 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Reactive attachment disorder

Reactive attachment disorder (RAD) is a disorder that can occur in children who have experienced extreme neglect, abuse, or other forms of trauma in their early years. It is characterized by a failure to form healthy attachments to caregivers or parents and can lead to significant social and emotional difficulties.
Symptoms of reactive attachment disorder may include a lack of responsiveness to comfort or affection, avoidance of eye contact or physical touch, a lack of interest in social interaction with others, and a failure to seek comfort or respond to comfort from others.
Treatment for reactive attachment disorder typically involves a combination of therapies, including play therapy, family therapy, and behavioral therapy. The goal of treatment is to help the child develop healthy relationships with caregivers or parents and to address any underlying emotional or behavioral issues.
Prevention of reactive attachment disorder involves providing a stable and nurturing environment for children in their early years. This can include responsive and attentive caregiving, as well as early interventions to address any developmental or emotional issues.
It is important to note that reactive attachment disorder is a complex and serious condition, and diagnosis should only be made by a qualified healthcare professional with expertise in child development and mental health. If you suspect that a child may be experiencing reactive attachment disorder, it is important to seek professional help right away.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Unwanted thoughts and fears (obsessions)
- Irritability
- Sad and listless appearance
- Failure to smile
- Unexplained withdrawal, fear, sadness or irritability
- Failing to ask for support or assistance
- No interest in playing peekaboo or other interactive games
Disease Causes
Reactive attachment disorder
To feel safe and develop trust, infants and young children need a stable, caring environment. Their basic emotional and physical needs must be consistently met. For instance, when a baby cries, the need for a meal or a diaper change must be met with a shared emotional exchange that may include eye contact, smiling and caressing.
A child whose needs are ignored or met with a lack of emotional response from caregivers does not come to expect care or comfort or form a stable attachment to caregivers.
It's not clear why some babies and children develop reactive attachment disorder and others don't. Various theories about reactive attachment disorder and its causes exist, and more research is needed to develop a better understanding and improve diagnosis and treatment options.
Disease Prevents
Reactive attachment disorder
While it's not known with certainty if reactive attachment disorder can be prevented, there may be ways to reduce the risk of its development. Infants and young children need a stable, caring environment and their basic emotional and physical needs must be consistently met. The following parenting suggestions may help.
- Take classes or volunteer with children if you lack experience or skill with babies or children. This will help you learn how to interact in a nurturing manner.
- Be actively engaged with your child by lots of playing, talking to him or her, making eye contact, and smiling.
- Learn to interpret your baby's cues, such as different types of cries, so that you can meet his or her needs quickly and effectively.
- Provide warm, nurturing interaction with your child, such as during feeding, bathing or changing diapers.
- Offer both verbal and nonverbal responses to the child's feelings through touch, facial expressions and tone of voice.
Disease Treatments
Children with reactive attachment disorder are believed to have the capacity to form attachments, but this ability has been hindered by their experiences.
Most children are naturally resilient. And even those who've been neglected, lived in a children's home or other institution, or had multiple caregivers can develop healthy relationships. Early intervention appears to improve outcomes.
There's no standard treatment for reactive attachment disorder, but it should involve both the child and parents or primary caregivers. Goals of treatment are to help ensure that the child:
- Has a safe and stable living situation
- Develops positive interactions and strengthens the attachment with parents and caregivers
Treatment strategies include:
- Encouraging the child's development by being nurturing, responsive and caring
- Providing consistent caregivers to encourage a stable attachment for the child
- Providing a positive, stimulating and interactive environment for the child
- Addressing the child's medical, safety and housing needs, as appropriate
Other services that may benefit the child and the family include:
- Individual and family psychological counseling
- Education of parents and caregivers about the condition
- Parenting skills classes
Controversial and coercive techniques
The American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and the American Psychiatric Association have criticized dangerous and unproven treatment techniques for reactive attachment disorder.
These techniques include any type of physical restraint or force to break down what's believed to be the child's resistance to attachments — an unproven theory of the cause of reactive attachment disorder. There is no scientific evidence to support these controversial practices, which can be psychologically and physically damaging and have led to accidental deaths.
If you're considering any kind of unconventional treatment, talk to your child's psychiatrist or psychologist first to make sure it's evidence based and not harmful.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Reactive attachment disorder and Learn More about Diseases

Vulvar cancer
Enlarged liver

Stuttering

Presbyopia
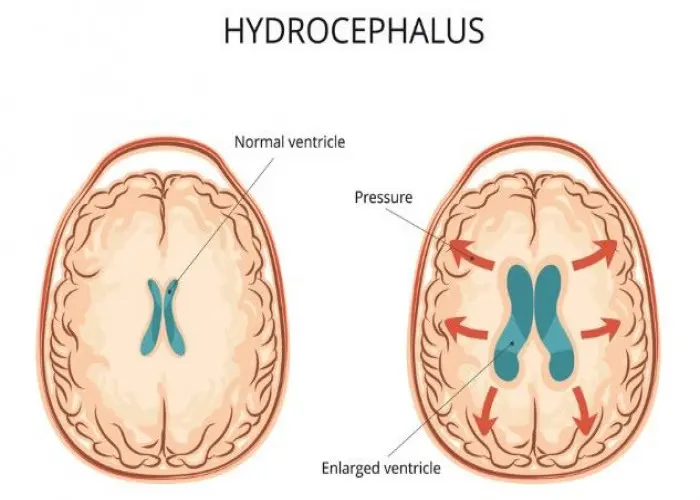
Hydrocephalus

Membranous nephropathy
Deviated septum
Fibrous dysplasia
reactive attachment disorder, প্রতিক্রিয়াশীল সংযুক্তি ব্যাধি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
