Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Tumor - Homeopathic remedies
A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells in the body. Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can occur in any part of the body. The cause of most tumors is not known, but factors that can contribute to their development include genetics, exposure to certain chemicals and radiation, and lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity.
Symptoms of a tumor can vary depending on its location and type, but common symptoms can include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Persistent cough or hoarseness
- Changes in the appearance of the skin or moles
Diagnosis of a tumor typically involves imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, as well as biopsies to examine a tissue sample under a microscope. Treatment for a tumor depends on its type and location, as well as the patient's overall health and other factors. Treatment options can include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these.
Early detection and treatment of tumors can improve the chances of a successful outcome. Regular screenings and self-examinations can help detect tumors early, and lifestyle factors such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding exposure to harmful substances can help reduce the risk of developing tumors.
Tuberculosis
Tumor

Typhoid fever
Lot of urine
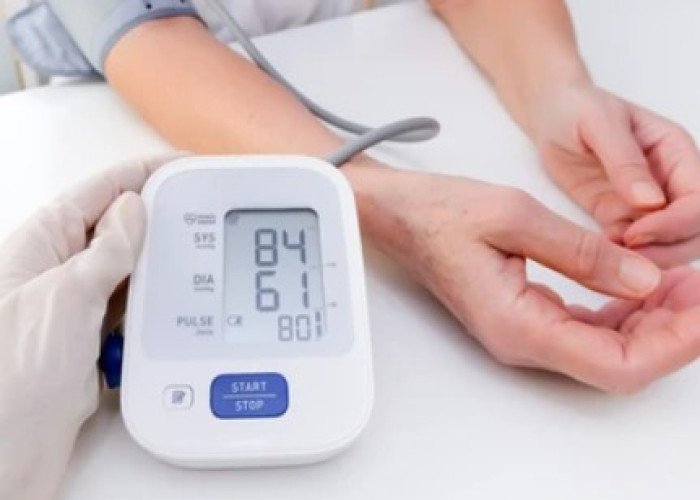
Hypotension

Unconsciousness
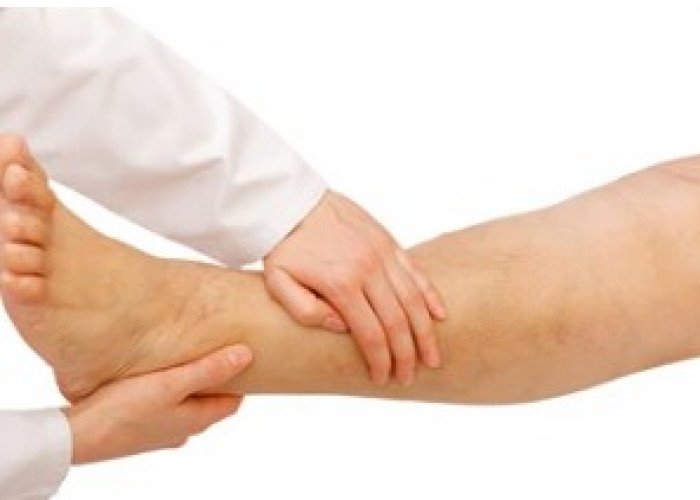
General edema
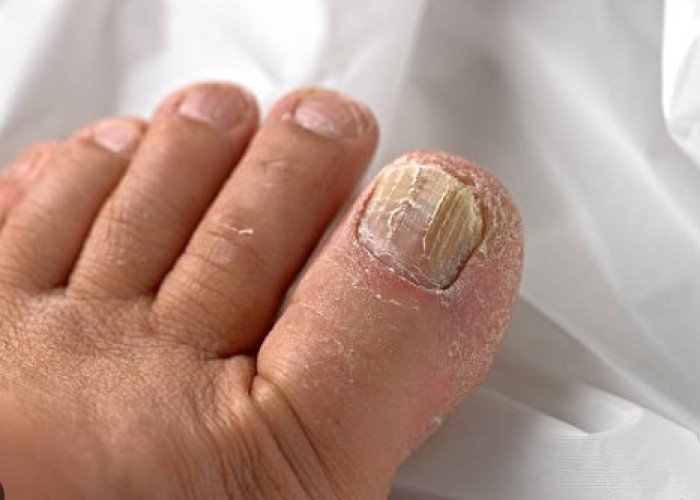
Spoiled nails
Tumor, টিউমার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.