
-
Sparfloxacin
2 pills on the first day. 1 pill daily from next day 8/10 days.
-
Roxithromycin
Medicines containing roxithromycin can be given for acute bronchitis.
150mg/300mg 1 pill daily for 10 days.
-
Paracetamol
Medicines containing paracetamol for chest, headache or fever.
1 pill 3 times a day. Stop the medicine when the pain subsides or the fever drops below 100 degrees.
-
Nimesulide
Medicines containing nimesulide for chest or back pain.
Adults 1 to 2 times a day.
-
Nimesulide
Medicines containing salbutamol in case of chest tightness or shortness of breath.
1/2, 1, 2 spoons 3 times a day.
-
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
For colds (if you have a runny or runny nose) medicine containing chlorpheniramine maleate.
1 pill or 1/2, 1, 2 spoons 3 times a day.
-
Pheniramine Maleate
1 pill 3 times a day. Or 1 pill of 75mg at night.
-
Promethazine Hydrochloride
1/2, 1 spoon 3 times a day.
-
Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride
1+0+0.
-
Vitamin B complex
Vitamin B-complex medicines for weakness.
1 capsule 2 times a day. Or 1/2 teaspoon of liquid 3 times a day after meals.
-
Ferrous Sulfate
Blood thinners can be given if the patient is healthy.
This medicine is taken 2 spoons a day after meals.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Bronchitis and Learn More about Diseases

Spina bifida

Prescription drug abuse

Vulvar cancer

Menopause
Amnesia

Thoracic outlet syndrome
Proctitis
Atrial fibrillation
Bronchitis, Acute bronchitis, Chronic bronchitis, Bronchitis treatment, ব্রঙ্কাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
