 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Bleeding - Homeopathic remedies
Bleeding refers to the loss of blood from the body, which can occur internally or externally. Bleeding can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, trauma, medical conditions, and medications.
External bleeding occurs when blood exits the body through a wound or an opening in the skin, such as from a cut, scrape, or puncture. External bleeding can be categorized as arterial, venous, or capillary bleeding, depending on the type of blood vessel that is damaged. Arterial bleeding is the most severe, as it involves blood being pumped from the heart at high pressure and can lead to rapid blood loss.
Internal bleeding occurs when blood leaks from blood vessels inside the body, such as from a damaged organ or tissue. Internal bleeding can be difficult to detect, but symptoms can include pain, swelling, or tenderness in the affected area, as well as weakness, dizziness, or fainting.
Treatment for bleeding depends on the cause and severity of the bleeding. For external bleeding, the first step is to apply direct pressure to the wound to stop the bleeding. Elevating the affected area and applying a bandage or dressing can also help. For more severe bleeding, a tourniquet may be necessary to stop the blood flow.
Internal bleeding may require medical intervention, such as surgery or blood transfusions, depending on the cause and extent of the bleeding.
If you experience bleeding that cannot be stopped or that is accompanied by severe pain or other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.

Infertility
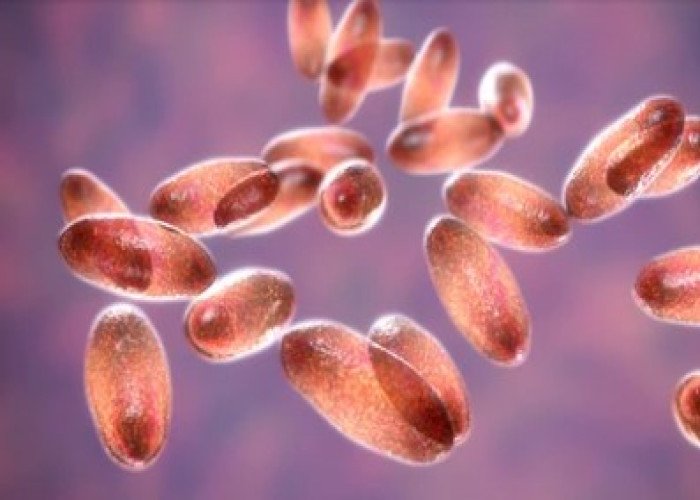
Plague
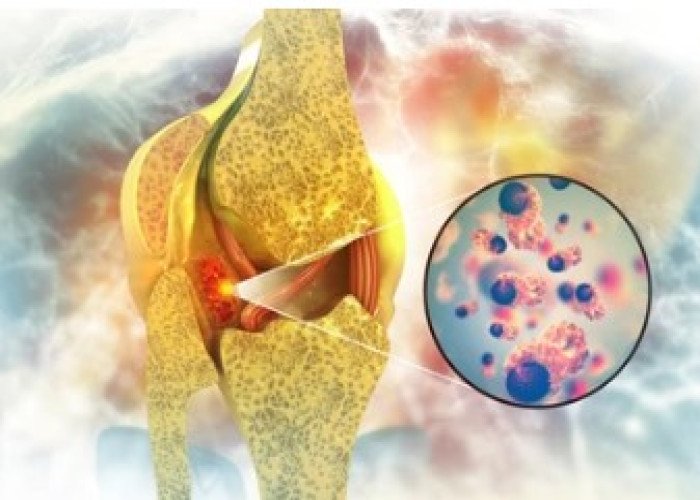
Bone cancer
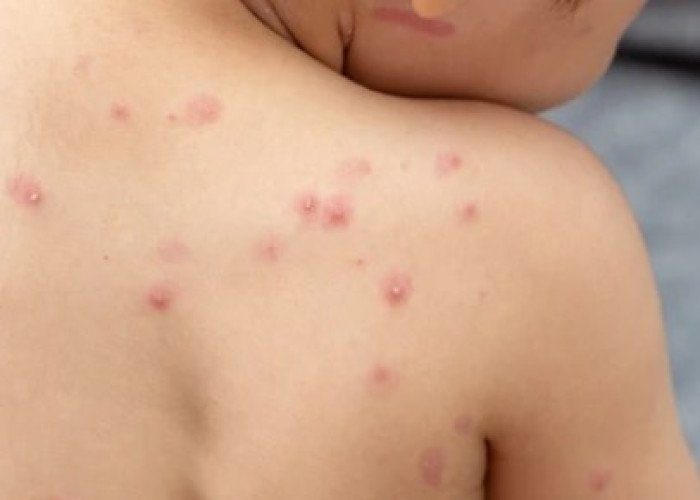
Chickenpox
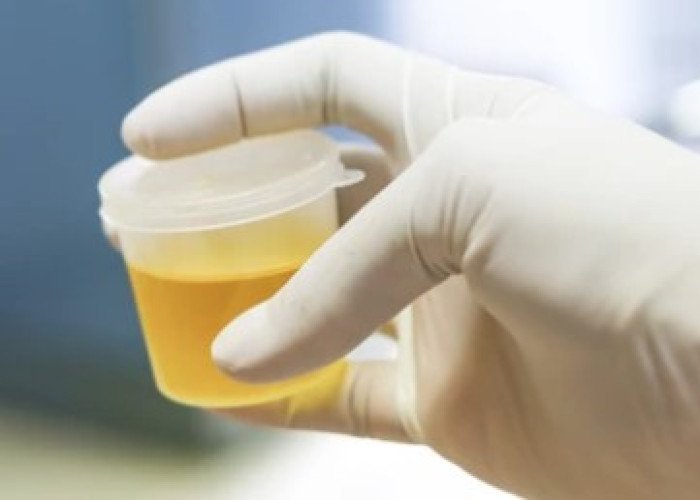
Scanty urine

Unconsciousness

Cold
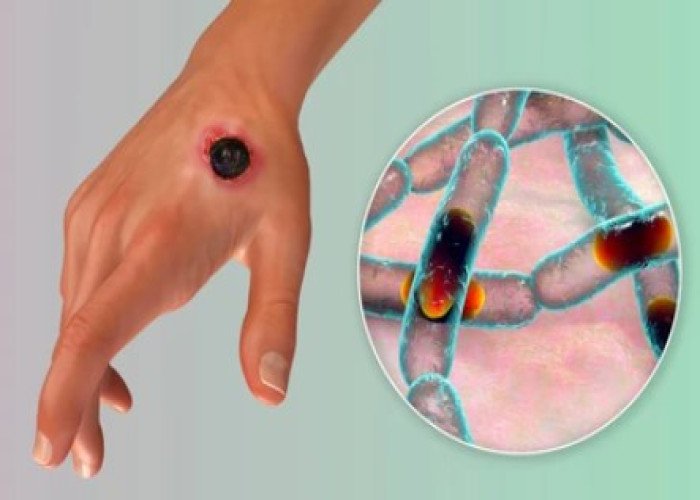
Anthrax
Bleeding, রক্তস্রাব
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.


