Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
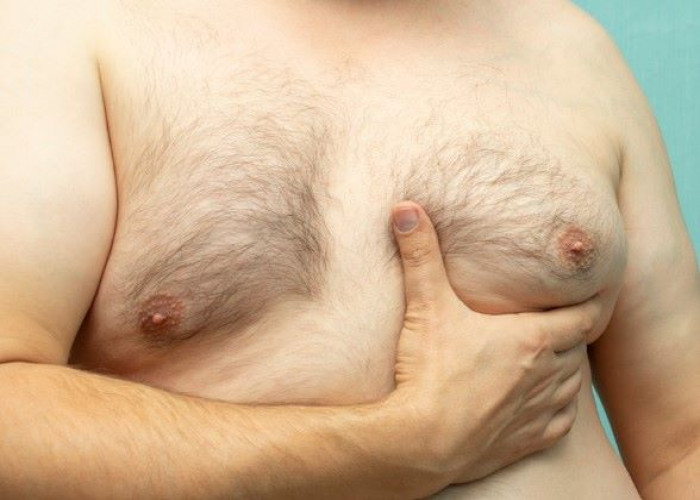
Enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia)
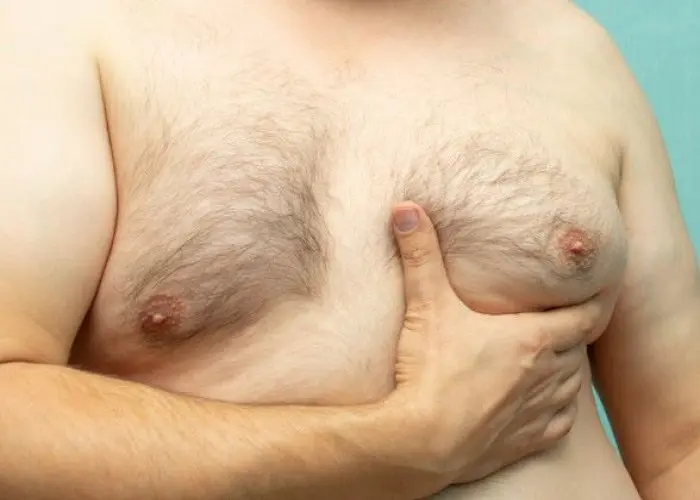
Enlarged breasts in men, also known as gynecomastia, is a condition in which the breast tissue in males swells and becomes enlarged. It is a common condition that affects up to 60% of males at some point in their lives, often during puberty or in later life.
Gynecomastia can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, medications, drug and alcohol use, obesity, and certain medical conditions. Hormonal imbalances, in particular, are a common cause, as they can disrupt the balance between estrogen and testosterone, leading to an increase in breast tissue.
The symptoms of gynecomastia can include breast enlargement, tenderness or sensitivity, and discharge from the nipples. It can also be associated with psychological distress, as it can cause embarrassment, self-consciousness, and anxiety.
Treatment for gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, the condition may resolve on its own, particularly if it is related to puberty or weight gain. In other cases, medications may be prescribed to correct hormonal imbalances or reduce breast tissue. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove excess breast tissue.
Gynecomastia is typically not a serious condition, and it does not increase the risk of breast cancer. However, it can be a source of physical and psychological discomfort, and it is important for men who experience breast enlargement to seek medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Breast pain
- Swollen breast
- Breast tenderness
- Nipple discharge
Disease Causes
Enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia)
Gynecomastia is triggered by a decrease in the amount of the hormone testosterone compared with estrogen. The decrease can be caused by conditions that block the effects of testosterone, reduce testosterone or increase your estrogen level.
Several things can upset the hormone balance, including the following.
Natural hormone changes
The hormones testosterone and estrogen control sex characteristics in both men and women. Testosterone controls male traits, such as muscle mass and body hair. Estrogen controls female traits, including the growth of breasts.
Most people think of estrogen as an exclusively female hormone, but men also produce it — though usually in small quantities. Male estrogen levels that are too high or are out of balance with testosterone levels can cause gynecomastia.
- Gynecomastia in infants. More than half of male infants are born with enlarged breasts due to the effects of their mother's estrogen. Generally, the swollen breast tissue goes away within two to three weeks after birth.
- Gynecomastia during puberty. Gynecomastia caused by hormone changes during puberty is relatively common. In most cases, the swollen breast tissue will go away without treatment within six months to two years.
- Gynecomastia in adults. Researchers have estimated that the prevalence among men ages 50 to 80 is between 24% and 65%. However, most men with the condition experience no symptoms.
Medications
A number of medications can cause gynecomastia. These include:
- Anti-androgens used to treat an enlarged prostate, prostate cancer and other conditions. Examples include flutamide, finasteride (Proscar, Propecia) and spironolactone (Aldactone, Carospir).
- Anabolic steroids and androgens to treat hormone deficiencies, delayed puberty, or muscle loss from another disease.
- AIDS medications. The estrogen-like properties of some HIV medications can cause gynecomastia, especially Efavirenz (Sustiva).
- ADHD medications that contain amphetamines, such as Adderall.
- Anti-anxiety medications, such as diazepam (Valium).
- Tricyclic antidepressants.
- Antibiotics.
- Ulcer medications, such as the over-the-counter drug cimetidine (Tagamet HB).
- Chemotherapy to treat cancer.
- Heart medications, such as digoxin (Lanoxin) and calcium channel blockers.
