Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
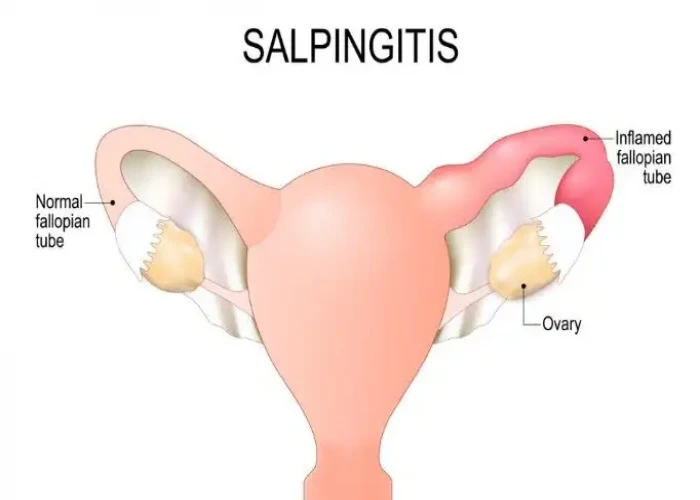
Salpingitis
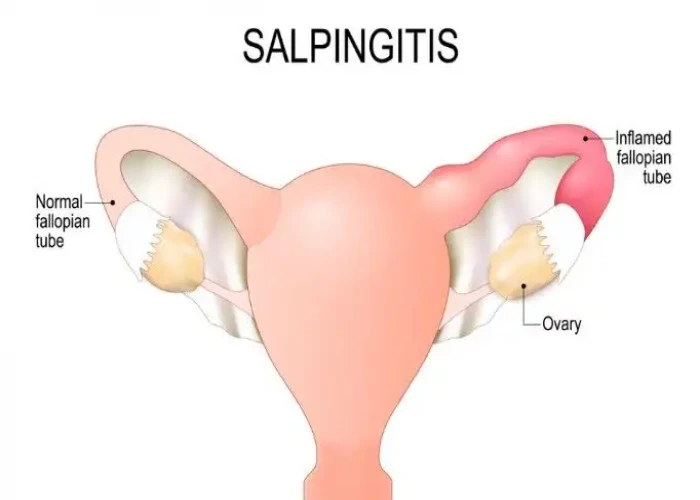
If inflammation occurs from a bacterial lesion, it is called oviductal inflammation or salpingitis. Gonococcus infections can cross the vagina and uterus and invade the fallopian tubes. Apart from this, Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and B. Coli bacteria can cause fallopian tube infections. It can also happen after a tumor or an operation. Tuberculosis can cause secondary infection.
Salpingitis is a medical condition that occurs when the fallopian tubes become inflamed, usually due to an infection. The infection is typically caused by bacteria, most commonly from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea.
The symptoms of salpingitis can vary, but may include:
- Lower abdominal pain
- Pelvic pain
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
In some cases, salpingitis may cause no symptoms at all.
Diagnosis of salpingitis may involve a physical exam, pelvic ultrasound, and laboratory tests to identify the presence of bacterial infections.
Treatment for salpingitis typically involves antibiotics to treat the underlying infection. In some cases, hospitalization may be required, particularly if the infection is severe or the patient is pregnant. If left untreated, salpingitis can cause long-term complications such as chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy.
Prevention of salpingitis includes practicing safe sex by using condoms and getting regular STI screenings, as well as promptly treating any infections or symptoms of infection. If you suspect you may have salpingitis or an STI, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Menstruation is white
- Menstruation is less
- Menstruation is foul smelling
- Menstruation is chronic
- Inflammation of fallopian tubes (Salpingitis)
Disease Causes
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin [Penicillin V]
5 lakh in the morning and 5 lakh in the evening should be given.
-
Oxytetracycline
2cc should be injected every morning for 5/7 days.
-
Ampicillin Sodium
1 pill 4 times a day at night (7 days).
-
Cephalexin
1 pill 4 times a day at night (7 days).
-
Paracetamol
Medicines containing paracetamol for pain.
1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Multivitamin & Multimineral
1 pill daily after meal.
-
Diazepam
1 pill in the morning and 1 pill at night or just 1 pill at night.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Salpingitis and Learn More about Diseases
Mumps
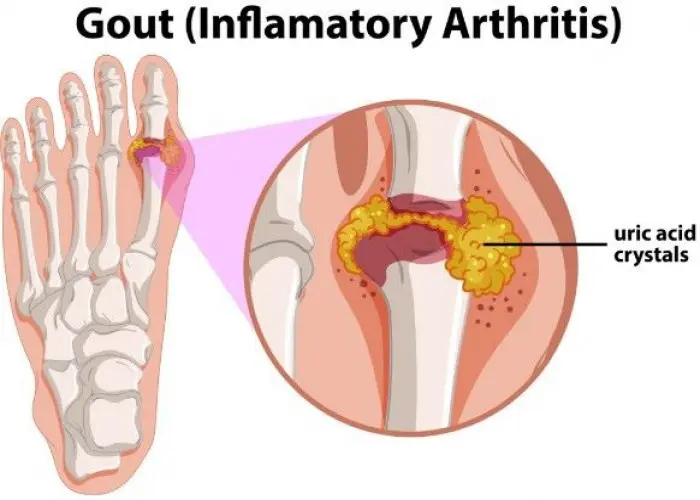
Gout

