 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Diaphragm - Diseases
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It plays a crucial role in breathing by contracting and relaxing to allow air to enter and exit the lungs.
The diaphragm is located at the base of the thoracic cavity and is attached to the lower ribs, sternum, and spine. It is innervated by the phrenic nerve, which controls its movement and helps to regulate breathing.
When the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and moves downward, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and causing air to be drawn into the lungs. When it relaxes, it returns to its dome shape and moves upward, decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and causing air to be expelled from the lungs.
In addition to its role in breathing, the diaphragm also helps to stabilize the spine and support the organs of the abdominal cavity. It is a vital muscle that plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and wellbeing.
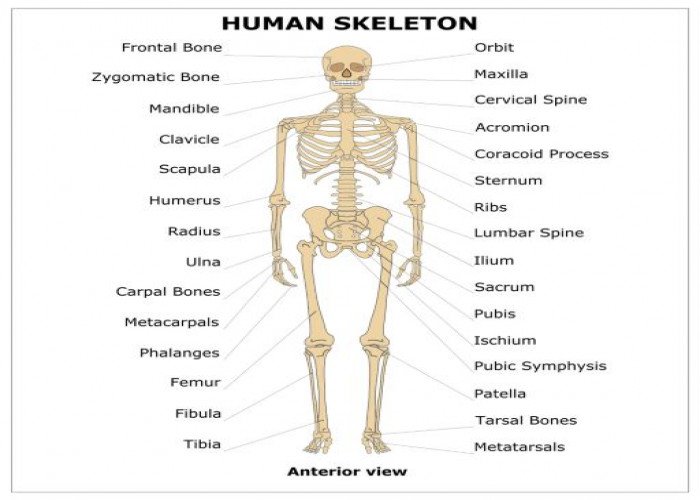
Skeleton

Testes
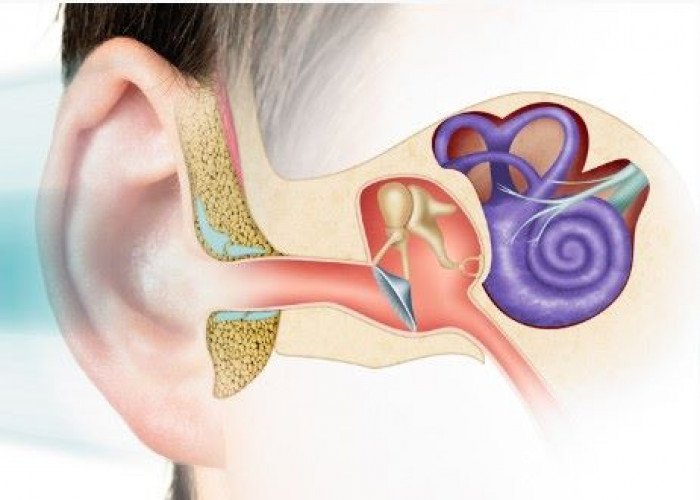
Semicircular canals Inner ear
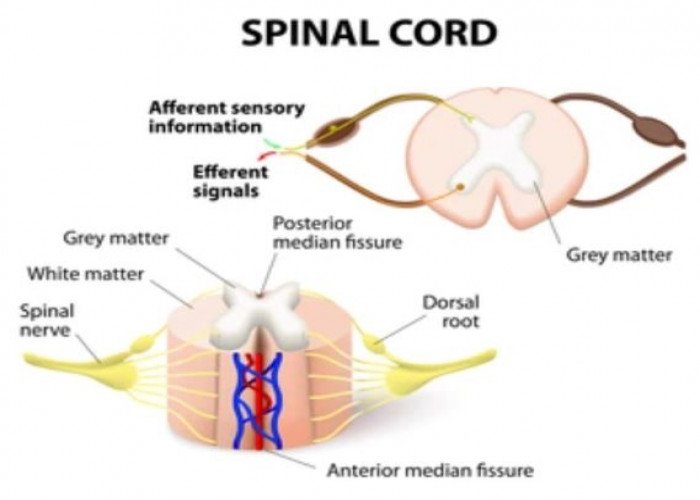
Spinal cord
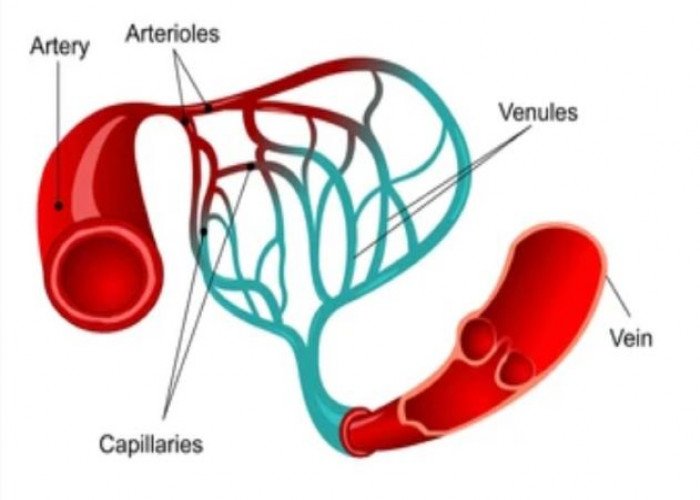
Capillaries
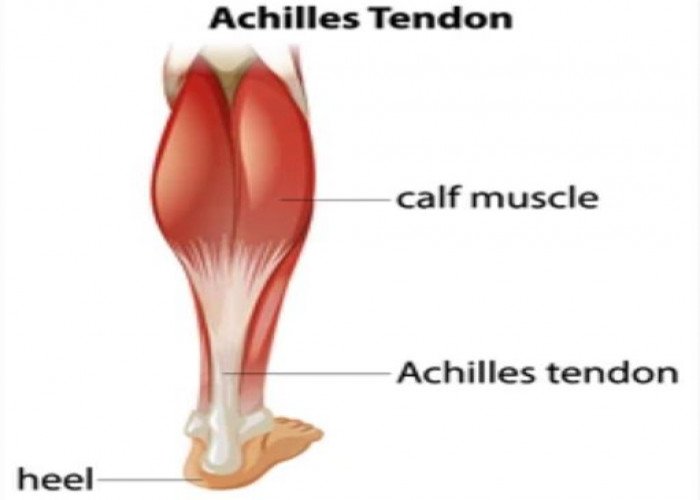
Tendons

Scalp
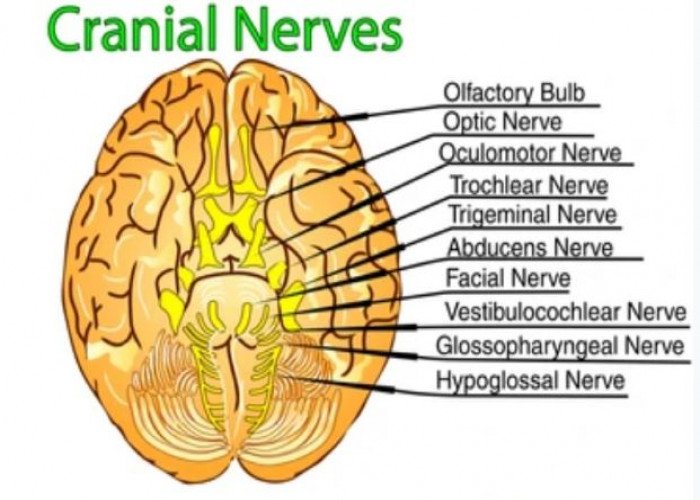
Cranial Nerves
Diaphragm, Diaphragm is, ডায়াফ্রাম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