- Stomach-emptying medications, such as metoclopramide (Reglan).
Recreational drugs, illicit drugs and alcohol
Substances that can cause gynecomastia include:
- Alcohol
- Anabolic steroids used to build muscle and enhance athletic performance
- Amphetamines
- Marijuana
- Heroin
- Methadone (Methadose)
Health conditions
Several health conditions can cause gynecomastia by affecting the balance of hormones. These include:
- Hypogonadism. Conditions that lower testosterone production, such as Klinefelter syndrome or pituitary insufficiency, can be associated with gynecomastia.
- Aging. Hormone changes that occur with aging can cause gynecomastia, especially in men who are overweight.
- Tumors. Some tumors, such as those involving the testes, adrenal glands or pituitary gland, can produce hormones that alter the male-female hormone balance.
- Hyperthyroidism. In this condition, the thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone thyroxine.
- Kidney failure. About half the people being treated with dialysis experience gynecomastia due to hormonal changes.
- Liver failure and cirrhosis. Changes in hormone levels related to liver problems and cirrhosis medications are associated with gynecomastia.
- Malnutrition and starvation. When your body is deprived of adequate nutrition, testosterone levels drop while estrogen levels remain the same, causing a hormonal imbalance. Gynecomastia can also happen when normal nutrition resumes.
Herbal products
Plant oils, such as tea tree or lavender, used in shampoos, soaps or lotions have been associated with gynecomastia. This is probably due to their weak estrogenic activity.
Disease Prevents
Enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia)
There are a few factors you can control that may reduce the risk of gynecomastia:
- Don't use drugs. Examples include anabolic steroids, amphetamines, heroin and marijuana.
- Avoid alcohol. Don't drink alcohol. If you do drink, do so in moderation.
Disease Treatments
Most cases of gynecomastia resolve over time without treatment. However, if gynecomastia is caused by an underlying condition — such as hypogonadism, malnutrition or cirrhosis — that underlying condition may need treatment.
If you're taking medications that may be the cause of gynecomastia, your doctor may recommend stopping them or substituting another medication.
In adolescents with no apparent cause of gynecomastia other than normal hormone changes during puberty, the doctor may recommend periodic reevaluations every three to six months to see if the condition improves on its own. Gynecomastia in adolescents often goes away without treatment in less than two years.
Treatment may be necessary if gynecomastia doesn't improve on its own or if it causes significant pain, tenderness or embarrassment.
Medications
Medications used to treat breast cancer and other conditions may be helpful for some men with gynecomastia. They include:
- Tamoxifen (Soltamox)
- Aromatase inhibitors, such as anastrozole (Arimidex)
Although these medications are approved by the Food and Drug Administration, they have not been approved specifically for use in people with gynecomastia.
Surgery to remove excess breast tissue
If enlarged breasts are significant and bothersome even after initial treatment or observation, your doctor may advise surgery.
Two gynecomastia surgery options are:
- Liposuction. This surgery removes breast fat but not the breast gland tissue itself.
- Mastectomy. This type of surgery removes the breast gland tissue. The surgery is often done using only small incisions. This less invasive type of surgery involves less recovery time.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia) and Learn More about Diseases

Cavernous malformations
Baker's cyst

Bradycardia

Toxic shock syndrome
ACL injury

Parkinson's disease

DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome)
Jaundice
enlarged breasts in men, gynecomastia, পুরুষদের বর্ধিত স্তন, গাইনোকোমাস্টিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.