 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Peripheral neuropathy

Peripheral neuropathy is a condition in which the peripheral nerves that carry signals between the body and the brain or spinal cord are damaged or dysfunctional. The condition can affect a single nerve or a group of nerves, and it can cause a variety of symptoms depending on the type and severity of the neuropathy.
Peripheral neuropathy can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Diabetes
- Infections, such as Lyme disease or HIV/AIDS
- Trauma or injury to the nerves
- Certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs
- Toxins, such as alcohol or heavy metals
- Autoimmune disorders
- Nutritional deficiencies, particularly vitamin B12 deficiency
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can include:
- Tingling or burning sensations in the affected area
- Numbness or loss of sensation
- Muscle weakness or cramping
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
- Pain, particularly in the feet or hands
- Changes in blood pressure or heart rate
Diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy may involve a physical exam, nerve conduction tests, electromyography (EMG), and blood tests to check for underlying conditions. Treatment may depend on the underlying cause and may include medications to manage symptoms, physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility, and lifestyle changes to address underlying risk factors.
The prognosis for peripheral neuropathy depends on the underlying cause and the extent of the nerve damage. In some cases, the condition may improve with treatment or may resolve on its own over time. However, some types of neuropathy may be progressive and can lead to permanent disability. Early diagnosis and treatment can help improve the outcome for people with peripheral neuropathy.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Weakness and numbness in arms
- Weakness and numbness in legs
- Muscle weakness
- Excessive sweat
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or faintness
- Motor nerves that control muscle movement
- Paralysis if motor nerves are affected
Disease Causes
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is nerve damage caused by a number of different conditions. Health conditions that can cause peripheral neuropathy include:
- Autoimmune diseases. These include Sjogren's syndrome, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and vasculitis.
- Diabetes. This is the most common cause. Among people with diabetes, more than halfwill develop some type of neuropathy.
- Infections. These include certain viral or bacterial infections, including Lyme disease, shingles, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and C, leprosy, diphtheria, and HIV.
- Inherited disorders. Disorders such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease are hereditary types of neuropathy.
- Tumors. Growths, cancerous (malignant) and noncancerous (benign), can develop on the nerves or press on nerves. Also, polyneuropathy can arise as a result of some cancers related to the body's immune response. These are a form of a degenerative disorder called paraneoplastic syndrome.
- Bone marrow disorders. These include an abnormal protein in the blood (monoclonal gammopathies), a form of bone cancer (myeloma), lymphoma and the rare disease amyloidosis.
- Other diseases. These include kidney disease, liver disease, connective tissue disorders and an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism).
Other causes of neuropathies include:
- Alcoholism. Poor dietary choices made by people with alcoholism can lead to vitamin deficiencies.
- Exposure to poisons. Toxic substances include industrial chemicals and heavy metals such as lead and mercury.
- Medications. Certain medications, especially those used to treat cancer (chemotherapy), can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Injury or pressure on the nerve. Injuries, such as from motor vehicle accidents, falls or sports injuries, can sever or damage peripheral nerves. Nerve pressure can result from having a cast or using crutches or repeating a motion such as typing many times.
- Vitamin deficiencies. B vitamins — including B-1, B-6 and B-12 — vitamin E and niacin are crucial to nerve health.
In a number of cases, no cause can be identified (idiopathic).
Disease Prevents
Peripheral neuropathy
Manage underlying conditions
The best way to prevent peripheral neuropathy is to manage medical conditions that put you at risk, such as diabetes, alcoholism or rheumatoid arthritis.
Make healthy lifestyle choices
These habits support your nerve health:
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean protein to keep nerves healthy. Protect against vitamin B-12 deficiency by eating meats, fish, eggs, low-fat dairy foods and fortified cereals. If you're vegetarian or vegan, fortified cereals are a good source of vitamin B-12, but talk to your doctor about B-12 supplements.
- Exercise regularly. With your doctor's OK, try to get at least 30 minutes to one hour of exercise at least three times a week.
- Avoid factors that may cause nerve damage, including repetitive motions, cramped positions that put pressure on nerves, exposure to toxic chemicals, smoking and overindulging in alcohol.
Disease Treatments
Treatment goals are to manage the condition causing your neuropathy and to relieve symptoms. If your lab tests indicate no underlying condition, your doctor might recommend watchful waiting to see if your neuropathy improves.
Medications
Besides medications used to treat conditions associated with peripheral neuropathy, medications used to relieve peripheral neuropathy signs and symptoms include:
- Pain relievers. Over-the-counter pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can relieve mild symptoms. For more-severe symptoms, your doctor might prescribe painkillers.
- Medications containing opioids, such as tramadol (Conzip, Ultram, others) or oxycodone (Oxycontin, Roxicodone, others), can lead to dependence and addiction, so these drugs generally are not prescribed unless all other treatments fail.
- Anti-seizure medications. Medications such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica), developed to treat epilepsy, may relieve nerve pain. Side effects can include drowsiness and dizziness.
- Topical treatments. Capsaicin cream, which contains a substance found in hot peppers, can cause modest improvements in peripheral neuropathy symptoms. You might have skin burning and irritation where you apply the cream, but this usually lessens over time. Some people, however, can't tolerate it.
- Lidocaine patches are another treatment you apply to your skin that might offer pain relief. Side effects can include drowsiness, dizziness and numbness at the site of the patch.
- Antidepressants. Certain tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, doxepin (Silenor, Zonalon) and nortriptyline (Pamelor), have been found to help relieve pain by interfering with chemical processes in your brain and spinal cord that cause you to feel pain.
- The serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor duloxetine (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle) and the extended-release antidepressants venlafaxine (Effexor XR) abd desvenlafaxine (Pristiq) also might ease the pain of peripheral neuropathy caused by diabetes.
- Side effects of antidepressants may include dry mouth, nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, changes in appetite, weight gain and constipation.
Therapies
Various therapies and procedures might help ease the signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Electrodes placed on the skin deliver a gentle electric current at varying frequencies. TENS should be applied for 30 minutes daily for about a month.
- Plasma exchange and intravenous immune globulin. These procedures, which help suppress immune system activity, might benefit people with certain inflammatory conditions.
- Plasma exchange involves removing your blood, then removing antibodies and other proteins from the blood and returning the blood to your body. In immune globulin therapy, you receive high levels of proteins that work as antibodies (immunoglobulins).
- Physical therapy. If you have muscle weakness, physical therapy can help improve your movements. You may also need hand or foot braces, a cane, a walker, or a wheelchair.
- Surgery. If you have neuropathies caused by pressure on nerves, such as pressure from tumors, you might need surgery to reduce the pressure.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Peripheral neuropathy and Learn More about Diseases
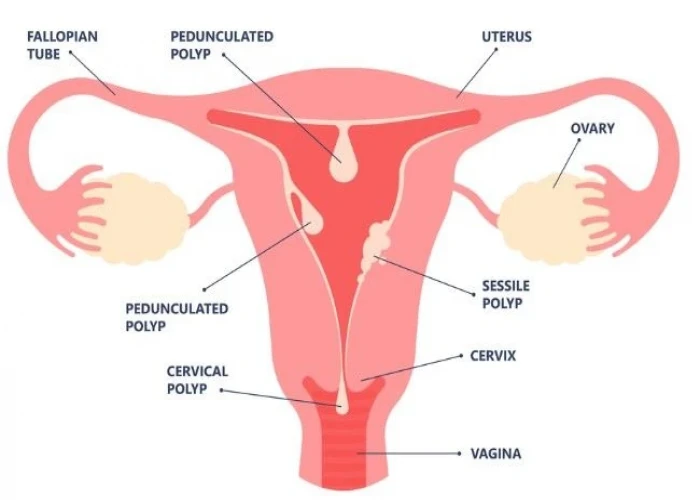
Menorrhagia (Heavy menstrual bleeding)
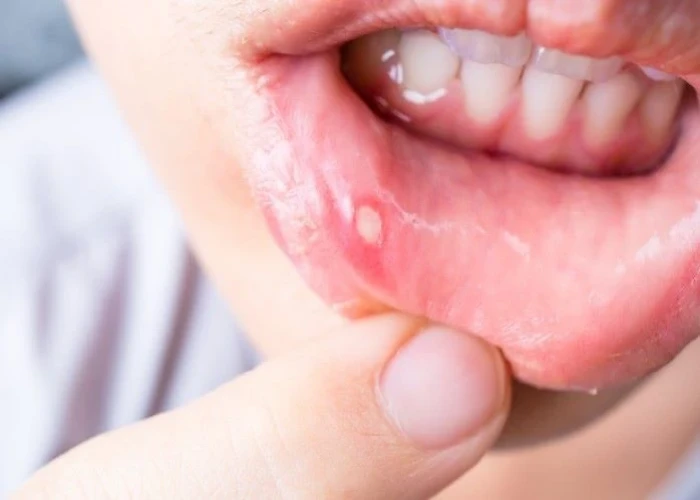
Mouth Ulcer

