Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
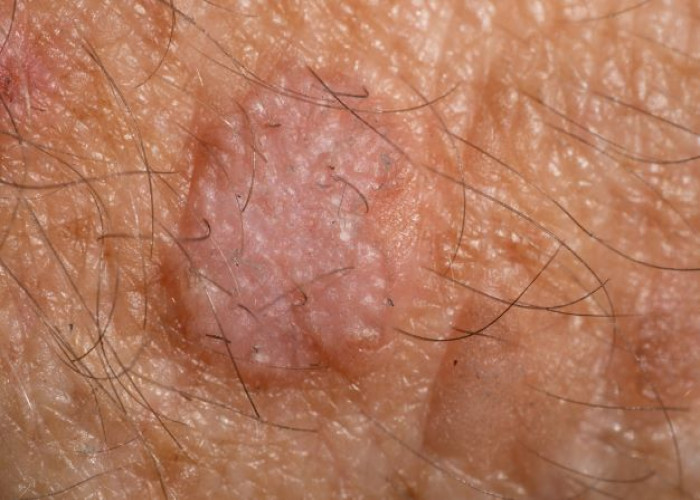
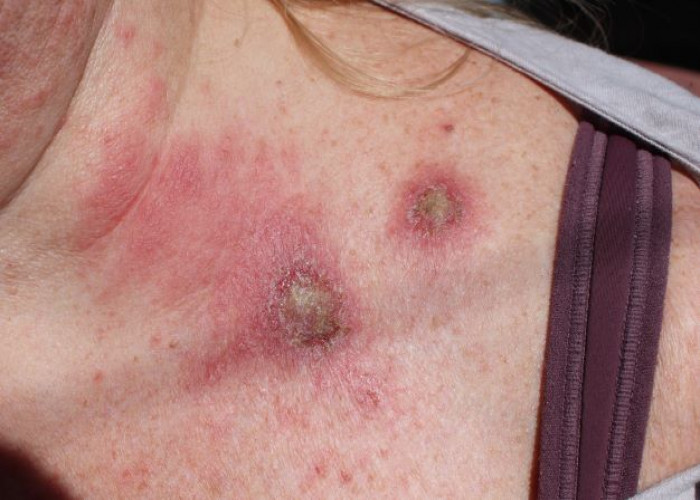
Actinic keratosis

