 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic bronchitis - Generics
Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis (AECB) refer to sudden worsening of symptoms in individuals with chronic bronchitis, a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that causes inflammation and excess mucus production in the airways. AECB is usually triggered by a respiratory infection or exposure to environmental irritants such as smoke or pollution.
Symptoms of AECB may include:
- Increased coughing
- Increased sputum production
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Wheezing
- Fatigue
- Fever
Treatment for AECB typically involves antibiotics to treat any bacterial infections that may be present, as well as bronchodilators and corticosteroids to help open up the airways and reduce inflammation. Oxygen therapy may also be necessary in severe cases.
Prevention is key in managing AECB. This may involve avoiding known triggers, such as cigarette smoke or other irritants, getting vaccinated against respiratory infections like the flu and pneumonia, and regularly monitoring lung function with a peak flow meter or other device. Individuals with chronic bronchitis may also benefit from pulmonary rehabilitation programs that include exercise, breathing techniques, and education on how to manage symptoms.
It is important for individuals with chronic bronchitis to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both the underlying condition and any acute exacerbations that may occur. Early recognition and prompt treatment of AECB can help to minimize symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life.

Renal colic

Contraception
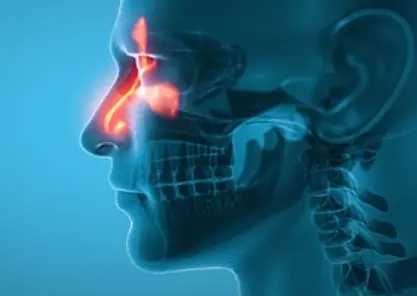
Sinusitis

Streptococcal pharyngitis...

Porphyria cutanea tarda

Itchy or watery eyes

Vertigo

Calcium deficiency
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic bronchitis, দীর্ঘস্থায়ী ব্রঙ্কাইটিসের তীব্র সংকট
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.