 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
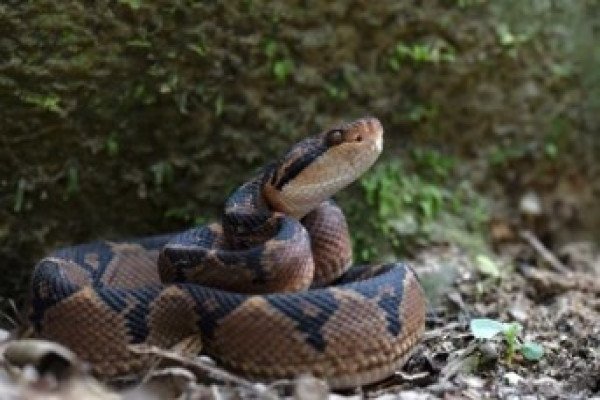
Erysipelas - Homeopathic remedies
Erysipelas is a type of bacterial skin infection that affects the top layer of the skin and the underlying connective tissue. It is usually caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pyogenes, which can enter the skin through a break, cut, or scratch.
Symptoms of erysipelas include redness, warmth, and swelling of the skin, typically on the face, arms, or legs. The affected area may also be painful and may develop blisters or a rash. In severe cases, the infection can spread to the lymph nodes and cause fever and chills.
Erysipelas is typically treated with antibiotics, such as penicillin or erythromycin. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary, especially if the infection is severe or if the person has other medical conditions that put them at risk for complications.
Preventive measures for erysipelas include good hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and treating any cuts or wounds promptly. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have erysipelas or if you have any signs of infection, as prompt treatment can help prevent complications.

Insomnia

Deafness
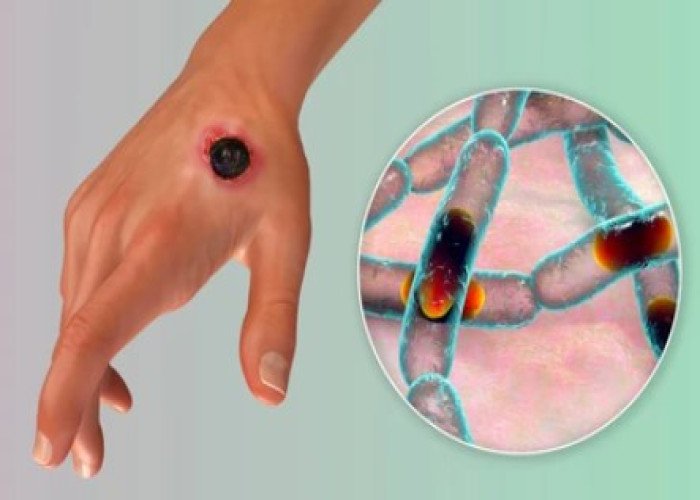
Anthrax
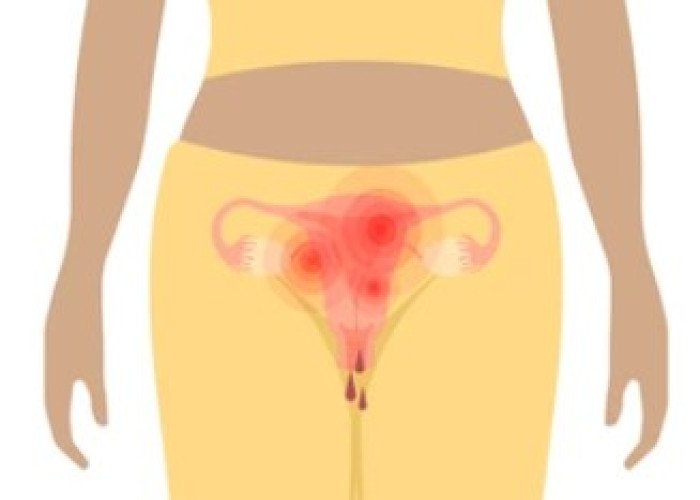
Bleeding from uterus
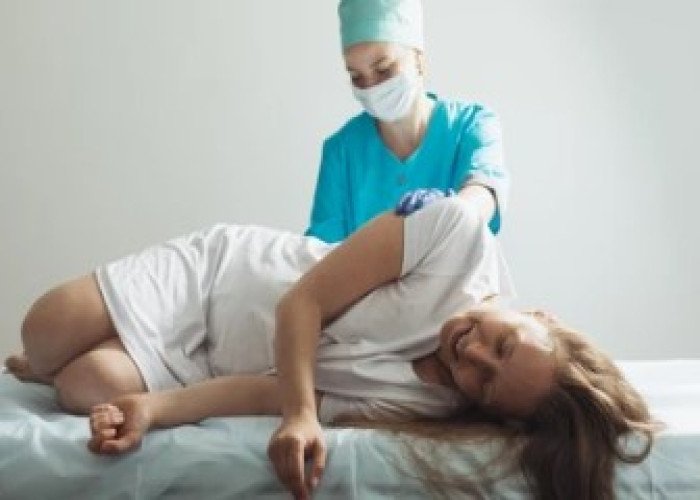

Artificial delivery pain
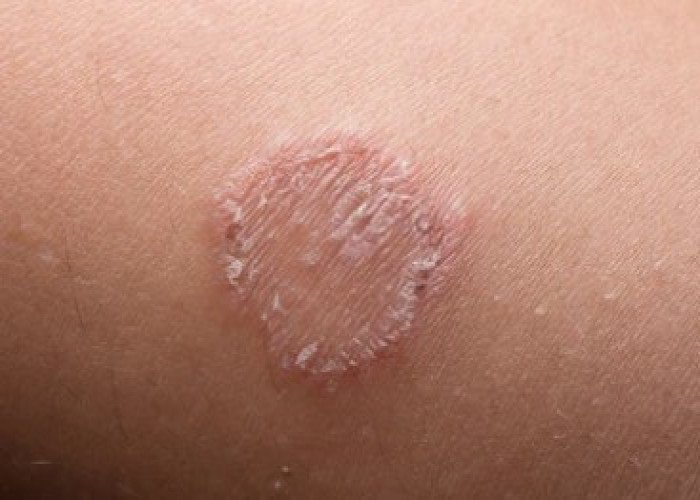
Ringworm

Weakness of metal
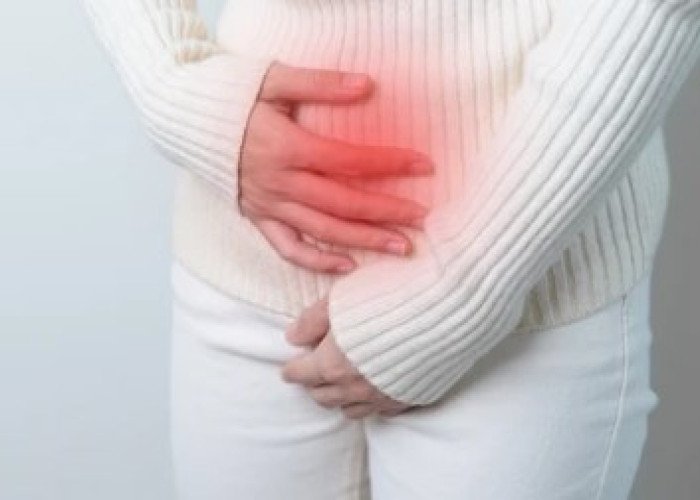

Uterine inflammation
Erysipelas, ইরিসিপেলাস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.






