 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Bronchiectasis - Generics
Bronchiectasis is a chronic respiratory condition that is characterized by the permanent enlargement and thickening of the bronchial tubes in the lungs. This leads to a buildup of mucus in the airways, which can increase the risk of respiratory infections and cause persistent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
The most common causes of bronchiectasis include lung infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, and genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis or primary ciliary dyskinesia. Other risk factors for bronchiectasis include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), autoimmune diseases, and exposure to environmental irritants, such as dust or pollution.
Symptoms of bronchiectasis may include:
- Persistent cough that produces thick, discolored mucus.
- Wheezing or shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
- Chest pain or tightness.
- Fatigue or malaise.
- Recurrent respiratory infections, such as pneumonia or sinusitis.
Diagnosis of bronchiectasis may involve a physical exam, medical history, and various imaging tests, such as chest X-rays or CT scans. Pulmonary function tests may also be performed to measure lung function.
Treatment for bronchiectasis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may include:
- Antibiotics to treat respiratory infections.
- Mucus-thinning medications to help clear the airways.
- Bronchodilators to open up the airways and ease breathing.
- Oxygen therapy to improve oxygen levels in the blood.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation, which involves exercise and breathing techniques to improve lung function.
- Surgery in severe cases to remove damaged lung tissue.
Prevention of bronchiectasis involves reducing the risk of respiratory infections, such as through vaccination and good hygiene practices. Treatment of underlying conditions, such as COPD or autoimmune diseases, may also help to prevent the development of bronchiectasis.

Myositis. Post-op conditi...

Keratosis pilaris

Skincare
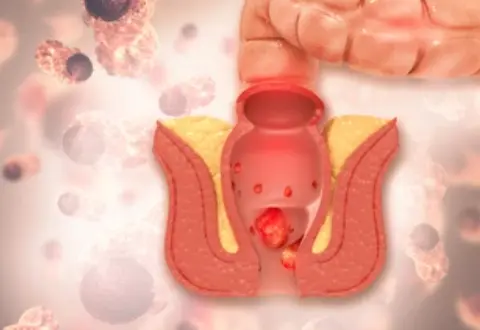
Hemorrhoids (piles)
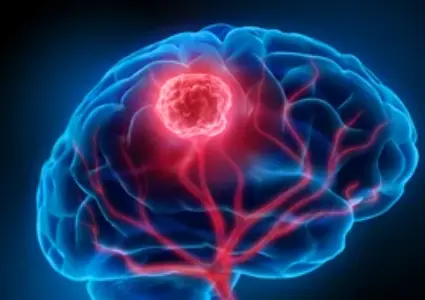
Squamous cell or testicul...

Myelodysplastic disease

Neuropathy

Enteritis
Bronchiectasis, ব্রঙ্কাইকেটেসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.