Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea
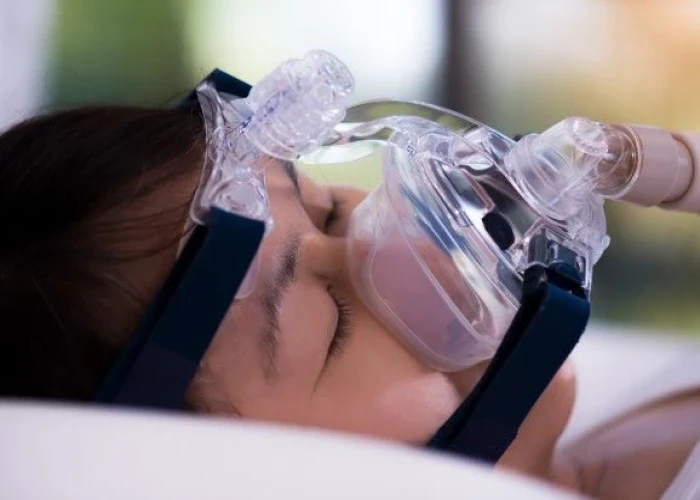
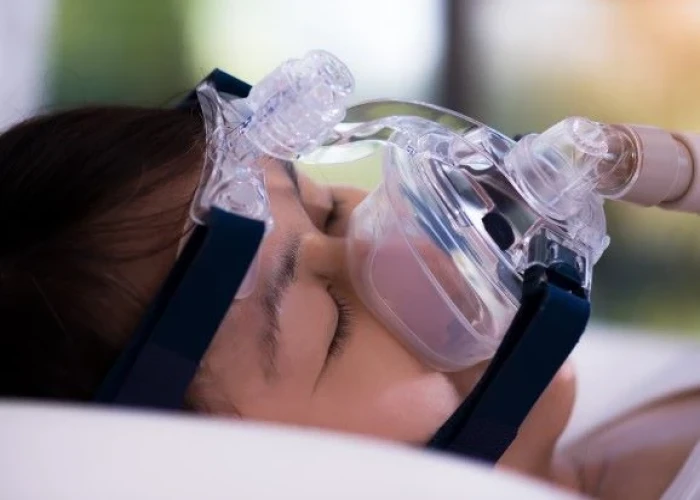
Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a condition that causes children to have partial or complete blockages in their upper airways during sleep. This blockage can result in a decrease in oxygen levels and a disruption in sleep patterns.
Some common symptoms of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea include snoring, difficulty breathing during sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, irritability, bedwetting, and difficulty concentrating. Children with obstructive sleep apnea may also experience developmental delays or behavioral problems.
The causes of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea can vary, but they are often related to anatomical abnormalities or underlying medical conditions. Obesity, allergies, enlarged tonsils or adenoids, and neuromuscular disorders can also contribute to the development of obstructive sleep apnea in children.
The treatment for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea typically depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. In mild cases, lifestyle changes such as weight loss and the avoidance of certain foods may be helpful. For more severe cases, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, surgery to remove enlarged tonsils or adenoids, or orthodontic treatment may be necessary.
It is essential to diagnose and treat pediatric obstructive sleep apnea early, as untreated OSA can lead to complications such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and cognitive impairment. Children with suspected obstructive sleep apnea should be evaluated by a pediatrician or a sleep specialist.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Loud snoring (Noisy breathing)
- Abrupt awakenings accompanied by gasping or choking
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Irritability
- Rapid mood chang
- Morning headaches
- Stopped breathing during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- A sprinkling of small purplish spots on the skin (called petechiae or purpura)
- Trouble paying attention and concentrating
- Rapid weight gain
- Sleep terrors (night terrors)
- Night sweats
- Difficulty concentrating during the day
Disease Causes
Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea
Obesity is a common factor underlying obstructive sleep apnea in adults. But in children the most common condition leading to obstructive sleep apnea is enlarged tonsils and adenoids. However, obesity also plays a role in children. Other underlying factors can be craniofacial anomalies and neuromuscular disorders.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Your doctor will work with you to find the most appropriate treatment for your child's sleep apnea. Treatment might include:
- Medications. Topical nasal steroids, such as fluticasone (Dymista) and budesonide (Rhinocort, Pulmicort Flexhaler, others), might ease sleep apnea symptoms for some children with mild obstructive sleep apnea. For kids with allergies, montelukast (Singulair) might help relieve symptoms when used alone, or with nasal steroids.
- Removal of the tonsils and adenoids. For moderate to severe sleep apnea, your doctor might refer your child to a pediatric ear, nose and throat specialist to discuss removing the tonsils and adenoids. An adenotonsillectomy (ad-uh-no-ton-sil-EK-tuh-me) might improve obstructive sleep apnea by opening the airway. Other forms of upper airway surgery might be recommended, based on the child's condition.
- Positive airway pressure therapy. In continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP), small machines gently blow air through a tube and mask attached to your child's nose, or nose and mouth. The machine sends air pressure into the back of your child's throat to keep your child's airway open. Doctors often treat pediatric obstructive sleep apnea with positive airway pressure therapy when medications or removal of adenoids and tonsils is not effective.
- Proper fitting of the mask and refitting as the child grows can help the child tolerate the mask over the face.
- Oral appliances. Oral appliances, such as dental devices or mouthpieces, may be recommended. Some devices help to expand the palate and nasal passages, or move your child's bottom jaw and tongue forward to keep your child's upper airway open. Only some children benefit from such devices.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea and Learn More about Diseases
Diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome

Heart arrhythmia

Mold allergy
Jaundice

Vitiligo (Leucoderma)

Secondary hypertension

Bad breath
COPD
pediatric obstructive sleep apnea, পেডিয়াট্রিক অবস্ট্রাকটিভ স্লিপ অ্যাপনিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.