Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
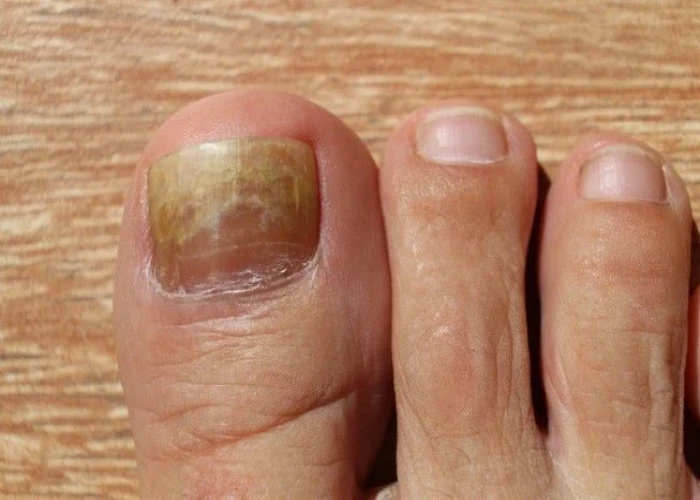
Nail fungus

Nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection that affects the nails of the fingers and toes. It is caused by various types of fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds.
Nail fungus is more common in toenails than fingernails and can occur due to a number of factors, such as warm and moist environments, walking barefoot in public areas, wearing tight-fitting shoes, and having a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of nail fungus may include thickening and discoloration of the nail, a foul odor, nail separation from the nail bed, and distorted or brittle nails. The infection can also cause pain and discomfort, especially when the nail becomes thickened and presses against the inside of shoes.
Treatment options for nail fungus include topical and oral antifungal medications, as well as surgical removal of the nail in severe cases. Topical treatments may include medicated nail polish or creams that are applied directly to the nail. Oral antifungal medications may be prescribed for more severe cases, and may be taken for several weeks or months.
Prevention of nail fungus includes keeping the feet clean and dry, wearing shoes that allow for proper ventilation, and avoiding walking barefoot in public areas such as gyms, showers, and swimming pools. Regularly trimming nails and avoiding sharing nail clippers or other personal grooming tools can also help prevent the spread of nail fungus.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Nails thick and hard
- Brittle nails
- Whitish to yellow-brown discoloration
- A dark color, caused by debris building up under your nail
- Have an exaggerated sense of self-importance
- Nail fungus
Disease Causes
Nail fungus
Fungal nail infections are caused by various fungal organisms (fungi). The most common cause is a type of fungus called dermatophyte. Yeast and molds also can cause nail infections.
Fungal nail infection can develop in people at any age, but it's more common in older adults. As the nail ages, it can become brittle and dry. The resulting cracks in the nails allow fungi to enter. Other factors — such as reduced blood circulation to the feet and a weakened immune system — also may play a role.
Toenail fungal infection can start from athlete's foot (foot fungus), and it can spread from one nail to another. But it is uncommon to get an infection from someone else.
Disease Prevents
Nail fungus
The following habits can help prevent nail fungus or reinfections and athlete's foot, which can lead to nail fungus:
- Wash your hands and feet regularly. Wash your hands after touching an infected nail. Moisturize your nails after washing.
- Trim nails straight across, smooth the edges with a file and file down thickened areas. Disinfect your nail clippers after each use.
- Wear sweat-absorbing socks or change your socks throughout the day.
- Choose shoes made of materials that breathe.
- Discard old shoes or treat them with disinfectants or antifungal powders.
- Wear footwear in pool areas and locker rooms.
- Choose a nail salon that uses sterilized manicure tools for each customer.
- Give up nail polish and artificial nails.
Disease Treatments
Fungal nail infections can be difficult to treat. Talk with your doctor if self-care strategies and over-the-counter (nonprescription) products haven't helped. Treatment depends on the severity of your condition and the type of fungus causing it. It can take months to see results. And even if your nail condition improves, repeat infections are common.
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe antifungal drugs that you take orally or apply to the nail. In some situations, it helps to combine oral and topical antifungal therapies.
- Oral antifungal drugs. These drugs are often the first choice because they clear the infection more quickly than do topical drugs. Options include terbinafine (Lamisil) and itraconazole (Sporanox). These drugs help a new nail grow free of infection, slowly replacing the infected part.
- You typically take this type of drug for six to 12 weeks. But you won't see the end result of treatment until the nail grows back completely. It may take four months or longer to eliminate an infection. Treatment success rates with these drugs appear to be lower in adults over age 65.
- Oral antifungal drugs may cause side effects ranging from skin rash to liver damage. You may need occasional blood tests to check on how you're doing with these types of drugs. Doctors may not recommend them for people with liver disease or congestive heart failure or those taking certain medications.
- Medicated nail polish. Your doctor may prescribe an antifungal nail polish called ciclopirox (Penlac). You paint it on your infected nails and surrounding skin once a day. After seven days, you wipe the piled-on layers clean with alcohol and begin fresh applications. You may need to use this type of nail polish daily for almost a year.
- Medicated nail cream. Your doctor may prescribe an antifungal cream, which you rub into your infected nails after soaking. These creams may work better if you first thin the nails. This helps the medication get through the hard nail surface to the underlying fungus.
- To thin nails, you apply a nonprescription lotion containing urea. Or your doctor may thin the surface of the nail (debride) with a file or other tool.
Surgery
Your doctor might suggest temporary removal of the nail so that he or she can apply the antifungal drug directly to the infection under the nail.
Some fungal nail infections don't respond to medicines. Your doctor might suggest permanent nail removal if the infection is severe or extremely painful.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Nail fungus and Learn More about Diseases
C. difficile infection

Ebola virus and Marburg virus
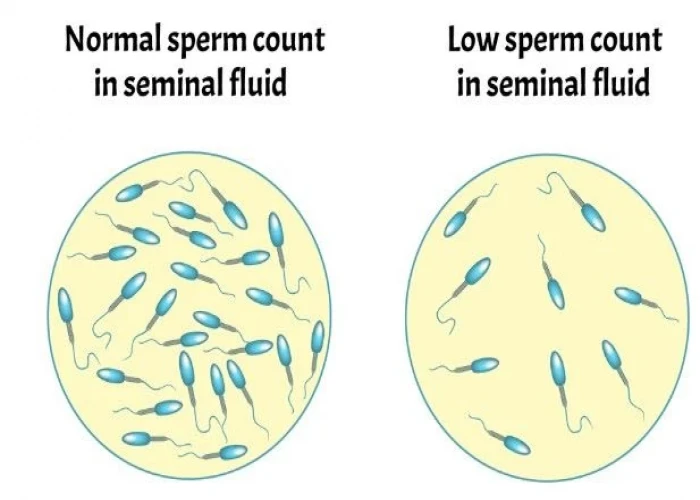
Low sperm count

Type 1 diabetes in children

Mittelschmerz

Glioma

Broken ribs

Sunburn
nail fungus, নখের ছত্রাক
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.