 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Immunodeficiency - Generics
Immunodeficiency is a condition in which the immune system, which is responsible for protecting the body from infection and disease, is not functioning properly. There are two types of immunodeficiency: primary and secondary.
Primary immunodeficiency is a genetic disorder in which the immune system is underdeveloped or absent. These disorders are usually present at birth or become apparent in the first few months or years of life. Examples of primary immunodeficiency disorders include severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), X-linked agammaglobulinemia, and common variable immunodeficiency.
Secondary immunodeficiency is a condition in which the immune system is weakened as a result of another disease or condition, such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, or malnutrition. Medications such as chemotherapy or immunosuppressive drugs can also cause secondary immunodeficiency.
Symptoms of immunodeficiency may include recurrent infections, such as ear infections, sinusitis, or pneumonia, as well as infections that are severe, persistent, or difficult to treat. People with immunodeficiency may also experience chronic or recurrent diarrhea, skin infections, or thrush (a fungal infection of the mouth or throat).
Diagnosis of immunodeficiency may involve blood tests to measure levels of immune system components such as antibodies or white blood cells, as well as tests to identify specific immune system disorders. Treatment for immunodeficiency depends on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics or antiviral drugs to treat infections, immune globulin therapy to supplement the immune system, or bone marrow or stem cell transplantation for severe cases of primary immunodeficiency.
Prevention of immunodeficiency includes practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding contact with sick people, as well as receiving recommended vaccinations to prevent infections. People with immunodeficiency should also avoid contact with people who are sick and should take steps to protect themselves from infection, such as wearing a mask in public places during flu season.
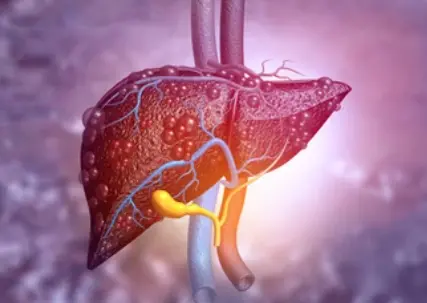
Fatty liver

Diabetes insipidus

Chronic Fatigue Syndrome

Increased demand for Calc...
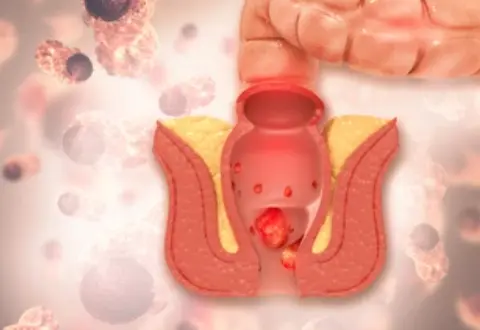
Piles

Thiamine and riboflavin d...

Grazes

Congenital adrenal hyperp...
Immunodeficiency, ইমিউনোডেফিসিয়েন্সি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.