 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Pericarditis - Generics
Pericarditis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pericardium, which is the sac-like membrane surrounding the heart. The pericardium normally helps to protect and lubricate the heart, but when it becomes inflamed, it can cause chest pain, difficulty breathing, and other symptoms.
The most common symptom of pericarditis is chest pain, which may be sharp or dull and can be felt in the center or left side of the chest. Other symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Cough
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Irregular heartbeat
- Anxiety
Pericarditis can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, cancer, or trauma to the chest. In some cases, the cause may be unknown.
Treatment for pericarditis may involve medications to reduce inflammation and manage pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or aspirin may be prescribed, along with colchicine or corticosteroids. Antibiotics may be prescribed if the pericarditis is caused by a bacterial infection. In severe cases, hospitalization and treatment with intravenous medications may be necessary.
It's important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of pericarditis, as this condition can be serious and potentially life-threatening. Your doctor will perform a physical exam, review your medical history, and may order tests such as an electrocardiogram or echocardiogram to help diagnose the condition and determine the best course of treatment.

Osteopetrosis
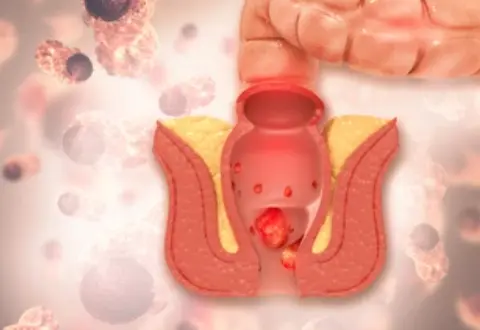
Haemorrhoids (piles)

Streptococcal pharyngitis...

Severe hypertension

Neurodermatitis

Auditory Vestibular and v...

Urinary Tract Infection c...
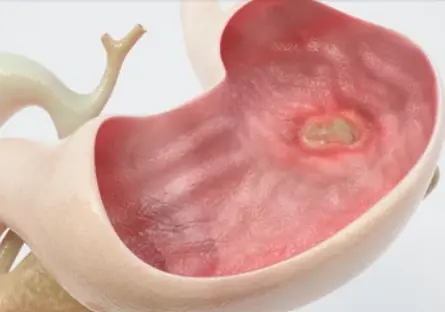
Ulcerative colitis
Pericarditis, পেরিকার্ডাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.