 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Scanty urine - Homeopathic remedies
Scanty urine refers to a condition where a person produces a lower volume of urine than usual. The amount of urine produced varies depending on a person's age, sex, and fluid intake. Normally, an adult produces about 1 to 2 liters of urine per day. However, when the volume of urine produced decreases, it may indicate an underlying medical condition.
Scanty urine can be caused by various factors such as dehydration, urinary tract infection, kidney disease, prostate problems, medication side effects, or obstruction of the urinary tract. Symptoms of scanty urine may include difficulty urinating, pain or burning during urination, fever, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain.
The treatment of scanty urine depends on the underlying cause. For example, if the condition is caused by dehydration, increasing fluid intake may be recommended. In cases where the cause is an infection or kidney disease, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove an obstruction in the urinary tract.
It is important to see a healthcare provider if you experience any changes in your urine production or if you have other symptoms such as pain or discomfort during urination. Prompt treatment can help prevent complications and promote a faster recovery.
Eczema
Hemoglobin deficiency
Gland is hard as stone

Obesity
Knee arthritis
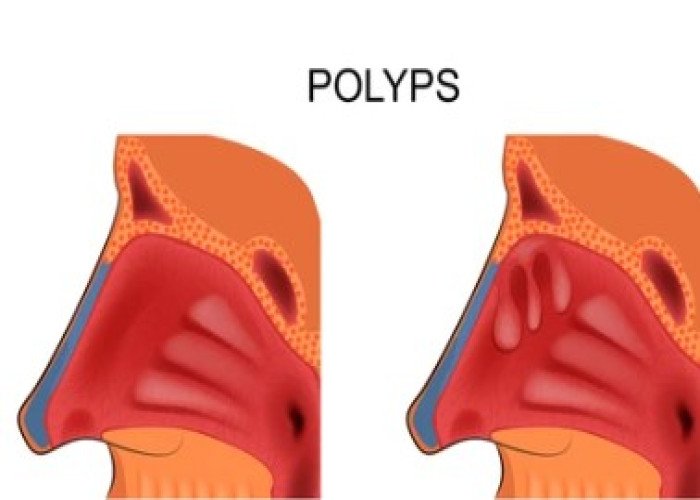
Polypus
Low blood pressure

Dream of a dead person
Scanty urine, অল্প প্রস্রাব
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
