 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Tendinitis
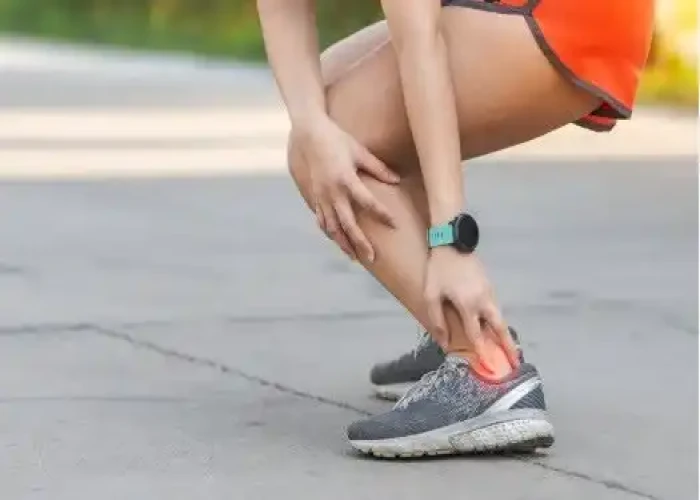

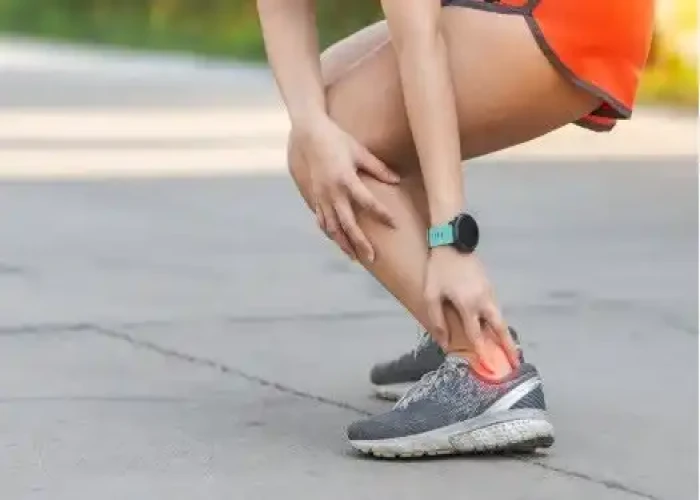
Tendinitis, also known as tendonitis, is a condition in which a tendon, the thick cord that attaches muscle to bone, becomes inflamed and irritated. Tendinitis can occur in any part of the body where there is a tendon, but it is most commonly found in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle.
Tendinitis is often caused by repetitive movements, overuse, or injury. Common symptoms of tendinitis may include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected area. The pain may be worse with movement or activity, and may improve with rest. Tendinitis can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term).
Treatment for tendinitis typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) of the affected area, as well as over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen. In some cases, physical therapy, massage, or ultrasound therapy may be helpful to reduce pain and inflammation and promote healing. If the tendinitis is severe or does not respond to other treatments, a healthcare provider may recommend a corticosteroid injection or surgery.
Prevention of tendinitis involves taking steps to avoid repetitive motions or overuse of the affected tendon. Proper stretching and strengthening exercises, as well as using proper equipment or technique during sports or other activities, can also help reduce the risk of tendinitis.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have tendinitis, as prompt treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening and improve the chances of a full recovery.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Limb pain
- Joint pain
Disease Causes
Tendinitis
Although tendinitis can be caused by a sudden injury, the condition is much more likely to stem from the repetition of a particular movement over time. Most people develop tendinitis because their jobs or hobbies involve repetitive motions, which put stress on the tendons.
Using proper technique is especially important when performing repetitive sports movements or job-related activities. Improper technique can overload the tendon — which can occur, for instance, with tennis elbow — and lead to tendinitis.
Disease Prevents
Tendinitis
To reduce your chance of developing tendinitis, follow these suggestions:
- Ease up. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your tendons, especially for prolonged periods. If you notice pain during a particular exercise, stop and rest.
- Mix it up. If one exercise or activity causes you a particular, persistent pain, try something else. Cross-training can help you mix up an impact-loading exercise, such as running, with lower impact exercise, such as biking or swimming.
- Improve your technique. If your technique in an activity or exercise is flawed, you could be setting yourself up for problems with your tendons. Consider taking lessons or getting professional instructions when starting a new sport or using exercise equipment.
- Stretch. Take time after exercise to stretch in order to maximize the range of motion of your joints. This can help to minimize repetitive trauma on tight tissues. The best time to stretch is after exercise, when your muscles are warmed up.
- Use proper workplace ergonomics. If possible, get an ergonomic assessment of your workspace and adjust your chair, keyboard and desktop as recommended for your height, arm length and usual tasks. This will help protect all your joints and tendons from excessive stress.
- Prepare your muscles to play. Strengthening muscles used in your activity or sport can help them better withstand stress and load.
Disease Treatments
The goals of tendinitis treatment are to relieve your pain and reduce inflammation. Often, taking care of tendinitis on your own — including rest, ice and over-the-counter pain relievers — may be all the treatment that you need.
Medications
For tendinitis, your doctor may recommend these medications:
- Pain relievers. Taking aspirin, naproxen sodium (Aleve) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) may relieve discomfort associated with tendinitis. Topical creams with anti-inflammatory medication — popular in Europe and becoming increasingly available in the United States — also may be effective in relieving pain without the potential side effects of taking anti-inflammatory medications by mouth.
- Corticosteroids. Sometimes your doctor may inject a corticosteroid medication around a tendon to relieve tendinitis. Injections of cortisone reduce inflammation and can help ease pain. Corticosteroids are not recommended for tendinitis lasting over three months (chronic tendinitis), as repeated injections may weaken a tendon and increase your risk of rupturing the tendon.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP). PRP treatment involves taking a sample of your own blood and spinning the blood to separate out the platelets and other healing factors. The solution is then injected into the area of chronic tendon irritation. Though research is still underway to determine optimal uses, concentrations and techniques, PRP injection in the region of chronic tendon irritation has shown promise in the treatment of many chronic tendon conditions.
Physical therapy
You might benefit from a program of specific exercise designed to stretch and strengthen the affected muscle-tendon unit. For instance, eccentric strengthening — which emphasizes contraction of a muscle while it's lengthening — has been shown to be a very effective treatment for many chronic tendon conditions, and is now considered first line treatment.
Surgical and other procedures
In situations where physical therapy hasn't resolved symptoms, your doctor might suggest:
- Dry needling. This procedure involves making small holes in the tendon with a fine needle to stimulate factors involved in tendon healing.
- Ultrasonic treatment. This minimally invasive procedure uses a small incision to insert a special device that removes tendon scar tissue with ultrasonic sound waves.
- Surgery. Depending on the severity of your tendon injury, surgical repair may be needed, especially if the tendon has torn away from the bone.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Tendinitis and Learn More about Diseases

Concussion
Indigestion

Gas and gas pains
Atypical hyperplasia of the breast
Supraventricular tachycardia
Enlarged liver
Cradle cap
Crohn's disease
tendinitis, টেন্ডিনাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
