Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Ureteral obstruction
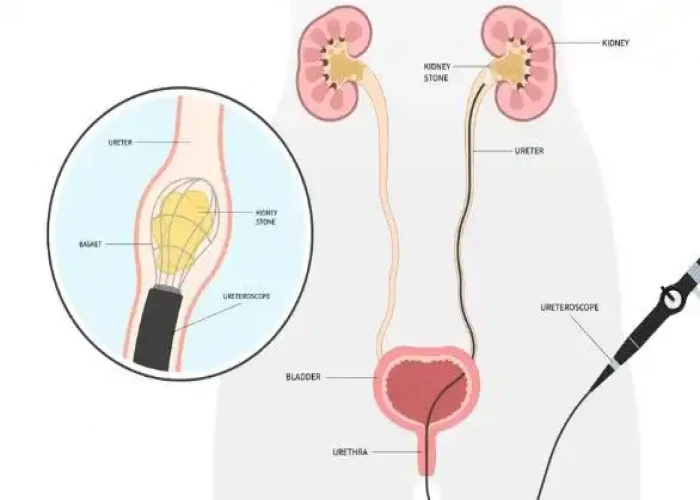
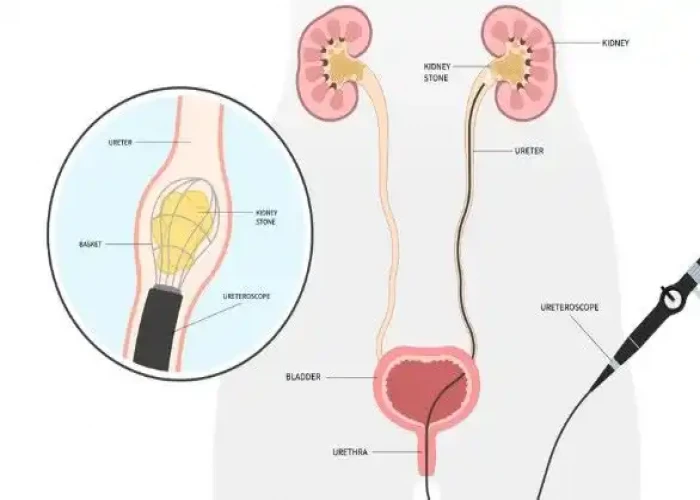
Ureteral obstruction occurs when there is a blockage in one or both of the ureters, which are the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Ureteral obstructions can be caused by a variety of factors, including kidney stones, tumors, scar tissue, and congenital abnormalities.
Symptoms of ureteral obstruction may include pain in the back or side, nausea or vomiting, and decreased urine output. If the obstruction is severe, it can lead to kidney damage or failure.
Diagnosis of ureteral obstruction typically involves imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan, as well as urine tests and blood tests. Treatment options for ureteral obstruction depend on the cause and severity of the blockage but may include medications to manage pain and inflammation, surgery to remove the blockage, or placement of a stent to help keep the ureter open.
The prognosis for ureteral obstruction depends on the cause and how quickly it is diagnosed and treated. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as kidney damage or failure. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have a ureteral obstruction or any other medical condition related to the urinary system.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Burning during urination
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
Disease Causes
Ureteral obstruction
Different types of ureteral obstruction have different causes, some of them present at birth (congenital). They include:
- A second (duplicated) ureter. This common condition, which is congenital, causes two ureters to form on the same kidney. The second ureter can be fully or only partially developed. If either ureter doesn't work properly, urine can back up into the kidney and cause damage.
- A blockage (obstruction) where the ureter connects to the kidney or bladder. This prevents urine flow. A blockage where the ureter and kidney meet (ureteropelvic junction) may cause the kidney to swell and eventually stop working. This condition can be congenital or can develop with typical childhood growth, result from an injury or scarring, or in rare cases, develop from a tumor. A blockage where the ureter and bladder meet (ureterovesical junction) may cause urine to back up into the kidneys.
- Ureterocele. If a ureter is too narrow and doesn't allow urine to flow completely, a tiny bulge in the ureter (ureterocele) may develop. When a ureterocele develops, it's usually in the section of the ureter closest to the bladder. This can block urine flow and cause urine to back up into the kidney, possibly leading to kidney damage.
- Retroperitoneal fibrosis. This rare disorder occurs when fibrous tissue grows in the area behind the abdomen. The fibers may grow as the result of cancer tumors or from taking certain medicines used to treat migraines. The fibers encircle and block the ureters, causing urine to back up into the kidneys.
Other possible causes
Various causes inside (intrinsic) or outside (extrinsic) the ureter can lead to ureteral obstruction, including:
- Kidney stones
- Cancerous and noncancerous tumors
- Blood clots
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Internal tissue growth, such as endometriosis in females
- Long-term swelling of the ureter wall, usually due to diseases such as tuberculosis or a parasite infection called schistosomiasis
Complications
Ureteral obstruction can lead to urinary tract infections and kidney damage, which can be irreversible.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
The goal of ureteral obstruction treatment is to remove blockages, if possible, or bypass the blockage, which may help repair damage to the kidneys. Treatment might include antibiotics to clear associated infections.
Drainage procedures
A ureteral obstruction that causes severe pain might require an immediate procedure to remove urine from your body and temporarily relieve the problems caused by a blockage. Your doctor (urologist) may recommend:
- A ureteral stent, which is a hollow tube inserted inside the ureter to keep it open.
- Percutaneous nephrostomy, during which your doctor inserts a tube through your back to drain the kidney directly (percutaneous nephrostomy).
- A catheter, which is a tube inserted through the urethra to connect the bladder to an external drainage bag. This may be especially important if problems with your bladder also contribute to poor drainage of your kidneys.
Your doctor can tell you which procedure or combination of procedures is best for you. Drainage procedures might provide temporary or permanent relief, depending on your condition.
Surgical procedures
There are a number of surgical procedures used to correct ureteral obstructions. The type of procedure depends on your situation.
Ureteral obstruction surgery may be performed through one of these surgical approaches:
- Endoscopic surgery. This minimally invasive procedure involves passing a lighted scope through the urethra into the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract. The surgeon makes a cut into the damaged or blocked part of the ureter to widen the area and then places a hollow tube (stent) in the ureter to keep it open. This procedure may be done to both diagnose and treat a condition.
- Open surgery. The surgeon makes an incision in your abdomen to remove the blockage and repair your ureter.
- Laparoscopic surgery. In this approach, the surgeon makes one or more small incisions through your skin to insert a small tube with a light, a camera and other instruments needed for the procedure.
- Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery. The surgeon uses a robotic system to perform a laparoscopic procedure.
The main differences among these surgical approaches are your recovery time after surgery and the number and size of incisions used for the procedure. Your doctor (urologist) determines the type of procedure and the best surgical approach to treat your condition.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Ureteral obstruction and Learn More about Diseases

High cholesterol
Renal artery stenosis

Pediatric thrombocytopenia
Polio
Hypoparathyroidism

Scarlet fever
Hamstring injury

Chronic fatigue syndrome
ureteral obstruction, ইউরেট্রাল অবস্ট্রাকশন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.