 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Jock itch - Generics
Jock itch, also known as tinea cruris, is a fungal infection that affects the skin in the groin area. It is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes and is similar to other fungal infections such as athlete's foot and ringworm.
Jock itch is most common in men, but it can also affect women. The infection typically begins with a red, itchy rash in the groin area that may spread to the inner thighs, buttocks, and anus. The affected skin may be scaly, cracked, or blistered, and it may be more intense in the folds of the skin.
Jock itch is spread through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or through contact with contaminated clothing or surfaces. It can also occur in people who sweat heavily or have a weakened immune system.
Treatment for jock itch usually involves over-the-counter antifungal creams or ointments that are applied to the affected area. In more severe cases, prescription-strength antifungal medications may be necessary.
To prevent jock itch, it is important to keep the groin area clean and dry, wear loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics, and avoid sharing clothing or personal items with others. It is also important to avoid prolonged exposure to moist environments, such as public showers or swimming pools.

Dyslipidemia

Cancer therapy-induced hy...

Hormone replacement thera...

Allergic dermatitis
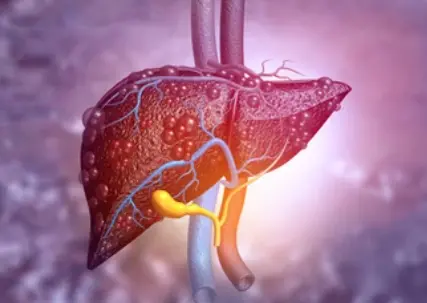
Fatty liver
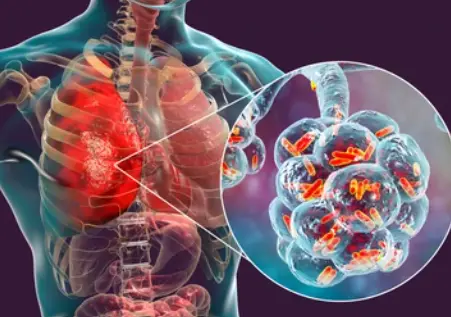
Bacteraemic pneumonia

Cerebral oedema

Wound infection
Jock itch, জক চুলকানি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.