Low sex drive in women

Dust mite allergy
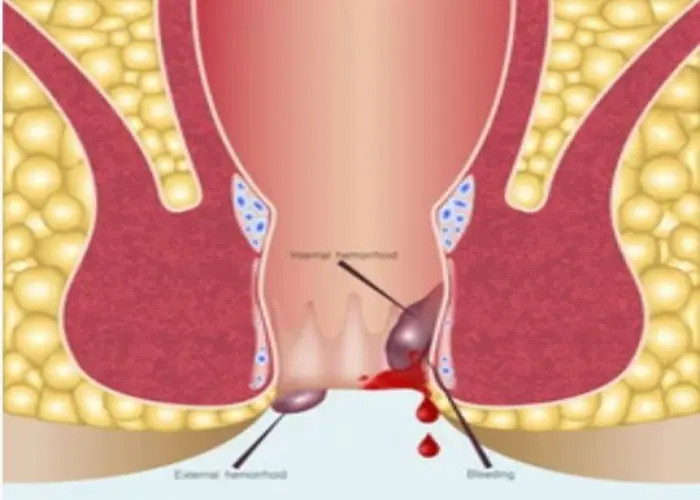
Anal fissure
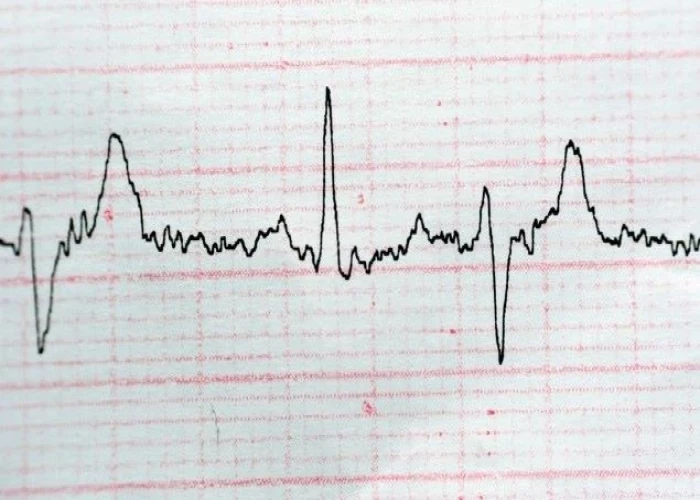
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
Colon polyps
Cataracts
peripheral neuropathy, পেরিফেরাল স্নায়ুরোগ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
