 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Pneumococcal pneumonia - Generics
Pneumococcal pneumonia is a type of bacterial pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, a bacterium that commonly resides in the nose and throat of healthy individuals but can cause serious infections if it enters the lungs. Pneumococcal pneumonia can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of pneumococcal pneumonia may include cough, fever, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and sometimes confusion or disorientation. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection and supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia involves vaccination with pneumococcal vaccines. The vaccines are recommended for people who are at high risk of pneumococcal disease, such as young children, older adults, and people with certain medical conditions that weaken the immune system. Other prevention measures include practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and managing underlying medical conditions that can increase the risk of pneumococcal pneumonia.

NSAID-induced ulcers
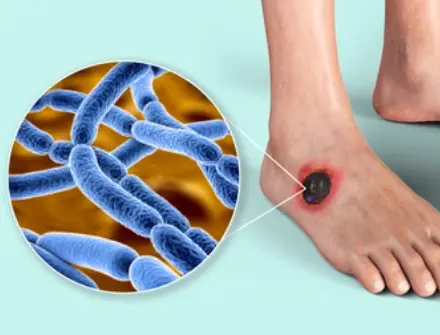
Anthrax

Gonococcal urethritis

Prophylaxis of miosis dur...

Secondary skin infections

Chancroid

Hypertrophic cardiomyopat...
Rhinorrhoea
Pneumococcal pneumonia, নিউমোকোকাল নিউমোনিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.