 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Profuse sweating - Homeopathic remedies
Profuse sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis, is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating beyond what is necessary to regulate body temperature. It can affect various parts of the body, such as the palms, feet, underarms, face, and groin.
Hyperhidrosis can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, certain medications, hormonal changes, and medical conditions such as diabetes, thyroid problems, and anxiety disorders. It can also be a side effect of certain medical treatments such as chemotherapy.
The symptoms of hyperhidrosis can be disruptive and embarrassing, leading to anxiety and social isolation. People with this condition may experience sweating even in cool environments, have difficulty gripping objects, and develop skin infections and rashes.
Treatment options for hyperhidrosis include antiperspirants, medications, iontophoresis, botox injections, and surgery. Antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can be applied to the affected area to reduce sweating. Medications such as anticholinergics and beta-blockers can also be used to reduce sweating, but they can have side effects such as dry mouth, constipation, and dizziness.
Iontophoresis involves the use of a device that delivers a low-level electrical current to the affected area to temporarily stop sweating. Botox injections can also be used to block the chemical signals that trigger sweating. Surgery is usually considered as a last resort and involves removing sweat glands or cutting nerves that trigger sweating.
If you are experiencing profuse sweating, it is important to talk to your doctor to determine the underlying cause and discuss treatment options that may be right for you.
Swollen tongue
Goitre
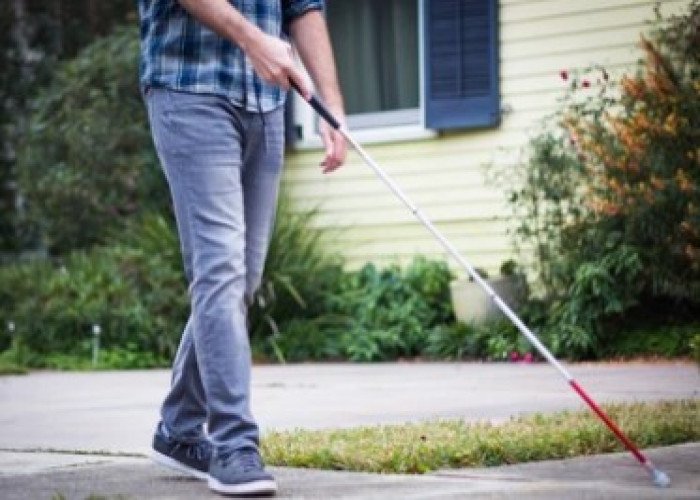

Blindness

Dream of a dead person
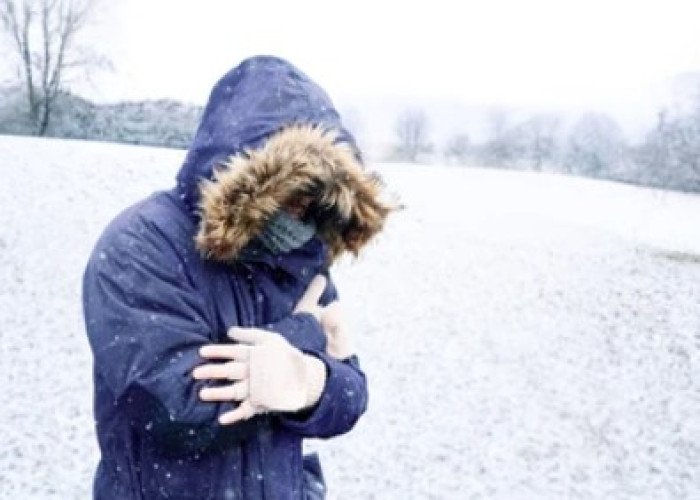

Cold sensitive

Profuse sweating

Burned by fire
Headache
Profuse sweating, প্রচুর ঘাম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.