Actinic keratosis (AK) is a precancerous skin condition characterized by scaly or crusty patches on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, scalp, arms, and hands. It is caused by cumulative damage from exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds.
AKs are usually not painful, but they can be unsightly and increase the risk of developing skin cancer. They may feel rough or scaly to the touch, and they may be pink, red, or flesh-colored.
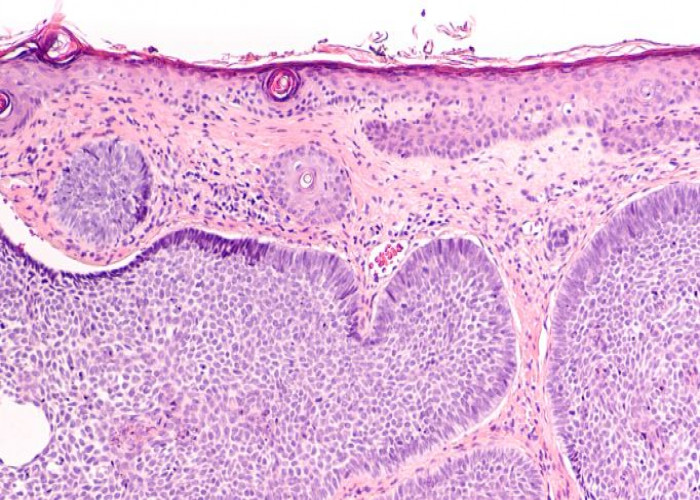
Diagnosis of AK is typically made through a physical examination by a dermatologist, who may also perform a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment for AK may include topical creams or gels, cryotherapy (freezing the lesion), or in some cases, surgical removal. In addition to treatment, it is important to protect your skin from further damage by limiting exposure to UV light and wearing protective clothing and sunblock when spending time outdoors.
If you have a lesion that you suspect may be an AK, it is important to see a dermatologist for a proper evaluation and treatment. Early treatment can help prevent the progression of AK to skin cancer, and it can also help improve the appearance of the affected skin.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Dry, rough skin in the areas with bumps
- Rough, dry or scaly patch of skin, usually less than 1 inch in diameter
- Skin bumps
- Red skin
- Itching
- Skin pain or burning sensation
- Skin darkening in areas exposed to the sun and in scars
Disease Causes
Actinic keratosis
An actinic keratosis is caused by frequent or intense exposure to UV rays from the sun or tanning beds.
Risk factors
Anyone can develop actinic keratoses. But you're at increased risk if you:
- Have red or blond hair and blue or light-colored eyes
- Have a history of a lot of sun exposure or sunburn
- Tend to freckle or burn when exposed to sunlight
- Are older than 40
- Live in a sunny place
- Work outdoors
- Have a weakened immune system
Disease Prevents
Actinic keratosis
Sun safety is necessary to help prevent development and recurrence of actinic keratosis patches and spots.
Take these steps to protect your skin from the sun:
- Limit your time in the sun. Especially avoid time in the sun between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. And avoid staying in the sun so long that you get a sunburn or a suntan.
- Use sunscreen. Before spending time outdoors, even on cloud days, apply a broad-spectrum water-resistant sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30, as the American Academy of Dermatology recommends.
- Use sunscreen on all exposed skin, and use lip balm with sunscreen on your lips. Apply sunscreen at least 15 minutes before going outside and reapply it every two hours — or more often if you're swimming or perspiring.
- Sunscreen is not recommended for babies under 6 months. Rather, keep them out of the sun if possible, or protect them with shade, hats, and clothing that covers the arms and legs.
- Cover up. For extra protection from the sun, wear tightly woven clothing that covers your arms and legs. Also wear a broad-brimmed hat, which provides more protection than does a baseball cap or golf visor.
- Avoid tanning beds. The UV exposure from a tanning bed can cause just as much skin damage as a tan acquired from the sun.
- Check your skin regularly and report changes to your doctor. Examine your skin regularly, looking for the development of new skin growths or changes in existing moles, freckles, bumps and birthmarks. With the help of mirrors, check your face, neck, ears and scalp. Examine the tops and undersides of your arms and hands.
Disease Treatments
An actinic keratosis sometimes disappears on its own but might return after more sun exposure. It's hard to tell which actinic keratoses will develop into skin cancer, so they're usually removed as a precaution.
Medications
If you have several actinic keratoses, your doctor might prescribe a medicated cream or gel to remove them, such as fluorouracil (Carac, Fluoroplex, others), imiquimod (Aldara, Zyclara), ingenol mebutate or diclofenac (Solaraze). These products might cause redness, scaling or a burning sensation for a few weeks.
Surgical and other procedures
Many methods are used to remove actinic keratosis, including:
- Freezing (cryotherapy). Actinic keratoses can be removed by freezing them with liquid nitrogen. Your doctor applies the substance to the affected skin, which causes blistering or peeling. As your skin heals, the damaged cells slough off, allowing new skin to appear. Cryotherapy is the most common treatment. It takes only a few minutes and can be done in your doctor's office. Side effects may include blisters, scarring, changes to skin texture, infection and changes in skin color of the affected area.
- Scraping (curettage). In this procedure, your doctor uses a device called a curet to scrape off damaged cells. Scraping may be followed by electrosurgery, in which the doctor uses a pencil-shaped instrument to cut and destroy the affected tissue with an electric current. This procedure requires local anesthesia. Side effects may include infection, scarring and changes in skin color of the affected area.
- Laser therapy. This technique is increasingly used to treat actinic keratosis. Your doctor uses an ablative laser device to destroy the patch, allowing new skin to appear. Side effects may include scarring and discoloration of the affected skin.
- Photodynamic therapy. Your doctor might apply a light-sensitive chemical solution to the affected skin and then expose it to a special light that will destroy the actinic keratosis. Side effects may include redness, swelling and a burning sensation during therapy.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Actinic keratosis and Learn More about Diseases

