Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
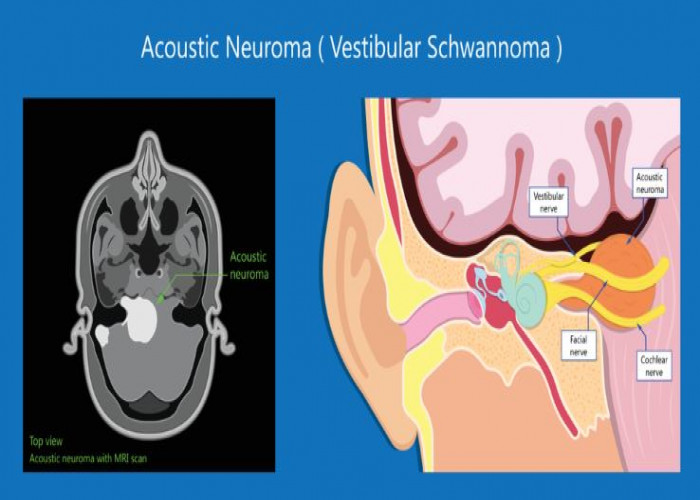
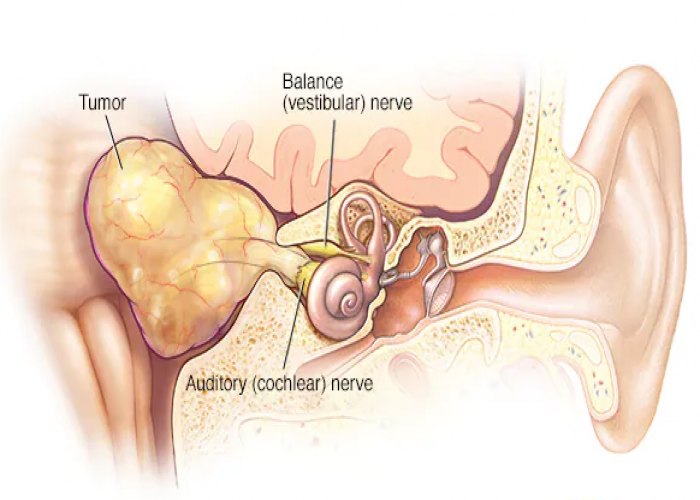
Acoustic neuroma

