 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Chronic hepatitis C - Generics
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which can lead to both acute and chronic hepatitis. Chronic hepatitis C is a long-term, ongoing infection that can cause severe liver damage if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of chronic hepatitis C.
Causes of Chronic Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is primarily transmitted through blood-to-blood contact. The most common causes of chronic hepatitis C are:
- Sharing needles or other equipment used for injecting drugs
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992, when screening for hepatitis C was not yet available
- Receiving medical treatment in countries where unsafe injection practices are common
- Being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
In rare cases, hepatitis C can also be transmitted through sexual contact, sharing personal hygiene items such as razors or toothbrushes, or from mother to baby during childbirth.
Symptoms of Chronic Hepatitis C
In many cases, people with chronic hepatitis C do not experience any symptoms until the disease has already caused significant liver damage. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Dark urine
- Pale stool
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Because these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, such as the flu or food poisoning, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis if you experience any of them.
Diagnosis of Chronic Hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C is diagnosed through a blood test that detects the presence of HCV antibodies in the bloodstream. If the test is positive, additional tests will be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of liver damage.
Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C
The goal of treatment for chronic hepatitis C is to cure the infection, prevent further liver damage, and reduce the risk of liver cancer and liver failure. Treatment typically involves a combination of antiviral medications that are taken over a period of several months.
The specific medications used will depend on the type of hepatitis C virus present, as well as the extent of liver damage. Commonly used medications include:
- Interferon alfa, which is injected once a week
- Ribavirin, which is taken orally twice a day
- Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), which are taken orally once a day
In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary if the liver has already sustained significant damage.
Prevention of Chronic Hepatitis C
The best way to prevent chronic hepatitis C is to avoid behaviors that can lead to infection. This includes not sharing needles or other equipment used for injecting drugs, avoiding unprotected sexual contact with multiple partners, and not sharing personal hygiene items.
For people who are at high risk of infection, such as healthcare workers or people with certain medical conditions, there is also a vaccine available that can protect against hepatitis C.
Conclusion
Chronic hepatitis C is a serious condition that can cause significant liver damage if left untreated. Fortunately, with early diagnosis and proper treatment, it is possible to cure the infection and prevent further complications. By taking steps to avoid behaviors that can lead to infection, and by getting vaccinated if necessary, you can reduce your risk of developing chronic hepatitis C and protect your liver health.

Grazes

Biliary colic
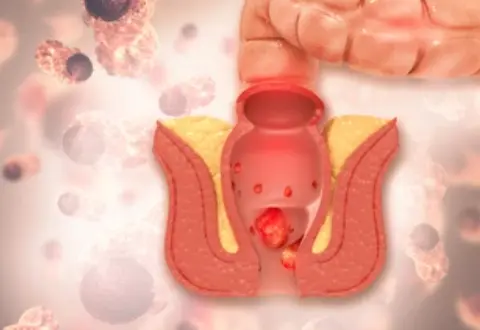
Haemorrhoids (piles)

Blepharospasm

Vasculitis

Warts
Anovulatory infertility

Peritoneal Dialysis
Chronic hepatitis C, দীর্ঘস্থায়ী হেপাটাইটিস সি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.