Mitral valve disease
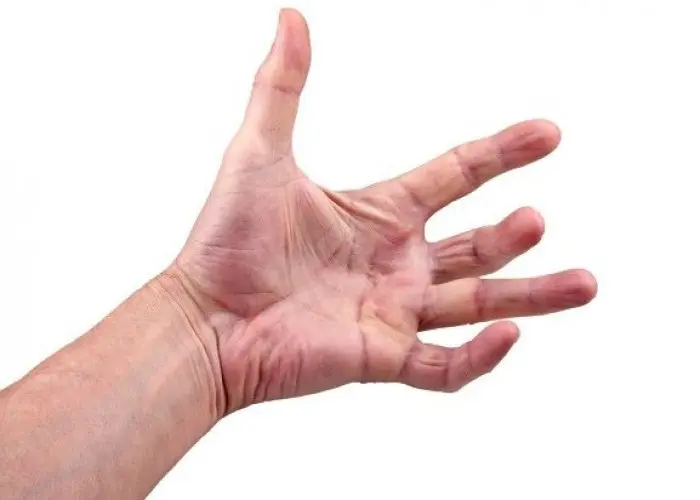
Dupuytren's contracture
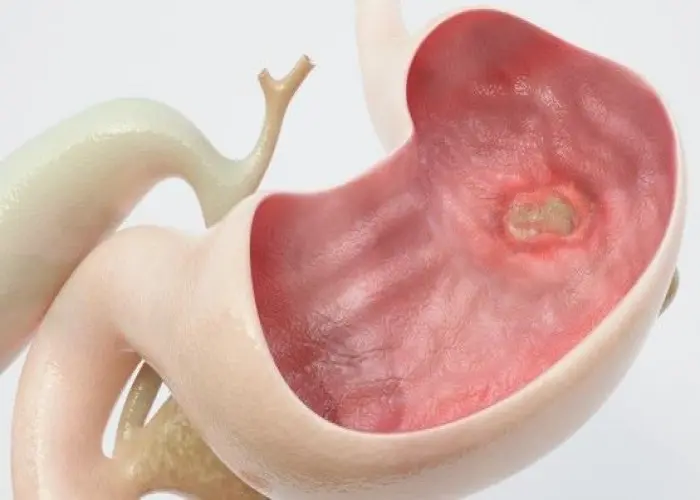
Gastric Ulcer
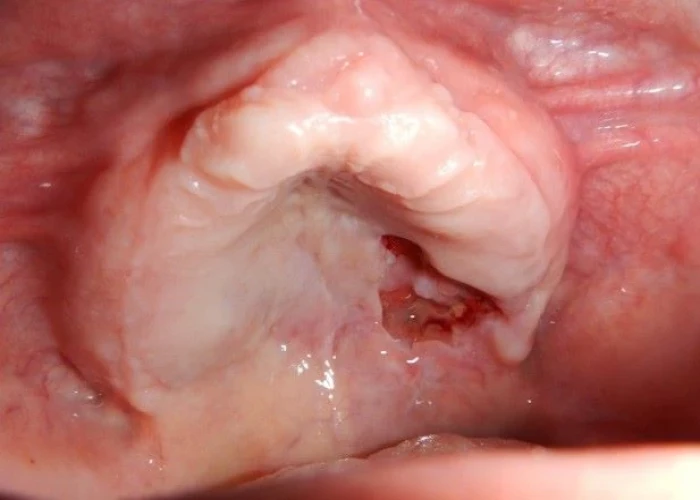
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma

Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)

Nasopharyngeal carcinoma

Corns and calluses
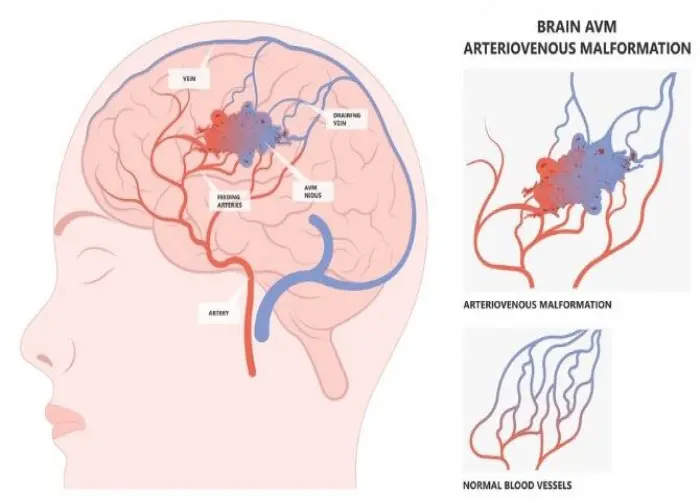
Intracranial venous malformations
Keratosis, Actinic keratosis treatment, Solar keratosis, অ্যাক্টিনিক কেরাটোসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.