Uterine prolapse
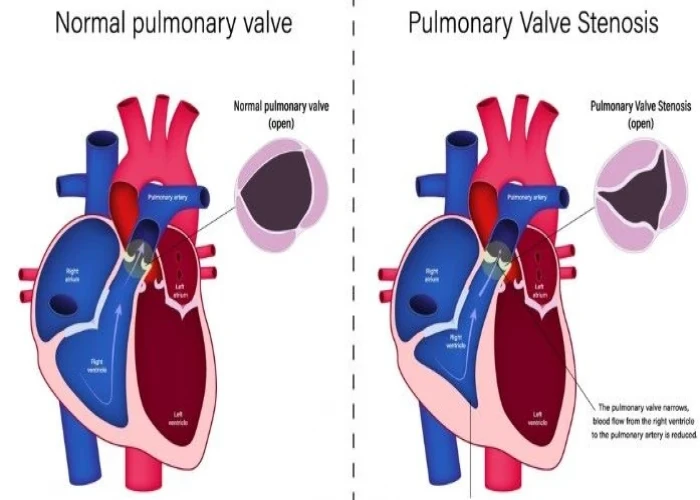
Pulmonary valve disease

Greenstick fractures

Age spots (liver spots)

Urinary incontinence
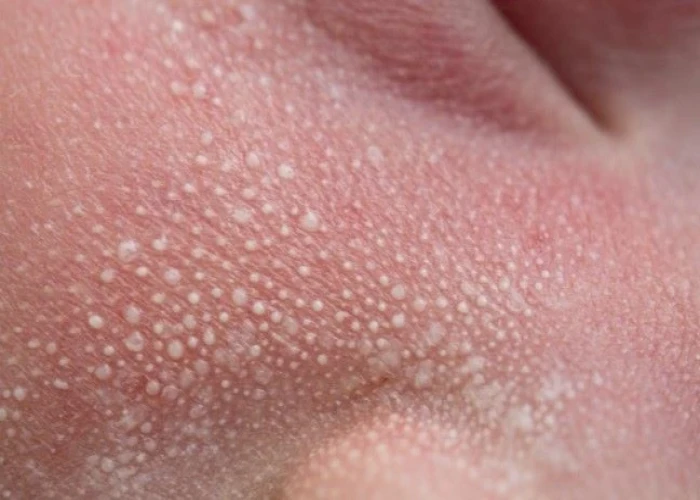
Milia
salpingitis, ডিম্বনালীর প্রদাহ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.