 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Tendonitis - Generics
Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of a tendon, which is a fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones. The condition is often caused by repetitive motions or overuse of a particular joint or muscle group, but can also be the result of an acute injury or underlying medical condition.
Symptoms of tendonitis may include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected area. The pain may be worse with movement or activity, and may improve with rest. In severe cases, the affected area may be tender to the touch, and there may be limited range of motion in the joint.
Treatment for tendonitis may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation of the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. Physical therapy and stretching exercises may be recommended to improve flexibility and strengthen the affected muscles.
Prevention of tendonitis involves good workplace ergonomics, proper equipment use and technique during sports and other activities, and gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activity. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of tendonitis, as early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent complications and improve outcomes.

Iron and folic acid defic...

Dilatation of pupil

Myeloproliferative disord...
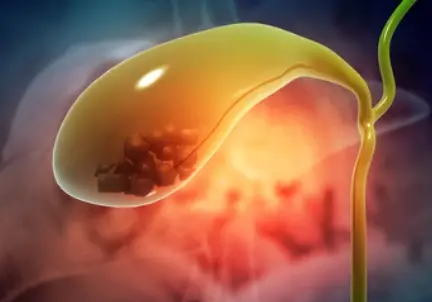
Chronic cholelithiasis
Body dysmorphic disorder

Parasomnia

Folliculitis

Cardiopulmonary Bypass Su...
Tendonitis, টেন্ডোনাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.