 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Typhoid fever - Generics
Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi. It is typically transmitted through contaminated food or water, or by close contact with an infected individual. Symptoms of typhoid fever can include high fever, weakness, stomach pain, headache, and loss of appetite.
The bacteria that cause typhoid fever can live in the bloodstream and intestinal tract of infected individuals, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the disease. If left untreated, typhoid fever can lead to serious complications, such as intestinal perforation or life-threatening bleeding.
Treatment for typhoid fever typically involves antibiotics, which can help clear the bacteria from the body and prevent complications. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated.
Prevention of typhoid fever involves measures such as good hygiene practices, including washing hands frequently and thoroughly, as well as avoiding potentially contaminated food and water sources. Vaccines are also available to help prevent typhoid fever, and may be recommended for individuals traveling to areas with a high risk of infection.

Trichinellosis

Filariasis

Acute asthma

Prurigo nodularis
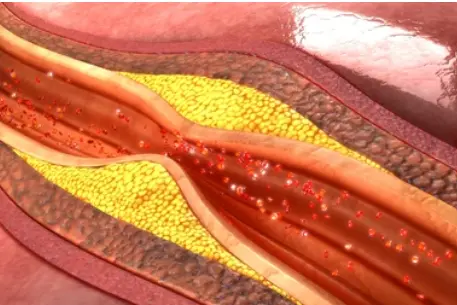
Angiography

Herpes zoster (shingles)

T-Cell Lymphoma

Sweat rash
Typhoid fever, টাইফয়েড জ্বর
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.