 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Bed sore - Generics
Bed sores, also known as pressure ulcers or decubitus ulcers, are areas of damaged skin and tissue that develop when sustained pressure is placed on a particular part of the body. Bed sores are most commonly found in individuals who are bedridden, wheelchair-bound, or otherwise immobilized for extended periods of time.
The pressure of the body against a surface, such as a bed or wheelchair, can cause the blood supply to be reduced to the affected area, leading to tissue damage and cell death. The areas most commonly affected by bed sores are bony prominences, such as the hips, tailbone, heels, and elbows.
Symptoms of bed sores may include redness or discoloration of the skin, swelling, warmth or coolness of the affected area, and the development of blisters or open sores. In severe cases, bed sores can lead to infection, sepsis, or even death.
Prevention of bed sores includes frequent repositioning of the body, use of specialized mattresses or cushions, keeping the skin clean and dry, and providing adequate nutrition and hydration. Treatment of bed sores may include cleaning and dressing the affected area, providing antibiotics if infection is present, and surgery in severe cases.
It is important to seek medical attention if you or a loved one develops bed sores, as prompt treatment can help prevent complications and promote healing.

Candidal cystitis

Heartburn & gastritis

Opioid overdosage
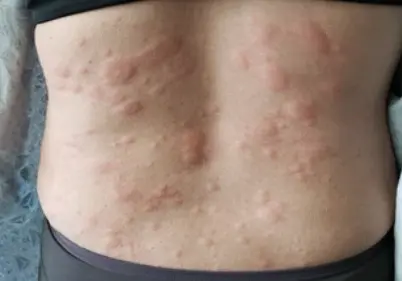
Hives

Fever

Enuresis

Skin moisturization
Vomiting
Bed sore, বিছানা ঘা, বেড সোর
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.