An acoustic neuroma, also known as a vestibular schwannoma, is a type of non-cancerous (benign) tumor that affects the vestibular nerve, which is responsible for transmitting balance and hearing information from the inner ear to the brain.
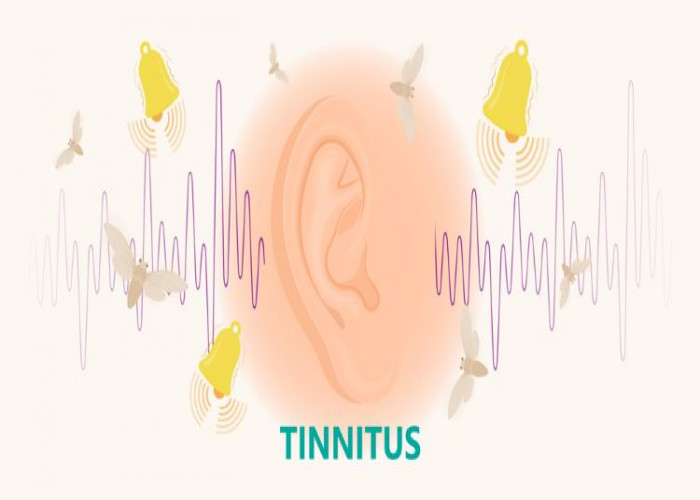
Symptoms of an acoustic neuroma can include hearing loss, ringing in the ear (tinnitus), dizziness or balance problems, and facial weakness or numbness. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all.
Diagnosis of an acoustic neuroma is typically made through a physical examination, imaging tests such as an MRI, and hearing tests.
Treatment for an acoustic neuroma can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's age, overall health, and the presence of any symptoms. Options may include observation and monitoring, radiation therapy, or surgery to remove the tumor.
It's important to seek medical attention if you have symptoms that suggest an acoustic neuroma, as prompt treatment can help prevent potential complications and preserve hearing and balance function. In some cases, early detection and treatment can also improve the long-term outlook for patients with this condition.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Dizziness, ringing in the ears and abrupt hearing loss may occur.
- Ringing in ears (tinnitus)
- Lose balance
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Dizziness when moving
Disease Causes
Acoustic neuroma
The cause of acoustic neuromas can be linked to a problem with a gene on chromosome 22. Normally, this gene produces a tumor suppressor protein that helps control the growth of Schwann cells covering the nerves.
Experts don't know what causes this problem with the gene. In most cases of acoustic neuroma, there is no known cause. This faulty gene is also inherited in neurofibromatosis type 2, a rare disorder that usually involves the growth of tumors on the hearing and balance nerves on both sides of your head (bilateral vestibular schwannomas).
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Your acoustic neuroma treatment may vary, depending on:
- The size and growth of the acoustic neuroma
- Your overall health
- Severity of symptoms
To treat acoustic neuroma, your doctor may suggest one or more of three potential options: monitoring, surgery or radiation therapy.
Surgery
You may need surgery to remove an acoustic neuroma, especially if the tumor is:
- Continuing to grow
- Very large
- Causing symptoms
Your surgeon may use one of several techniques for removing an acoustic neuroma, depending on the size of your tumor, hearing status and other factors.
The goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and preserve the facial nerve to prevent facial paralysis. Removing the entire tumor may not be possible in certain cases — for example, if the tumor is too close to important parts of the brain or the facial nerve.
Surgery for an acoustic neuroma is performed under general anesthesia and involves removing the tumor through the inner ear or through a window in your skull.
Sometimes, surgical removal of the tumor may worsen symptoms if the hearing, balance, or facial nerves are irritated or damaged during the operation. Hearing may be lost on the side where the surgery is performed, and balance is usually affected temporarily.
Complications may include:
- Leaking cerebrospinal fluid through the wound or nose
- Hearing loss
- Facial weakness or numbness
- Ringing in the ear
- Balance problems
- Persistent headache
- Rarely, infection of the cerebrospinal fluid (meningitis)
- Very rarely, stroke or brain bleeding
Radiation therapy
There are several types of radiation therapy used to treat acoustic neuroma:
- Stereotactic radiosurgery. Your doctor may recommend a type of radiation therapy known as stereotactic radiosurgery. It's often used if your tumor is small (less than 2.5 centimeters in diameter), you are an older adult or you cannot tolerate surgery for health reasons.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery, such as Gamma Knife radiosurgery, uses many tiny gamma rays to deliver a precisely targeted dose of radiation to a tumor without damaging the surrounding tissue or making an incision.
- The goal of stereotactic radiosurgery is to stop the growth of a tumor, preserve the facial nerve's function and possibly preserve hearing.
- It may take weeks, months or years before you notice the effects of radiosurgery. Your doctor will monitor your progress with follow-up imaging studies and hearing tests.
- Risks of radiosurgery include:
- Hearing loss
- Ringing in the ear
- Facial weakness or numbness
- Balance problems
- Continued tumor growth
- Stereotactic radiotherapy. Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) delivers a small dose of radiation to the tumor over several sessions. SRT is done to curb the growth of the tumor without damaging surrounding brain tissue.
- Proton beam therapy. This type of radiation therapy uses high-energy beams of positively charged particles called protons. Protons are delivered to the affected area in targeted doses to treat tumors and minimize radiation exposure to the surrounding area.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Acoustic neuroma and Learn More about Diseases

X-linked agammaglobulinemia
Frostbite

Female sexual dysfunction

Child abuse
Hashimoto's disease

Tendinitis
Preeclampsia

Depression (major depressive disorder)
Acoustic neuroma, Acoustic schwannoma, Acoustic neuroma treatment, অ্যাকাস্টিক নিউরোমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.