 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis - Generics
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA), also known as juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), is a type of arthritis that affects children under the age of 16. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation and joint damage.
JRA is characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and swelling that can affect one or many joints. The symptoms can be mild or severe and can come and go. Other symptoms may include fever, rash, and eye inflammation. JRA can also affect growth and development, as well as cause fatigue and difficulty with physical activities.
There are three main types of JRA: oligoarticular JRA, polyarticular JRA, and systemic JRA. Oligoarticular JRA is the most common type and affects up to four joints in the first six months of the disease. Polyarticular JRA affects five or more joints and can start at any age. Systemic JRA is less common and can cause fever, rash, and inflammation of internal organs, in addition to joint pain and swelling.
The exact cause of JRA is unknown, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. There is no cure for JRA, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Treatment for JRA typically involves a combination of medications and physical therapy. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, while disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can slow down the progression of the disease. Biologic agents, which are newer medications that target specific components of the immune system, may also be used in some cases.
Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and strength, and may also help reduce pain and inflammation. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct joint deformities or replace damaged joints.
In conclusion, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is a type of arthritis that affects children under the age of 16. It is an autoimmune disorder that causes joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. There is no cure for JRA, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage. Treatment typically involves a combination of medications and physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery may be necessary.

Porphyria cutanea tarda

Leukemia
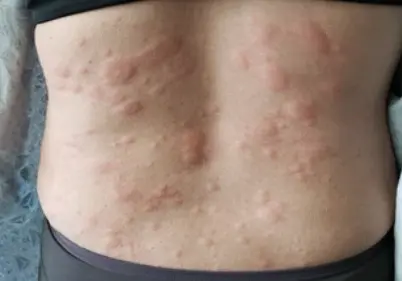
Hives

Breast cancer and bone me...

Cardiopulmonary Bypass Su...

Renal disease

Superficial dermatophyte...

Lung carcinoma
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, জুভেনাইল রিউমাটয়েড আর্থ্রাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.