Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
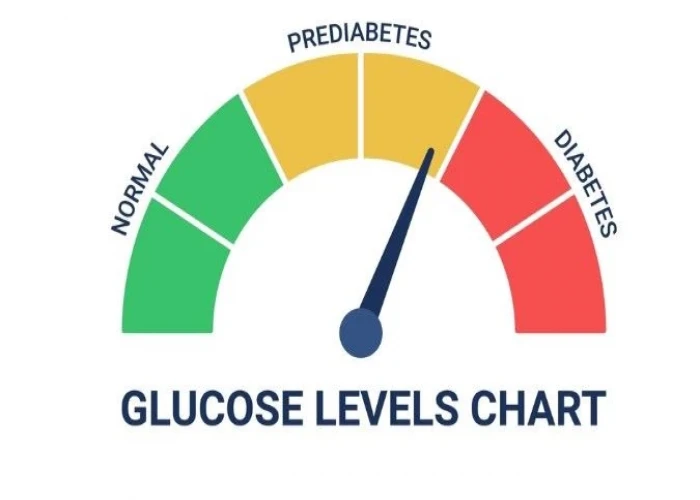
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a warning sign that a person may be at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition in which the body does not produce enough insulin or is unable to use it effectively.
Prediabetes typically does not cause any symptoms, but it can be detected through a blood test that measures the level of glucose in the blood. Risk factors for prediabetes include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being physically inactive, and having high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
The treatment for prediabetes typically involves lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, increasing physical activity, and making dietary changes to reduce the intake of sugary and high-carbohydrate foods. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
In some cases, medications such as metformin may also be prescribed to help lower blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider is important for individuals with prediabetes to track their progress and manage their risk of developing diabetes.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Blurred vision of eye
- Numbness
- Frequent infections
- Weight loss
Disease Causes
Prediabetes
The exact cause of prediabetes is unknown. But family history and genetics appear to play an important role. What is clear is that people with prediabetes don't process sugar (glucose) properly anymore.
Most of the glucose in your body comes from the food you eat. When food is digested, sugar enters your bloodstream. Insulin allows sugar to enter your cells — and lowers the amount of sugar in your blood.
Insulin is produced by a gland located behind the stomach called the pancreas. Your pancreas sends insulin to your blood when you eat. When your blood sugar level starts to drop, the pancreas slows down the secretion of insulin into the blood.
When you have prediabetes, this process doesn't work as well. As a result, instead of fueling your cells, sugar builds up in your bloodstream. This can happen because:
- Your pancreas may not make enough insulin
- Your cells become resistant to insulin and don't allow as much sugar in
Disease Prevents
Prediabetes
Healthy lifestyle choices can help you prevent prediabetes and its progression to type 2 diabetes — even if diabetes runs in your family. These include:
- Eating healthy foods
- Getting active
- Losing excess weight
- Controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol
- Not smoking
Disease Treatments
Healthy lifestyle choices can help you bring your blood sugar level back to normal, or at least keep it from rising toward the levels seen in type 2 diabetes.
To prevent prediabetes from progressing to type 2 diabetes, try to:
- Eat healthy foods. A diet high in fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains and olive oil is associated with a lower risk of prediabetes. Choose foods low in fat and calories and high in fiber. Eat a variety of foods to help you achieve your goals without compromising taste or nutrition.
- Be more active. Physical activity helps you control your weight, uses up sugar for energy and helps the body use insulin more effectively. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity a week, or a combination of moderate and vigorous exercise.
- Lose excess weight. If you're overweight, losing just 5% to 7% of your body weight — about 14 pounds (6.4 kilograms) if you weigh 200 pounds (91 kilograms) — can significantly reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. To keep your weight in a healthy range, focus on permanent changes to your eating and exercise habits.
- Stop smoking. Stopping smoking can improve the way insulin works, improving your blood sugar level.
- Take medications as needed. If you're at high risk of diabetes, your health care provider might recommend metformin (Glumetza). Medications to control cholesterol and high blood pressure might also be prescribed.
Children and prediabetes treatment
Children with prediabetes should follow the lifestyle changes recommended for adults with type 2 diabetes, including:
- Losing weight
- Eating fewer refined carbohydrates and fats, and more fiber
- Reducing portion sizes
- Eating out less often
- Spending at least one hour every day in physical activity
Medication generally isn't recommended for children with prediabetes unless lifestyle changes aren't improving blood sugar levels. If medication is needed, metformin is usually the recommended drug.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Prediabetes and Learn More about Diseases
Fibromuscular dysplasia
Small bowel prolapse (enterocele)
Ovarian cancer

Nearsightedness

Asthma

Athlete's foot

Rett syndrome
Central sleep apnea
prediabetes, প্রিডাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.