 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Oral thrush
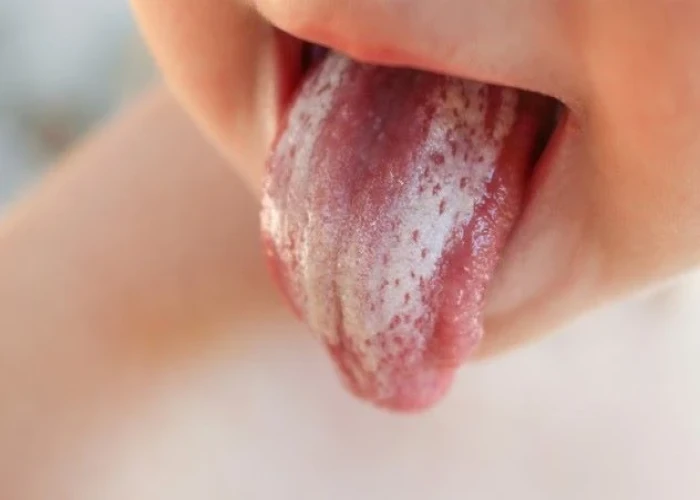

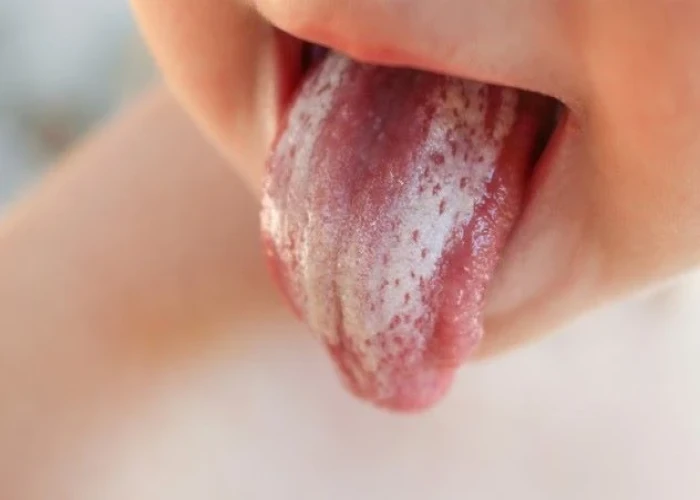
Oral thrush, also known as oropharyngeal candidiasis, is a fungal infection of the mouth and throat caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans. It is commonly seen in infants, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems, but can also affect healthy people.
Symptoms of oral thrush may include:
- White or yellowish patches or plaques on the tongue, gums, roof of the mouth, or inner cheeks
- Redness, soreness, or burning sensation in the affected areas
- Difficulty swallowing or a sensation of food being stuck in the throat
- Loss of taste
- Cracking or bleeding at the corners of the mouth
Risk factors for oral thrush may include the use of antibiotics or corticosteroids, poorly fitting dentures, medical conditions that weaken the immune system such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or cancer, and lifestyle factors such as smoking or poor oral hygiene.
Diagnosis of oral thrush may involve a physical exam of the mouth and throat and microscopic examination of a sample of the affected tissue. Treatment may involve antifungal medications such as topical or oral agents to eliminate the Candida fungus, as well as management of any underlying medical conditions.
Prevention of oral thrush may involve good oral hygiene, including brushing the teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and rinsing the mouth after meals. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also reduce the risk of developing oral thrush.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Mouth sores
- Stabbing pains deep within the breast
- Shiny or flaky skin on the darker, circular area around the nipple (areola)
- Redness, irritation and pain under dentures (denture stomatitis)
- A cottony feeling in the mouth
- Cracking and redness at the corners of the mouth
- Slight bleeding if the lesions are rubbed or scraped
- Redness, burning or soreness that may be severe enough to cause difficulty eating or swallowing
- Unusually red, sensitive, cracked or itchy nipples
- Loss of taste
- Swelling in one or both testicles
Disease Causes
Oral thrush
Normally, your immune system works to repel harmful invading organisms, such as viruses, bacteria and fungi, while maintaining a balance between "good" and "bad" microbes that normally inhabit your body. But sometimes these protective mechanisms fail, increasing the number of candida fungus and allowing an oral thrush infection to take hold.
The most common type of candida fungus is Candida albicans. Several factors, such as a weakened immune system, can increase your risk of oral thrush.
Disease Prevents
Oral thrush
These measures may help reduce your risk of developing candida infections:
- Rinse your mouth. If you need to use a corticosteroid inhaler, be sure to rinse your mouth with water or brush your teeth after taking your medication.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily or as often as your dentist recommends.
- Check your dentures. Remove your dentures at night. Make sure dentures fit properly and don't cause irritation. Clean your dentures daily. Ask your dentist for the best way to clean your type of dentures.
- See your dentist regularly, especially if you have diabetes or wear dentures. Ask your dentist how often you need to be seen.
- Watch what you eat. Try limiting the amount of sugar-containing foods you eat. These may encourage the growth of candida.
- Maintain good blood sugar control if you have diabetes. Well-controlled blood sugar can reduce the amount of sugar in your saliva, discouraging the growth of candida.
- Treat a vaginal yeast infection as soon as possible.
- Treat dry mouth. Ask your doctor about ways to avoid or treat your dry mouth.
Disease Treatments
The goal of any oral thrush treatment is to stop the rapid spread of the fungus, but the best approach may depend on your age, your overall health and the cause of the infection. Eliminating underlying causes, when possible, can prevent recurrence.
- Healthy adults and children. Your doctor may recommend antifungal medication. This comes in several forms, including lozenges, tablets, or a liquid that you swish in your mouth and then swallow. If these topical medications are not effective, medication may be given that works throughout your body.
- Infants and nursing mothers. If you're breast-feeding and your infant has oral thrush, you and your baby could pass the infection back and forth. Your doctor may prescribe a mild antifungal medication for your baby and an antifungal cream for your breasts.
- Adults with weakened immune systems. Most often your doctor will recommend antifungal medication.
Thrush may return even after it's been treated if the underlying cause, such as poorly disinfected dentures or inhaled steroid use, isn't addressed.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Oral thrush and Learn More about Diseases
Basal cell carcinoma

Wilson's disease

Anorexia nervosa

Infertility (Sterility)

Temporal lobe seizure
Esthesioneuroblastoma
Gout

Umbilical hernia
oral thrush, ওরাল থ্রাশ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
