 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Diabetic foot ulcer - Generics
A diabetic foot ulcer is a common complication of diabetes that occurs when a wound or sore develops on the foot, typically on the bottom of the foot or toes. It is a serious and potentially dangerous condition that can lead to infection, gangrene, and even amputation of the affected foot or leg.
Diabetes can cause nerve damage, or neuropathy, which can lead to reduced sensation in the feet. This, combined with poor circulation, can make it more difficult for the body to heal wounds and fight off infection. High blood sugar levels can also damage the small blood vessels that supply the feet, further reducing the body's ability to heal.
Prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers involves careful monitoring of blood sugar levels, regular foot exams by a healthcare provider, and proper foot care, including daily washing and drying, wearing properly fitting shoes and socks, and avoiding walking barefoot.
If a diabetic foot ulcer does develop, treatment typically involves cleaning the wound and removing any dead tissue, applying a dressing or bandage, and taking antibiotics if necessary to prevent infection. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue or amputate the affected foot or leg.
It is important for people with diabetes to seek medical attention promptly if they notice any signs or symptoms of a foot ulcer, such as redness, swelling, or drainage from a wound, as early intervention can help prevent serious complications.

Breast cancers and gliobl...

VTB

Following pancreatic surg...
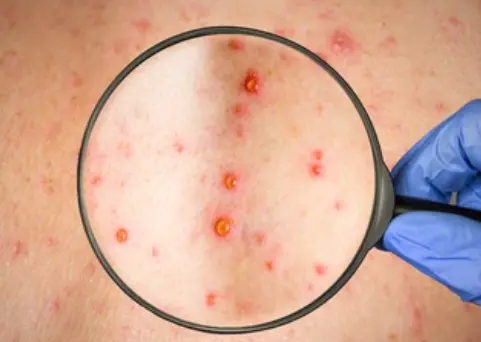
Syphilis

Wet ARMD

Adult Respiratory Distres...
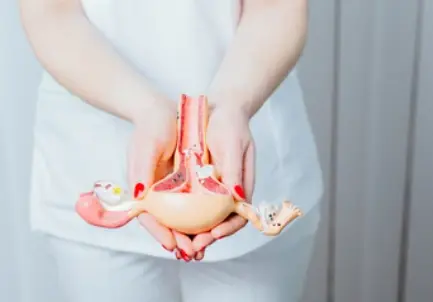
Cervicitis and salpingiti...

Generalized anxiety disor...
Diabetic foot ulcer, ডায়াবেটিক পায়ের আলসার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.